
Solve the following and find the value of
$\log \left( a+ib \right)=\left( \text{where}a>0,b>0 \right)$
a) $\log \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
b) $\dfrac{1}{2}\log \left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right)+i{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
c) $\dfrac{1}{2}\log \left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right)-i{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
d) $\dfrac{1}{2}\log \left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right)+i{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{a}{b} \right)$
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: To solve the question given above, we will convert the given complex number into polar form by putting the value of a as $r\cos \theta $ and putting the value of b as $r\sin \theta $ where r is the modulus of the given complex number. Then we will convert it into the form of $r{{e}^{i\theta }}$ . After that, we will take logarithms on both sides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For solving the given question above, first we will find the value of a + ib in terms of polar form. For this we will put the value of a as $r\cos \theta $ and we will put the value of b as $r\sin \theta $ . Thus we will get the following
$\begin{align}
& a=r\cos \theta ..............\left( i \right) \\
& b=r\sin \theta .............(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Here r is the modulus of the above complex number. The modulus of any complex number z= x + iy is represented by $\left| z \right|$ and it is given by the formula
$\left| z \right|=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}$
Thus the value of $r=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(iii)$
Now we will multiply the equation (ii) with ‘i’ and then we will add it into equation (i). Thus we get:
$a+ib=r\cos \theta +i\left( r\sin \theta \right)..............\left( iv \right)$
Now we will convert the polar form of the complex number into Euler’s form. According to Euler’s form we have
$A\cos B+i\left( A\sin B \right)=A{{e}^{iB}}$
Using this Euler’s form, we can rewrite equation (iv) as
$a+ib=r{{e}^{i\theta }}$
Now we will take a logarithm with base ‘e’ on both sides. Thus we will get
${{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}\left( r{{e}^{i\theta }} \right)$
Now, we will use a logarithm identity here
$\log \left( a\times b \right)=\log a+\operatorname{logb}$
Thus we will get
${{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+{{\log }_{e}}{{e}^{i\theta }}$
Now, we will use another logarithmic identity which is as shown below
$\log {{a}^{b}}=b\log a$
Thus we will get
$\begin{align}
& {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+i\theta {{\log }_{e}}e \\
& \Rightarrow {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+i\theta \left( 1 \right)\left\{ {{\log }_{a}}a=1 \right\} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+i\theta ..................(v) \\
\end{align}$
Now it is given in question that a > 0 and b > 0 so, we have
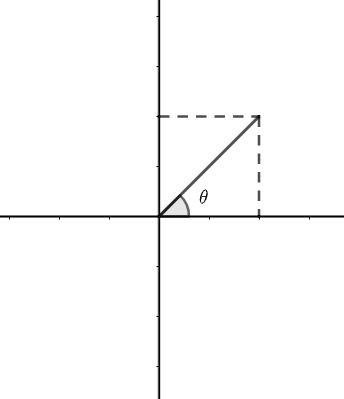
Thus
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{b}{a} \\
& \therefore \theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)...............\left( vi \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will substitute the value of $\theta $ from (vi) and ‘r’ from (iii) into equation (v). Thus, we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}+i{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
Now, we will use another identity:
$\log \sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\log x$
Thus we will get
${{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\log \left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right)+i{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
Hence, option (b) is correct.
Note: Here, while using the identity given below we have assumed that in
$\log \sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\log x$
x > 0. For this ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}>0$ . Thus a and b both should be real numbers. Also while the identity ${{\log }_{a}}a$ , a should be greater than zero and it should not be equal to 1.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For solving the given question above, first we will find the value of a + ib in terms of polar form. For this we will put the value of a as $r\cos \theta $ and we will put the value of b as $r\sin \theta $ . Thus we will get the following
$\begin{align}
& a=r\cos \theta ..............\left( i \right) \\
& b=r\sin \theta .............(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Here r is the modulus of the above complex number. The modulus of any complex number z= x + iy is represented by $\left| z \right|$ and it is given by the formula
$\left| z \right|=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}$
Thus the value of $r=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(iii)$
Now we will multiply the equation (ii) with ‘i’ and then we will add it into equation (i). Thus we get:
$a+ib=r\cos \theta +i\left( r\sin \theta \right)..............\left( iv \right)$
Now we will convert the polar form of the complex number into Euler’s form. According to Euler’s form we have
$A\cos B+i\left( A\sin B \right)=A{{e}^{iB}}$
Using this Euler’s form, we can rewrite equation (iv) as
$a+ib=r{{e}^{i\theta }}$
Now we will take a logarithm with base ‘e’ on both sides. Thus we will get
${{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}\left( r{{e}^{i\theta }} \right)$
Now, we will use a logarithm identity here
$\log \left( a\times b \right)=\log a+\operatorname{logb}$
Thus we will get
${{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+{{\log }_{e}}{{e}^{i\theta }}$
Now, we will use another logarithmic identity which is as shown below
$\log {{a}^{b}}=b\log a$
Thus we will get
$\begin{align}
& {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+i\theta {{\log }_{e}}e \\
& \Rightarrow {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+i\theta \left( 1 \right)\left\{ {{\log }_{a}}a=1 \right\} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}r+i\theta ..................(v) \\
\end{align}$
Now it is given in question that a > 0 and b > 0 so, we have

Thus
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{b}{a} \\
& \therefore \theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)...............\left( vi \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will substitute the value of $\theta $ from (vi) and ‘r’ from (iii) into equation (v). Thus, we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)={{\log }_{e}}\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}+i{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
Now, we will use another identity:
$\log \sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\log x$
Thus we will get
${{\log }_{e}}\left( a+ib \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\log \left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right)+i{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
Hence, option (b) is correct.
Note: Here, while using the identity given below we have assumed that in
$\log \sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\log x$
x > 0. For this ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}>0$ . Thus a and b both should be real numbers. Also while the identity ${{\log }_{a}}a$ , a should be greater than zero and it should not be equal to 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




