
How do you solve \[12{x^2} = - 11x + 15\] by graphing?
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: In this question we are asked to solve the quadratic equation using graphical method, for this we will consider each term in the equation as a variable let it be \[y\] , i.e., \[y = 12{x^2}\] and \[y = - 11x + 15\] , and then we will plot each equation individually and find their point of intersection, and the \[x\] -coordinates of the point of intersection are the requires solutions for the given quadratic equation.
Complete step by step solution:
A graph is the picture of the points that make a function true. The roots of a quadratic equation are the \[x\] -intercepts of the graph. A graph is a useful representation for determining the solution of a quadratic equation. To best use a graph, think about a quadratic equation as written in two parts: \[a{x^2} + bx + c = k\] ,
Graph each part of the quadratic equation: \[a{x^2} + bx + c = k\] and \[y = k\] , Look for the intersection of the two graphs. The \[x\] -coordinates of the intersection points will tell you the values of \[x\] that are solutions to the original equation,
Given equation is \[12{x^2} = - 11x + 15\] ,
Let us consider each term in the equation as a variable, i.e.,
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[y = 12{x^2}\] and \[y = - 11x + 15\] ,
Now plot the graphs of these equations we get,
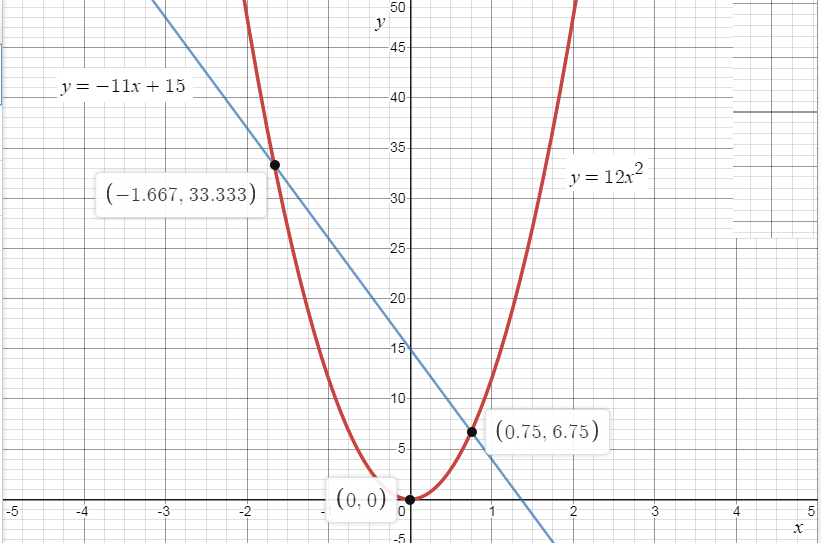
From the graph it is clear that the two equations \[y = 12{x^2}\] which is a curve and \[y = - 11x + 15\] which is a straight line intersect at points \[\left( { - 1.67,33.33} \right)\] and \[\left( {0.75,6.75} \right)\] ,
So, the solution for the given equation is \[x = - 1.67\] and \[x = 0.75\] .
The required solution for the given equation \[12{x^2} = - 11x + 15\] is equal to \[ - 1.67\] and \[0.75\] .
Note: It is important to note that the solution of the given equation is only \[x\] -coordinates of the point of intersection.
A quadratic equation has two roots if its graph has two \[x\] -intercepts
A quadratic equation has one root it its graph has one \[x\] -intercept
A quadratic equation has no real solutions if its graph has no \[x\] -intercepts.
Complete step by step solution:
A graph is the picture of the points that make a function true. The roots of a quadratic equation are the \[x\] -intercepts of the graph. A graph is a useful representation for determining the solution of a quadratic equation. To best use a graph, think about a quadratic equation as written in two parts: \[a{x^2} + bx + c = k\] ,
Graph each part of the quadratic equation: \[a{x^2} + bx + c = k\] and \[y = k\] , Look for the intersection of the two graphs. The \[x\] -coordinates of the intersection points will tell you the values of \[x\] that are solutions to the original equation,
Given equation is \[12{x^2} = - 11x + 15\] ,
Let us consider each term in the equation as a variable, i.e.,
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[y = 12{x^2}\] and \[y = - 11x + 15\] ,
Now plot the graphs of these equations we get,

From the graph it is clear that the two equations \[y = 12{x^2}\] which is a curve and \[y = - 11x + 15\] which is a straight line intersect at points \[\left( { - 1.67,33.33} \right)\] and \[\left( {0.75,6.75} \right)\] ,
So, the solution for the given equation is \[x = - 1.67\] and \[x = 0.75\] .
The required solution for the given equation \[12{x^2} = - 11x + 15\] is equal to \[ - 1.67\] and \[0.75\] .
Note: It is important to note that the solution of the given equation is only \[x\] -coordinates of the point of intersection.
A quadratic equation has two roots if its graph has two \[x\] -intercepts
A quadratic equation has one root it its graph has one \[x\] -intercept
A quadratic equation has no real solutions if its graph has no \[x\] -intercepts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




