
Solve graphically. Express answers in both inequality and interval notation.
\[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}} \leqslant 0\]
Answer
529.8k+ views
Hint: Linear inequalities are the expressions where any two values are compared by the inequality such as, '<', '>', '≤' or '≥'. This represents inequalities as: < (less than) > (greater than) ≤ (less than or equal to) and ≥ (greater than or equal to). Hence, to graph the solution we need to find the domain i.e., the interval with respect to the given inequality in \[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}} \leqslant 0\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
\[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}} \leqslant 0\]
We have the inequality as,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x - \left( { - 4} \right)}}{{ - \left( {x - 1} \right)}} \leqslant 0\]
\[g\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - \left( { - 4} \right)}}{{ - \left( {x - 1} \right)}} \leqslant 0\]
Find all the values where the expression switches from negative to positive by setting each factor equal to 0 and solving i.e.,
\[x - \left( { - 4} \right) = 0\] and \[x - 1 = 0\] .
Hence, let us solve for:
\[x - \left( { - 4} \right) = 0\]
Subtract -4 from both sides of the equation we get:
\[ \Rightarrow x + 4 - 4 = 0 - 4\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 4\] …………………….. 1
Now, for,
\[x - 1 = 0\]
Add 1 to both sides of the equation we get:
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + 1 = 0 + 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 1\] ………………………… 2
Solve for each factor to find the values where the absolute value expression goes from negative to positive, we have:
\[x = - 4\] and \[x = 1\] .
Therefore, the critical points are \[x = - 4\] and \[x = 1\] .
Now, let us find the domain of \[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}}\] .
Set the denominator in \[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}}\] equal to 0 to find where the expression is undefined, we get from equation 1 as:
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 4\] , the domain is all values of x that make the expression defined.
\[g\left( x \right)\] is positive in \[x \in \left( { - \infty , - 4} \right] \cup \left( {1,\infty } \right)\] .
Thus, the entire solution is the union of the two positive intervals:
\[x \in \left( { - \infty , - 4} \right] \cup \left( {1,\infty } \right)\]
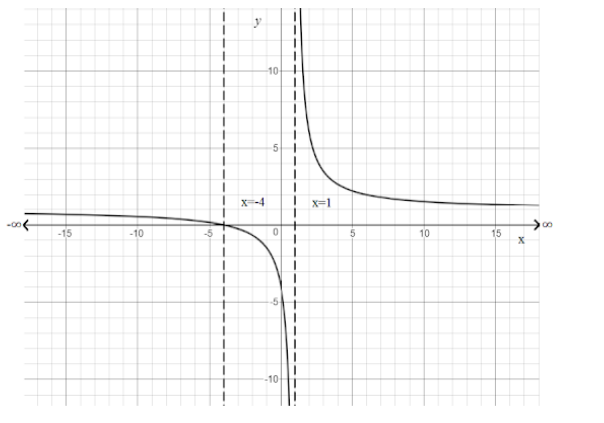
Note: An inequality does not change if any number or variable are added or subtracted on both sides. Similarly, its value is not affected if the same number or variable is multiplied on both sides. Except when inequality is divided by a negative variable or number on both the sides, then the inequality is flipped or reversed. On dividing inequality by a positive number, it does not require any change.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
\[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}} \leqslant 0\]
We have the inequality as,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x - \left( { - 4} \right)}}{{ - \left( {x - 1} \right)}} \leqslant 0\]
\[g\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - \left( { - 4} \right)}}{{ - \left( {x - 1} \right)}} \leqslant 0\]
Find all the values where the expression switches from negative to positive by setting each factor equal to 0 and solving i.e.,
\[x - \left( { - 4} \right) = 0\] and \[x - 1 = 0\] .
Hence, let us solve for:
\[x - \left( { - 4} \right) = 0\]
Subtract -4 from both sides of the equation we get:
\[ \Rightarrow x + 4 - 4 = 0 - 4\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 4\] …………………….. 1
Now, for,
\[x - 1 = 0\]
Add 1 to both sides of the equation we get:
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + 1 = 0 + 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 1\] ………………………… 2
Solve for each factor to find the values where the absolute value expression goes from negative to positive, we have:
\[x = - 4\] and \[x = 1\] .
Therefore, the critical points are \[x = - 4\] and \[x = 1\] .
Now, let us find the domain of \[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}}\] .
Set the denominator in \[\dfrac{{x + 4}}{{1 - x}}\] equal to 0 to find where the expression is undefined, we get from equation 1 as:
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 4\] , the domain is all values of x that make the expression defined.
\[g\left( x \right)\] is positive in \[x \in \left( { - \infty , - 4} \right] \cup \left( {1,\infty } \right)\] .
Thus, the entire solution is the union of the two positive intervals:
\[x \in \left( { - \infty , - 4} \right] \cup \left( {1,\infty } \right)\]

Note: An inequality does not change if any number or variable are added or subtracted on both sides. Similarly, its value is not affected if the same number or variable is multiplied on both sides. Except when inequality is divided by a negative variable or number on both the sides, then the inequality is flipped or reversed. On dividing inequality by a positive number, it does not require any change.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





