
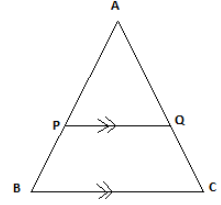
Solve the following:
A $(\triangle ABC)\; =\; 360\; cm^2$
A $(\square BPQC)\; =\; 110\; cm^2$
AP = 10 cm
Then find \[\dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\]

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Use the Triangle Proportionality Theorem, which states that if a line is parallel to one side of the triangle and it intersects with the other two sides, then that side is divided proportionally. If two triangles have two pairs of sides in the same ratio and the included angles are equal, then the triangles are similar.
If the triangles are similar, then the angles of the pairs of the corresponding angles are the same. Also, their corresponding pairs of the side are in the same proportion. Similar triangles have the same shape but do not have the same size.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given figure
PQ is parallel to BC, hence by using parallel line theorem, we can say
\[\angle APQ = \angle ABC\]
\[\angle AQP = \angle ACB\]
\[\angle A\] is common in both the triangle; hence we can say both the triangles are similar
Given the area
A $(\triangle ABC)\; =\; 360\; cm^2$
A $(\square BPQC)\; =\; 110\; cm^2$
And as the \[\vartriangle APQ\] and \[\vartriangle ABC\] are similar so we can write the area of the triangles will also be in the same proportion
\[\dfrac{{\vartriangle ABC}}{{\vartriangle APQ}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}}\]
Where the area \[\vartriangle APQ\] can be written as the difference of area of \[\vartriangle ABC\] and the area of a trapezoid $\square BPQC$
Now substituting the values, we can write
\[\dfrac{{\vartriangle ABC}}{{\vartriangle APQ}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{360}}{{360 - 110}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{360}}{{250}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{36}}{{25}}} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{6}{5} \\
\]
Hence the ratio of the length of the side \[\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{6}{5}\]
Since length of \[AP = 10cm\]
Hence we can write
\[
AB = \dfrac{6}{5} \times AP \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{6}{5} \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow12cm \\
\]
Since length of \[PB = AB - AP\]
Hence, \[PB = 12 - 10 = 2cm\]
Triangle Proportionality Theorem which states that if a line is parallel to one side of the triangle and it intersects with the other two sides, we can say
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\]
Hence by substituting the values
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}} = \dfrac{{12}}{2} = 6\]
We get, \[\dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}} = 6\]
Note: To prove two triangles to be similar, students must check whether all the angles are equal and/or, the corresponding pairs of sides are in the same ratio. Students should not get confused with the area of the quadrilateral given in the question; it is actually given as so that the area of both the triangles can be determined.
If the triangles are similar, then the angles of the pairs of the corresponding angles are the same. Also, their corresponding pairs of the side are in the same proportion. Similar triangles have the same shape but do not have the same size.
Complete step by step solution:
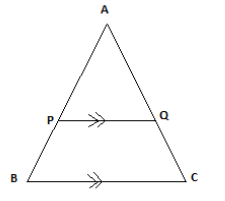
In the given figure

PQ is parallel to BC, hence by using parallel line theorem, we can say
\[\angle APQ = \angle ABC\]
\[\angle AQP = \angle ACB\]
\[\angle A\] is common in both the triangle; hence we can say both the triangles are similar
Given the area
A $(\triangle ABC)\; =\; 360\; cm^2$
A $(\square BPQC)\; =\; 110\; cm^2$
And as the \[\vartriangle APQ\] and \[\vartriangle ABC\] are similar so we can write the area of the triangles will also be in the same proportion
\[\dfrac{{\vartriangle ABC}}{{\vartriangle APQ}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}}\]
Where the area \[\vartriangle APQ\] can be written as the difference of area of \[\vartriangle ABC\] and the area of a trapezoid $\square BPQC$
Now substituting the values, we can write
\[\dfrac{{\vartriangle ABC}}{{\vartriangle APQ}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{360}}{{360 - 110}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{360}}{{250}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{36}}{{25}}} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{6}{5} \\
\]
Hence the ratio of the length of the side \[\dfrac{{AB}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{6}{5}\]
Since length of \[AP = 10cm\]
Hence we can write
\[
AB = \dfrac{6}{5} \times AP \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{6}{5} \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow12cm \\
\]
Since length of \[PB = AB - AP\]
Hence, \[PB = 12 - 10 = 2cm\]
Triangle Proportionality Theorem which states that if a line is parallel to one side of the triangle and it intersects with the other two sides, we can say
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\]
Hence by substituting the values
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}} = \dfrac{{12}}{2} = 6\]
We get, \[\dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}} = 6\]
Note: To prove two triangles to be similar, students must check whether all the angles are equal and/or, the corresponding pairs of sides are in the same ratio. Students should not get confused with the area of the quadrilateral given in the question; it is actually given as so that the area of both the triangles can be determined.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




