
How do you solve the equation $ - {x^2} + 14x - 49 = 0$ by graphing the related function?
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the given quadratic equation, remember the graph of every quadratic equation is a parabola. If the coefficient of ${x^2}$ is negative then it is a downward open parabola otherwise it is an upward open parabola. The x-intercepts are the root or solution of the equation and y-intercept can be obtained by putting $x = 0$in the equation.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a quadratic equation as $ - {x^2} + 14x - 49 = 0$.
We can write the given equation as:
As per the question, we have to find the important parts of the equation which will give us a better picture of the graph.
As we know, the graph of every quadratic equation is always a parabola. Parabola is basically a vague ’U’ Shaped graph.
Since the coefficient of variable $x$ is negative, we can conclude that the parabola will be a downward opening parabola.
Now, to check how many times this parabola will intersect with the x-axis, we have to find the determinant $D$ of the equation.
Let’s first compare the given equation $y = - {x^2} + 14x - 49$ with the standard quadratic equation $a{x^2} + bx + c$ to get the values of $a,b,c$, we get
$
a = - 1 \\
b = 14 \\
c = - 49 \;
$
Determinant $D$ of quadratic equation is given as $D = {b^2} - 4ac$
Putting the values of $a,b,c$, we get the determinant as
\[
D = {\left( {14} \right)^2} - 4\left( { - 1} \right)\left( { - 49} \right) \\
D = 196 - 196 \\
D = 0 \;
\]
Since, we got $D = 0$, which means there are two equal real roots or in other words the equation has one x-intercepts.
The Root or intercepts of x-axis are $x = \dfrac{{ - b}}{{2a}}$
$
\Rightarrow {x_1}/{x_2} = \dfrac{{ - 14}}{{2\left( { - 1} \right)}} \\
{x_1}/{x_2} = \dfrac{{ - 14}}{{\left( { - 2} \right)}} = 7 \\
$
$x = 7\,$is the intercept of x-axis which we can plot.
For the y-intercept put $x = 0$in the equation $y = - {x^2} + 14x - 49$, we get
$
y = - {x^2} + 14x - 49 \\
y = - {\left( 0 \right)^2} + 14\left( 0 \right) - 49 \\
y = - 49 \;
$
$y = - 49$this is our y-intercept.
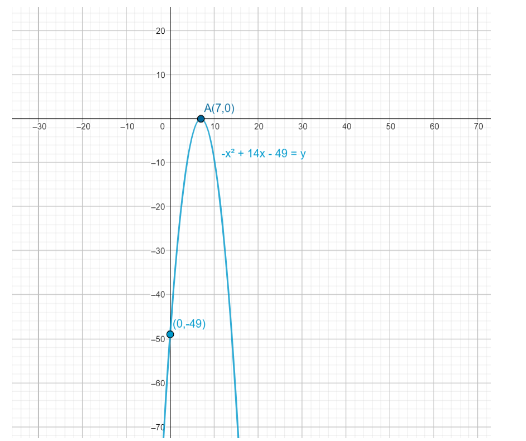
By drawing the graph and placing our points, we get, the x-intercepts as $x = 7$ and y-intercept as $y = - 49$:
Note: Quadratic Equation: A quadratic equation is a equation which can be represented in the form of $a{x^2} + bx + c$ where $x$ is the unknown variable and a, b, c are the numbers known where $a \ne 0$.If $a = 0$then the equation will become linear equation and will no more quadratic .
The degree of the quadratic equation is of the order 2.
Every Quadratic equation has 2 roots.
Discriminant: $D = {b^2} - 4ac$
Using Discriminant, we can find out the nature of the roots
If D is equal to zero, then both of the roots will be the same and real.
If D is a positive number then, both of the roots are real solutions.
If D is a negative number, then the root are the pair of complex solutions
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a quadratic equation as $ - {x^2} + 14x - 49 = 0$.
We can write the given equation as:
As per the question, we have to find the important parts of the equation which will give us a better picture of the graph.
As we know, the graph of every quadratic equation is always a parabola. Parabola is basically a vague ’U’ Shaped graph.
Since the coefficient of variable $x$ is negative, we can conclude that the parabola will be a downward opening parabola.
Now, to check how many times this parabola will intersect with the x-axis, we have to find the determinant $D$ of the equation.
Let’s first compare the given equation $y = - {x^2} + 14x - 49$ with the standard quadratic equation $a{x^2} + bx + c$ to get the values of $a,b,c$, we get
$
a = - 1 \\
b = 14 \\
c = - 49 \;
$
Determinant $D$ of quadratic equation is given as $D = {b^2} - 4ac$
Putting the values of $a,b,c$, we get the determinant as
\[
D = {\left( {14} \right)^2} - 4\left( { - 1} \right)\left( { - 49} \right) \\
D = 196 - 196 \\
D = 0 \;
\]
Since, we got $D = 0$, which means there are two equal real roots or in other words the equation has one x-intercepts.
The Root or intercepts of x-axis are $x = \dfrac{{ - b}}{{2a}}$
$
\Rightarrow {x_1}/{x_2} = \dfrac{{ - 14}}{{2\left( { - 1} \right)}} \\
{x_1}/{x_2} = \dfrac{{ - 14}}{{\left( { - 2} \right)}} = 7 \\
$
$x = 7\,$is the intercept of x-axis which we can plot.
For the y-intercept put $x = 0$in the equation $y = - {x^2} + 14x - 49$, we get
$
y = - {x^2} + 14x - 49 \\
y = - {\left( 0 \right)^2} + 14\left( 0 \right) - 49 \\
y = - 49 \;
$
$y = - 49$this is our y-intercept.
By drawing the graph and placing our points, we get, the x-intercepts as $x = 7$ and y-intercept as $y = - 49$:

Note: Quadratic Equation: A quadratic equation is a equation which can be represented in the form of $a{x^2} + bx + c$ where $x$ is the unknown variable and a, b, c are the numbers known where $a \ne 0$.If $a = 0$then the equation will become linear equation and will no more quadratic .
The degree of the quadratic equation is of the order 2.
Every Quadratic equation has 2 roots.
Discriminant: $D = {b^2} - 4ac$
Using Discriminant, we can find out the nature of the roots
If D is equal to zero, then both of the roots will be the same and real.
If D is a positive number then, both of the roots are real solutions.
If D is a negative number, then the root are the pair of complex solutions
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





