
Solve the following activity: zeroes of the polynomial ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2$ graphically.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: We first convert the given polynomial form into its conic form to place in the graph. We try to find the points where the curve intersects the X-axis. We take the x coordinates of those points. In the end, we evaluate the result with the algebraic solution of the curve.
Complete step-by-step solution
We have a quadratic equation ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2$. This is a parabolic curve.
Let $y\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-3x+2$. So, $y+\dfrac{1}{4}={{\left( x-\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}$.
We are finding the zeros of the polynomial. The solutions are the points of x at which the polynomial value is 0. In the graphical form, we are finding the intersection points of the curve with the X-axis.
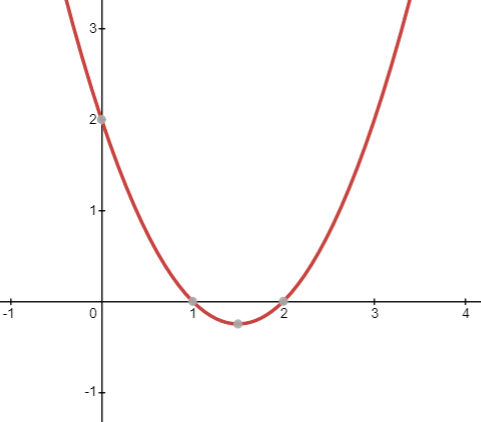
From the graph, we can see there are 2 such points at which the value of y is 0. The points are $\left( 1,0 \right),\left( 2,0 \right)$. So, the zeroes or the roots of the polynomial are the x coordinates of the points. The zeroes of the polynomial are 1 and 2.
Now we verify it with the algebraic version of the solution.
We factorise the polynomial $y\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-3x+2$.
So, at those root points the equational value is 0. So, we are solving the equation ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2=0$.
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-3x+2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2x-x+2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\left( x-2 \right)-\left( x-2 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x-2 \right)\left( x-1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
The multiplication of two terms is 0. So, at least one of them will be 0.
Solving we get $x=1,2$.
This satisfies the graphical assertion.
So, the zeroes of the polynomial ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2$ are 1,2.
Note: We need to understand that the polynomial value has to be 0. Zeroes of the polynomial are the roots of the polynomial. So, at those points the functional value of the curve is 0. The slope of the curve at those points is similar in value wise. We can also verify this result by substituting values of zeroes in the given equation ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2$ and check if the results satisfy or not.
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-3x+2 \\
& ={{1}^{2}}-3.1+2 \\
& =1-3+2 \\
& =0 \\
\end{align}$
and
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-3x+2 \\
& ={{2}^{2}}-3.2+2 \\
& =4-6+2 \\
& =0 \\
\end{align}$.
So, the zeroes satisfy the polynomial.
Complete step-by-step solution
We have a quadratic equation ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2$. This is a parabolic curve.
Let $y\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-3x+2$. So, $y+\dfrac{1}{4}={{\left( x-\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}$.
We are finding the zeros of the polynomial. The solutions are the points of x at which the polynomial value is 0. In the graphical form, we are finding the intersection points of the curve with the X-axis.

From the graph, we can see there are 2 such points at which the value of y is 0. The points are $\left( 1,0 \right),\left( 2,0 \right)$. So, the zeroes or the roots of the polynomial are the x coordinates of the points. The zeroes of the polynomial are 1 and 2.
Now we verify it with the algebraic version of the solution.
We factorise the polynomial $y\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-3x+2$.
So, at those root points the equational value is 0. So, we are solving the equation ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2=0$.
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-3x+2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2x-x+2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\left( x-2 \right)-\left( x-2 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x-2 \right)\left( x-1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
The multiplication of two terms is 0. So, at least one of them will be 0.
Solving we get $x=1,2$.
This satisfies the graphical assertion.
So, the zeroes of the polynomial ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2$ are 1,2.
Note: We need to understand that the polynomial value has to be 0. Zeroes of the polynomial are the roots of the polynomial. So, at those points the functional value of the curve is 0. The slope of the curve at those points is similar in value wise. We can also verify this result by substituting values of zeroes in the given equation ${{x}^{2}}-3x+2$ and check if the results satisfy or not.
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-3x+2 \\
& ={{1}^{2}}-3.1+2 \\
& =1-3+2 \\
& =0 \\
\end{align}$
and
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-3x+2 \\
& ={{2}^{2}}-3.2+2 \\
& =4-6+2 \\
& =0 \\
\end{align}$.
So, the zeroes satisfy the polynomial.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




