
How do you solve $\cos x+1=0$ and find all solutions in the interval $0\le x<360$?
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: We explain the function $\cos x+1=0$. We express the inverse function of cos in the form of $\arccos \left( x \right)={{\cos }^{-1}}x$. We draw the graph of $\cos x$ and the line $y=-1$ to find the intersection point as the solution for the interval $0\le x<360$.
Complete step by step answer:
The given expression is the inverse function of trigonometric ratio cos.
If \[{{\cos }^{-1}}x=\alpha \] then we can say $\cos \alpha =x$.
Each of the trigonometric functions is periodic in the real part of its argument, running through all its values twice in each interval of $2\pi $.
The general solution for that value where $\cos \alpha =x$ will be $2n\pi \pm \alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
But for $\arccos \left( x \right)$, we won’t find the general solution. We use the principal value. For ratio cos we have $0\le \arccos \left( x \right)\le \pi $.
Now we take the function as $y=\cos x=-1$. The graph of the function $y=\cos x$ is
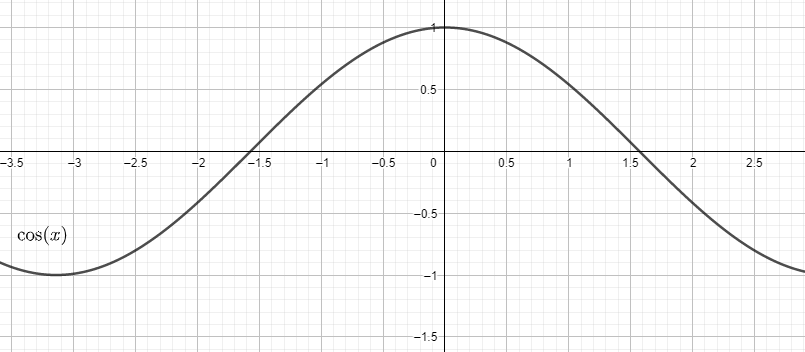
Let the angle be $\theta $ for which $\arccos \left( x \right)={{\cos }^{-1}}x=\theta $. This gives $\cos \theta =-1$.
We know that $\cos \theta =-1=\cos \left( \pi \right)$ which gives $\theta =\pi $. For this we take the line of $y=-1$ and see the intersection of the line with the graph $\arccos \left( x \right)$.
The general solution of the function $\cos x+1=0$ is $2n\pi \pm \alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$
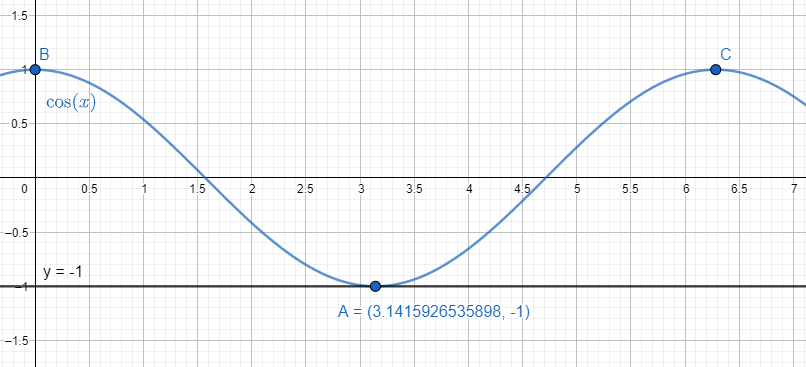
We get the value of y coordinates as $\pi $. The points B and C are the points $B\equiv \left( 0,1 \right)$ and $C\equiv \left( 2\pi ,1 \right)$. In the interval of $0\le x<360$, the only intersection of the curve $y=\cos x$ and the line $y=-1$ is point $A\equiv \left( \pi ,-1 \right)$.
The general solution of the function $\cos x+1=0$ is $2n\pi \pm \pi ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$. The simplified solution for $\cos x+1=0$ is $\left( 2n\pm 1 \right)\pi ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
Note:
If we are finding an $\arccos \left( x \right)$ of a positive value, the answer is between $0\le \arccos \left( x \right)\le \dfrac{\pi }{2}$. If we are finding the $\arccos \left( x \right)$ of a negative value, the answer is between $\dfrac{\pi }{2}\le \arccos \left( x \right)\le \pi $.
Complete step by step answer:
The given expression is the inverse function of trigonometric ratio cos.
If \[{{\cos }^{-1}}x=\alpha \] then we can say $\cos \alpha =x$.
Each of the trigonometric functions is periodic in the real part of its argument, running through all its values twice in each interval of $2\pi $.
The general solution for that value where $\cos \alpha =x$ will be $2n\pi \pm \alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
But for $\arccos \left( x \right)$, we won’t find the general solution. We use the principal value. For ratio cos we have $0\le \arccos \left( x \right)\le \pi $.
Now we take the function as $y=\cos x=-1$. The graph of the function $y=\cos x$ is

Let the angle be $\theta $ for which $\arccos \left( x \right)={{\cos }^{-1}}x=\theta $. This gives $\cos \theta =-1$.
We know that $\cos \theta =-1=\cos \left( \pi \right)$ which gives $\theta =\pi $. For this we take the line of $y=-1$ and see the intersection of the line with the graph $\arccos \left( x \right)$.
The general solution of the function $\cos x+1=0$ is $2n\pi \pm \alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$

We get the value of y coordinates as $\pi $. The points B and C are the points $B\equiv \left( 0,1 \right)$ and $C\equiv \left( 2\pi ,1 \right)$. In the interval of $0\le x<360$, the only intersection of the curve $y=\cos x$ and the line $y=-1$ is point $A\equiv \left( \pi ,-1 \right)$.
The general solution of the function $\cos x+1=0$ is $2n\pi \pm \pi ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$. The simplified solution for $\cos x+1=0$ is $\left( 2n\pm 1 \right)\pi ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
Note:
If we are finding an $\arccos \left( x \right)$ of a positive value, the answer is between $0\le \arccos \left( x \right)\le \dfrac{\pi }{2}$. If we are finding the $\arccos \left( x \right)$ of a negative value, the answer is between $\dfrac{\pi }{2}\le \arccos \left( x \right)\le \pi $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




