
How do you solve $\dfrac{3}{7}x + \dfrac{1}{2} = 3$ by clearing the fractions?
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: First we have to find the least common multiple (LCM) of all the denominators in the given equation. Next, we have to multiply both sides of the equation with the LCM of denominators. Next step is to isolate the variable terms on one side, and the constant terms on the other side. Next step is to make the coefficient of the variable equal to $1$ using multiplication or division property.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The algebraic equation is $\dfrac{3}{7}x + \dfrac{1}{2} = 3$.
We have to find the value of $x$.
First we have to find the least common multiple (LCM) of all the denominators in the given equation.
Denominator of $\dfrac{3}{7}$ is $7$ and denominator of $\dfrac{1}{2}$ is $2$.
So, we have to find the LCM of $7$and $2$.
Here, $7$and $2$ are prime numbers. So, their LCM will be their product
LCM of $7$and $2$$ = 7 \times 2 = 14$
Now, we have to multiply both sides of the equation with the LCM of $7$and $2$.
So, multiplying both sides of equation $\dfrac{3}{7}x + \dfrac{1}{2} = 3$ by $14$.
Now we can write it as,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 14}}{7}} \right)x + \left( {\dfrac{{1 \times 14}}{2}} \right) = 3 \times 14$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow 6x + 7 = 42$
Next step is to isolate the variable terms on one side, and the constant terms on the other side.
So, subtracting $7$ from both sides of the equation $6x + 7 = 42$
$6x = 35$
Next step is to make the coefficient of the variable equal to $1$.
So, multiplying both sides of equation $6x = 35$ by $\dfrac{1}{6}$.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{35}}{6}$
Therefore, $x = \dfrac{{35}}{6}$ is the solution of $\dfrac{3}{7}x + \dfrac{1}{2} = 3$.
Note: An algebraic equation is an equation involving variables. It has an equality sign. The expression on the left of the equality sign is the Left Hand Side (LHS). The expression on the right of the equality sign is the Right Hand Side (RHS).
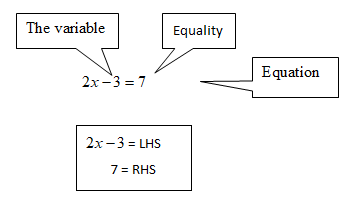
In an equation the values of the expressions on the LHS and RHS are equal. This happens to be true only for certain values of the variable. These values are the solutions of the equation.
How to find the solution of an equation?
We assume that the two sides of the equation are balanced. We perform the same mathematical operations on both sides of the equation, so that the balance is not disturbed.
Solving Equations having the Variable on both sides:
Transpose variable term to LHS.
Transpose constant term on RHS.
Then it will become the algebraic equation. It can be solved as explained above.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The algebraic equation is $\dfrac{3}{7}x + \dfrac{1}{2} = 3$.
We have to find the value of $x$.
First we have to find the least common multiple (LCM) of all the denominators in the given equation.
Denominator of $\dfrac{3}{7}$ is $7$ and denominator of $\dfrac{1}{2}$ is $2$.
So, we have to find the LCM of $7$and $2$.
Here, $7$and $2$ are prime numbers. So, their LCM will be their product
LCM of $7$and $2$$ = 7 \times 2 = 14$
Now, we have to multiply both sides of the equation with the LCM of $7$and $2$.
So, multiplying both sides of equation $\dfrac{3}{7}x + \dfrac{1}{2} = 3$ by $14$.
Now we can write it as,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 14}}{7}} \right)x + \left( {\dfrac{{1 \times 14}}{2}} \right) = 3 \times 14$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow 6x + 7 = 42$
Next step is to isolate the variable terms on one side, and the constant terms on the other side.
So, subtracting $7$ from both sides of the equation $6x + 7 = 42$
$6x = 35$
Next step is to make the coefficient of the variable equal to $1$.
So, multiplying both sides of equation $6x = 35$ by $\dfrac{1}{6}$.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{35}}{6}$
Therefore, $x = \dfrac{{35}}{6}$ is the solution of $\dfrac{3}{7}x + \dfrac{1}{2} = 3$.
Note: An algebraic equation is an equation involving variables. It has an equality sign. The expression on the left of the equality sign is the Left Hand Side (LHS). The expression on the right of the equality sign is the Right Hand Side (RHS).

In an equation the values of the expressions on the LHS and RHS are equal. This happens to be true only for certain values of the variable. These values are the solutions of the equation.
How to find the solution of an equation?
We assume that the two sides of the equation are balanced. We perform the same mathematical operations on both sides of the equation, so that the balance is not disturbed.
Solving Equations having the Variable on both sides:
Transpose variable term to LHS.
Transpose constant term on RHS.
Then it will become the algebraic equation. It can be solved as explained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Convert 40circ C to Fahrenheit A 104circ F B 107circ class 8 maths CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE





