
Why is the small intestine called “small”?
Answer
481.2k+ views
Hint: The small intestine, also known as the small bowel, is an organ in the digestive tract that is responsible for the majority of nutritional absorption from food. It is located between the stomach and the large intestine, and it gets bile and pancreatic juice via the pancreatic duct to help in digestion.
Complete answer:
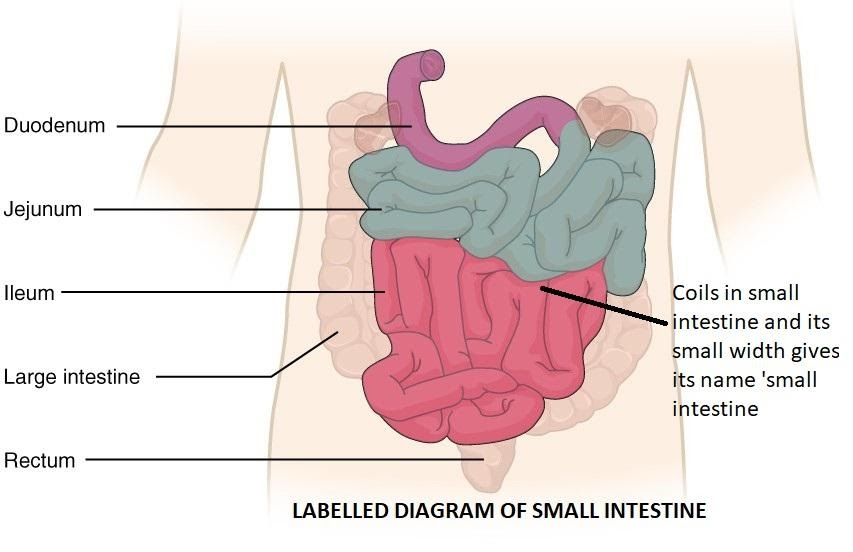
The duodenum, jejunum, and ileum are all parts of the small intestine (small bowel), which is located between the stomach and the large intestine (large bowel). The small intestine is approximately six meters in length and coils several times to conform into the abdomen. The small intestine gets its name from the fact that its lumen width is smaller than that of the large intestine, despite the fact that it is longer than the large intestine.
Food from the stomach is mixed with pancreatic enzymes and gallbladder bile in the duodenum of the small intestine. Food is broken up by enzymes and bile. Jejunum also aids in digestion. Bile acids and vitamins are collected by the ileum, which are required by the body for a range of processes.
Additional information:
Because of its enormous inner surface area, the small intestine is ideal for absorption. The plicae circulares, which deploy many tiny finger-like projections of tissue called villi, serve this purpose. Individual epithelial cells also have protrusion that resemble fingers, known as microvilli.
Note:
The small intestine is a tube-like structure in the abdominal cavity that transports food from the stomach to the colon, where it is transferred to the large intestine, which then transports it to the rectum and out of the body through the anus. This organ's primary task is to assist digestion.
Complete answer:
The duodenum, jejunum, and ileum are all parts of the small intestine (small bowel), which is located between the stomach and the large intestine (large bowel). The small intestine is approximately six meters in length and coils several times to conform into the abdomen. The small intestine gets its name from the fact that its lumen width is smaller than that of the large intestine, despite the fact that it is longer than the large intestine.
Food from the stomach is mixed with pancreatic enzymes and gallbladder bile in the duodenum of the small intestine. Food is broken up by enzymes and bile. Jejunum also aids in digestion. Bile acids and vitamins are collected by the ileum, which are required by the body for a range of processes.

Additional information:
Because of its enormous inner surface area, the small intestine is ideal for absorption. The plicae circulares, which deploy many tiny finger-like projections of tissue called villi, serve this purpose. Individual epithelial cells also have protrusion that resemble fingers, known as microvilli.
Note:
The small intestine is a tube-like structure in the abdominal cavity that transports food from the stomach to the colon, where it is transferred to the large intestine, which then transports it to the rectum and out of the body through the anus. This organ's primary task is to assist digestion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




