
Why is sodium metal not used in the lab preparation of hydrogen?
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we must first understand how hydrogen is produced in labs. In that, we need to observe the reactants and the conditions used to carry out the experiments. Then we must compare the chemical properties of both sodium and the corresponding reactant to find out the reason for the other compound to be better.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Dihydrogen or just Hydrogen is one of the most widely found gases. Various reactions release hydrogen gas as either a major product or as a by – product. But in most of these cases, the hydrogen gas formed is directly released into the atmosphere. It is very difficult to trap and collect the hydrogen formed because of its light weight and low density.
To collect this hydrogen, a very efficient laboratory method has been developed. The details about this process are as follows:
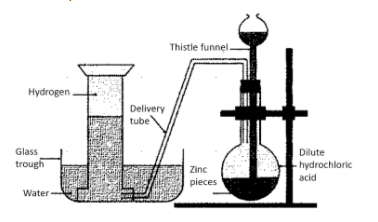
This process involves 4 major steps:
1.First of all, a certain amount of zinc granules is placed in a flask
2.After this, hydrochloric acid needs to be added to these zinc granules. This is done with the help of a thistle funnel. A replacement for hydrochloric acid could be sulphuric acid.
3.The reaction between the acid and the zinc granules would release hydrogen gas. The gas thus produced is transferred to a vessel filled with water, via a delivery tube.
4.The transferred hydrogen is now collected via a method known as downward displacement of water.
The chemical reaction for this process can be given as:
\[Zn + {H_2}S{O_{4(dil.)}} \to ZnS{o_4} + {H_2}\]
Zinc granules are widely preferred for laboratory preparation of hydrogen gas because these granules usually have a small quantity of Cu, which has the ability to act as a catalyst in the given process.
Now, Sodium is highly reactive when compared to zinc. Sodium would directly form a hydroxide compound with hydrogen in air. Because of this reason, sodium is not used in the laboratory preparation of hydrogen
Note: Before collecting the hydrogen gas with the help of the apparatus, precautions must be taken in order to ensure that all the air inside the apparatus has been displaced. This is because hydrogen gas reacts explosively with air.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Dihydrogen or just Hydrogen is one of the most widely found gases. Various reactions release hydrogen gas as either a major product or as a by – product. But in most of these cases, the hydrogen gas formed is directly released into the atmosphere. It is very difficult to trap and collect the hydrogen formed because of its light weight and low density.
To collect this hydrogen, a very efficient laboratory method has been developed. The details about this process are as follows:

This process involves 4 major steps:
1.First of all, a certain amount of zinc granules is placed in a flask
2.After this, hydrochloric acid needs to be added to these zinc granules. This is done with the help of a thistle funnel. A replacement for hydrochloric acid could be sulphuric acid.
3.The reaction between the acid and the zinc granules would release hydrogen gas. The gas thus produced is transferred to a vessel filled with water, via a delivery tube.
4.The transferred hydrogen is now collected via a method known as downward displacement of water.
The chemical reaction for this process can be given as:
\[Zn + {H_2}S{O_{4(dil.)}} \to ZnS{o_4} + {H_2}\]
Zinc granules are widely preferred for laboratory preparation of hydrogen gas because these granules usually have a small quantity of Cu, which has the ability to act as a catalyst in the given process.
Now, Sodium is highly reactive when compared to zinc. Sodium would directly form a hydroxide compound with hydrogen in air. Because of this reason, sodium is not used in the laboratory preparation of hydrogen
Note: Before collecting the hydrogen gas with the help of the apparatus, precautions must be taken in order to ensure that all the air inside the apparatus has been displaced. This is because hydrogen gas reacts explosively with air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




