
How do you solve it \[\cos 2x + \sin x = 0\]. Over the interval \[0\] to \[2pi\]?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint: We need to know the trigonometric formula \[\cos 2\theta \]to make the easy calculation. We try to make the given expression into quadratic equation form by using the trigonometric formula. Also, we need to know how to factorize the quadratic equation. We need to know how to find\[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\& {\cos ^{ - 1}}\]values for different\[\theta \]values by using a scientific calculator. Also, we need to know in which quadrant \[\sin \theta \]has a positive value.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given equation is shown below,
\[\cos 2x + \sin x = 0 \to equation\left( 1 \right)\]
We know that,
\[\cos 2x = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}x \to equation\left( 2 \right)\]
Let’s substitute the equation\[\left( 2 \right)\]in the equation\[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[equation\left( 1 \right) \to \cos 2x + \sin x = 0\]
\[1 - 2{\sin ^2}x + \sin x = 0\]
The above equation can also be written as,
\[ - 2{\sin ^2}x + \sin x + 1 = 0 \to equation\left( 3 \right)\]
The above equation is in the form of a quadratic equation (Here we take\[\sin x\]instead of\[x\]).
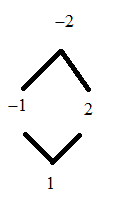
By solving the equation\[\left( 3 \right)\], we get
\[\sin x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}\]
Or
\[\sin x = \dfrac{2}{2} = 1\]
Let’s find the value of\[x\]from the above equations,
\[\sin x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}\]
\[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( 1 \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
So, we get
\[x = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( 1 \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{2} \to \left( 4 \right)\]
So, we get
\[x = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\sin x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}\], here we have \[\sin x\]is negative. We know that \[\sin x\]is negative in the third quadrant and fourth quadrant.
We know that,
\[\pi + \theta \to \]Third quadrant
\[2\pi - \theta \to \]Fourth quadrant
So, we get
\[x = \pi + \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}\]
Or
\[x = 2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{13\pi }}{6}\]
So, we get the final answer,
\[
x = \dfrac{\pi }{2}, \\
x = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}or\dfrac{{13\pi }}{6} \\
\]
Note: Note that the First quadrant has\[\left( {0 + \theta } \right)or\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \theta } \right)\], the Second quadrant have\[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + \theta } \right)or\left( {\pi - \theta } \right)\], the Third quadrant have\[\left( {\pi + \theta } \right)or\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \theta } \right)\] and the Fourth quadrant have\[\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} + \theta } \right)or\left( {2\pi - \theta } \right)\]. In the first quadrant all\[\sin ,\cos ,\]and\[\tan \]are positive, in the second quadrant\[\sin \]is positive, in the third quadrant\[\tan \]is positive and in the fourth quadrant\[\cos \]is positive. By using this information we can easily find the angle is positive or negative in the particular quadrant. Also, remember the trigonometric conditions to solve these types of questions. And remember the trigonometric table values for these types of questions.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given equation is shown below,
\[\cos 2x + \sin x = 0 \to equation\left( 1 \right)\]
We know that,
\[\cos 2x = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}x \to equation\left( 2 \right)\]
Let’s substitute the equation\[\left( 2 \right)\]in the equation\[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[equation\left( 1 \right) \to \cos 2x + \sin x = 0\]
\[1 - 2{\sin ^2}x + \sin x = 0\]
The above equation can also be written as,
\[ - 2{\sin ^2}x + \sin x + 1 = 0 \to equation\left( 3 \right)\]
The above equation is in the form of a quadratic equation (Here we take\[\sin x\]instead of\[x\]).

By solving the equation\[\left( 3 \right)\], we get
\[\sin x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}\]
Or
\[\sin x = \dfrac{2}{2} = 1\]
Let’s find the value of\[x\]from the above equations,
\[\sin x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}\]
\[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( 1 \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
So, we get
\[x = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( 1 \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{2} \to \left( 4 \right)\]
So, we get
\[x = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\sin x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}\], here we have \[\sin x\]is negative. We know that \[\sin x\]is negative in the third quadrant and fourth quadrant.
We know that,
\[\pi + \theta \to \]Third quadrant
\[2\pi - \theta \to \]Fourth quadrant
So, we get
\[x = \pi + \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}\]
Or
\[x = 2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{13\pi }}{6}\]
So, we get the final answer,
\[
x = \dfrac{\pi }{2}, \\
x = \dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}or\dfrac{{13\pi }}{6} \\
\]
Note: Note that the First quadrant has\[\left( {0 + \theta } \right)or\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \theta } \right)\], the Second quadrant have\[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + \theta } \right)or\left( {\pi - \theta } \right)\], the Third quadrant have\[\left( {\pi + \theta } \right)or\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \theta } \right)\] and the Fourth quadrant have\[\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} + \theta } \right)or\left( {2\pi - \theta } \right)\]. In the first quadrant all\[\sin ,\cos ,\]and\[\tan \]are positive, in the second quadrant\[\sin \]is positive, in the third quadrant\[\tan \]is positive and in the fourth quadrant\[\cos \]is positive. By using this information we can easily find the angle is positive or negative in the particular quadrant. Also, remember the trigonometric conditions to solve these types of questions. And remember the trigonometric table values for these types of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




