
Solve $\dfrac{{\left( {2x + 3} \right){{\left( {4 - 3x} \right)}^3}\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}^2}{x^3}}} \leqslant 0$
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: We have given an inequality we have to find the interval in which the value of x lies and satisfies the integrity. Firstly, we have to solve the inequality and find the factor. This factor will give us a critical point. These critical points help us to find the interval. We check the inequality and find the interval.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given inequality.
$\dfrac{{\left( {2x + 3} \right){{\left( {4 - 3x} \right)}^3}\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}^2}{x^3}}} \leqslant 0$
We have to find the interval in which the value of x lies and satisfies the inequality.
Now $\dfrac{{\left( {2x + 3} \right){{\left( {4 - 3x} \right)}^3}\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}^2}{x^3}}} \leqslant 0$
Taking the terms in the denominator to the right-hand side with zero.
$\left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \leqslant 0{\left( {x - 2} \right)^2}{x^3}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \leqslant 0$
Multiplying both sides with a negative sign changes the inequality sign from ‘$ \leqslant $’ to ‘$ \geqslant $’.
$ \Rightarrow - \left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \geqslant 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \geqslant 0$ ---(i)
From the above inequality, we get three values of x.
We draw these values on the number line.
The values are $ - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3},4$
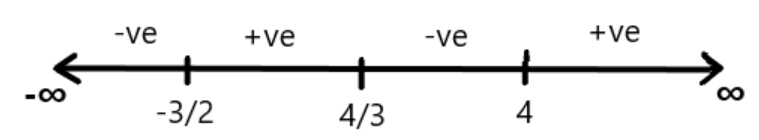
Now, we have four intervals $\left( { - \infty , - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right],\left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right],\left[ {\dfrac{4}{3},4} \right],\left[ {4,\infty } \right)$
Now, if we put values from the interval $\left[ {4,\infty } \right)$, the value of inequality will be greater than zero.
If we put the value from the interval $\left[ {\dfrac{4}{3},4} \right]$, the value of inequality will be less than equal to zero.
If we put the value of ‘$x$’ from the interval $\left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right]$ the value of inequality will be greater than equal to zero.
If we put the value of ‘$x$’ from the interval $\left( { - \infty , - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right]$, the value of inequality will be less than equal to zero.
Now, the inequality is positive or zero in the interval $\left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right],\left[ {4,\infty } \right)$
So, $x \in \left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right] \cup \left[ {4,\infty } \right)$
Note: Inequality: In mathematics, an inequality is a relation that makes a non-equal comparison between two numbers or other mathematical expressions. It is used most often to compare two numbers on the number line by their size. There are several different kinds of inequalities.
The notation $a < b$ means that $a$ is less than $b$.
The notation $a > b$ means that $a$ is greater than $b$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given inequality.
$\dfrac{{\left( {2x + 3} \right){{\left( {4 - 3x} \right)}^3}\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}^2}{x^3}}} \leqslant 0$
We have to find the interval in which the value of x lies and satisfies the inequality.
Now $\dfrac{{\left( {2x + 3} \right){{\left( {4 - 3x} \right)}^3}\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}^2}{x^3}}} \leqslant 0$
Taking the terms in the denominator to the right-hand side with zero.
$\left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \leqslant 0{\left( {x - 2} \right)^2}{x^3}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \leqslant 0$
Multiplying both sides with a negative sign changes the inequality sign from ‘$ \leqslant $’ to ‘$ \geqslant $’.
$ \Rightarrow - \left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \geqslant 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2x + 3} \right){\left( {4 - 3x} \right)^3}\left( {x - 4} \right) \geqslant 0$ ---(i)
From the above inequality, we get three values of x.
We draw these values on the number line.
The values are $ - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3},4$

Now, we have four intervals $\left( { - \infty , - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right],\left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right],\left[ {\dfrac{4}{3},4} \right],\left[ {4,\infty } \right)$
Now, if we put values from the interval $\left[ {4,\infty } \right)$, the value of inequality will be greater than zero.
If we put the value from the interval $\left[ {\dfrac{4}{3},4} \right]$, the value of inequality will be less than equal to zero.
If we put the value of ‘$x$’ from the interval $\left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right]$ the value of inequality will be greater than equal to zero.
If we put the value of ‘$x$’ from the interval $\left( { - \infty , - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right]$, the value of inequality will be less than equal to zero.
Now, the inequality is positive or zero in the interval $\left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right],\left[ {4,\infty } \right)$
So, $x \in \left[ { - \dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right] \cup \left[ {4,\infty } \right)$
Note: Inequality: In mathematics, an inequality is a relation that makes a non-equal comparison between two numbers or other mathematical expressions. It is used most often to compare two numbers on the number line by their size. There are several different kinds of inequalities.
The notation $a < b$ means that $a$ is less than $b$.
The notation $a > b$ means that $a$ is greater than $b$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




