
How do you solve and graph $3b+2<5b-6\le 2b+9?$
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: In the given question, we are supposed to find the solutions to the inequality $3b+2<5b-6\le 2b+9$ . We solve the given question by finding out the solutions of the linear equations by isolating the variable b to get the desired result.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given an inequality and are asked to find the solutions for the same. We will be solving the given question by solving the linear equations by isolating the variable b.
Algebraic expressions in mathematics are made up of variables, constants, and operators.
Every algebraic expression has variables, coefficients, constants, and terms.
Arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division can be performed on Algebraic expressions.
The like terms in algebra mean that the terms have the same variable and same power.
In Algebra, Only like terms can be added or subtracted.
The inequality in the question is given as follows,
$\Rightarrow 3b+2<5b-6\le 2b+9$
We find the value of b by solving the inequalities $3b+2<5b-6$ and $5b-6\le 2b+9$
Following the same, we get,
$\Rightarrow 3b+2<5b-6$
Subtracting the term 3b from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 3b+2-3b<5b-6-3b$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 2< 2b-6$
Dividing the above inequality by 2 on both sides, we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{2}< \dfrac{2b}{2}-\dfrac{6}{2}$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 1< b-3$
Adding the number 3 on both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 1+3< b-3+3$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 4< b$
The above expression can also be written as follows,
$\Rightarrow b> 4$
Solving the inequality $5b-6\le 2b+9$ , we get,
$\Rightarrow 5b-6\le 2b+9$
Subtracting the term 2b from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 5b-6-2b\le 2b+9-2b$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 3b-6\le 9$
Dividing the above inequality by 3 on both sides, we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3b}{3}-\dfrac{6}{3}\le \dfrac{9}{3}$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow b-2\le 3$
Adding the number 2 on both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow b-2+2\le 3+2$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow b\le 5$
Now, we know that the value of the variable is given by inequalities $b>4$ and $b\le 5$
From the above, the value of b can be written in the form of inequality as follows,
$\Rightarrow 4< b\le 5$
The internal notation for the above inequality is given as follows,
$\Rightarrow b\in \left( 4, \right.\left. 5 \right]$
The graph of the inequality is given as follows,
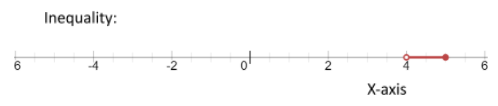
$\therefore$ The solutions to the inequality $3b+2<5b-6\le 2b+9$ are in the internal of $b\in \left( 4, \right.\left. -5 \right]$
Note: The result obtained in the given question can be cross-checked by substituting the values of b in the inequality in the interval of $b\in \left( 4, \right.\left. -5 \right]$ . If the result on substitution satisfies the inequality, then the result attained is correct.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given an inequality and are asked to find the solutions for the same. We will be solving the given question by solving the linear equations by isolating the variable b.
Algebraic expressions in mathematics are made up of variables, constants, and operators.
Every algebraic expression has variables, coefficients, constants, and terms.
Arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division can be performed on Algebraic expressions.
The like terms in algebra mean that the terms have the same variable and same power.
In Algebra, Only like terms can be added or subtracted.
The inequality in the question is given as follows,
$\Rightarrow 3b+2<5b-6\le 2b+9$
We find the value of b by solving the inequalities $3b+2<5b-6$ and $5b-6\le 2b+9$
Following the same, we get,
$\Rightarrow 3b+2<5b-6$
Subtracting the term 3b from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 3b+2-3b<5b-6-3b$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 2< 2b-6$
Dividing the above inequality by 2 on both sides, we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{2}< \dfrac{2b}{2}-\dfrac{6}{2}$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 1< b-3$
Adding the number 3 on both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 1+3< b-3+3$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 4< b$
The above expression can also be written as follows,
$\Rightarrow b> 4$
Solving the inequality $5b-6\le 2b+9$ , we get,
$\Rightarrow 5b-6\le 2b+9$
Subtracting the term 2b from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 5b-6-2b\le 2b+9-2b$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow 3b-6\le 9$
Dividing the above inequality by 3 on both sides, we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3b}{3}-\dfrac{6}{3}\le \dfrac{9}{3}$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow b-2\le 3$
Adding the number 2 on both sides of the inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow b-2+2\le 3+2$
Simplifying the above inequality, we get,
$\Rightarrow b\le 5$
Now, we know that the value of the variable is given by inequalities $b>4$ and $b\le 5$
From the above, the value of b can be written in the form of inequality as follows,
$\Rightarrow 4< b\le 5$
The internal notation for the above inequality is given as follows,
$\Rightarrow b\in \left( 4, \right.\left. 5 \right]$
The graph of the inequality is given as follows,
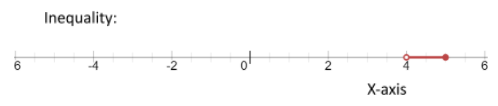
$\therefore$ The solutions to the inequality $3b+2<5b-6\le 2b+9$ are in the internal of $b\in \left( 4, \right.\left. -5 \right]$
Note: The result obtained in the given question can be cross-checked by substituting the values of b in the inequality in the interval of $b\in \left( 4, \right.\left. -5 \right]$ . If the result on substitution satisfies the inequality, then the result attained is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




