
How do you sketch the graph \[y={{x}^{3}}-4{{x}^{2}}\] using the first and second derivatives?
Answer
549.9k+ views
Hint: To graph the function using its equation and derivative, we need to follow some steps. First, find the value of the roots that can be found using the equation. Differentiate the function to find the increasing and decreasing intervals for the function. Again, differentiate the function to find the points where the curve is concave upward or concave downward. Using the roots, increasing decreasing intervals, and concavity conditions, we can graph the equation.
Complete step by step solution:
The given equation is \[y={{x}^{3}}-4{{x}^{2}}\]. We know the steps to follow to graph an equation using its derivatives. First, let’s find the roots of the equation. As the constant term of the equation is zero, one root must be \[x=0\]. Factoring the equation, we get \[y=x\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x \right)\]. We can factorize this quadratic equation to further factorize equation as \[y={{x}^{2}}\left( x-4 \right)\]
We can say that this cubic equation has three roots, one of them is a repeated root. So together the given equation has two real roots.
Differentiating the equation, we get
\[\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( {{x}^{3}}-4{{x}^{2}} \right)}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( {{x}^{3}} \right)}{dx}-\dfrac{d\left( 4{{x}^{2}} \right)}{dx}\]
\[\dfrac{dy}{dx}=3{{x}^{2}}-8x\]
We can easily find the roots of the above quadratic equation as \[x=0\And x=\dfrac{8}{3}\].
Further factoring the derivative to get second derivative, we get \[\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}y}{d{{x}^{2}}}=6x-8\]. This linear equation has only one real root, \[x=\dfrac{8}{6}=\dfrac{4}{3}\].
Now, we have the first and second derivative of the function, and their roots. We can use this information to plot the given equation as follows,
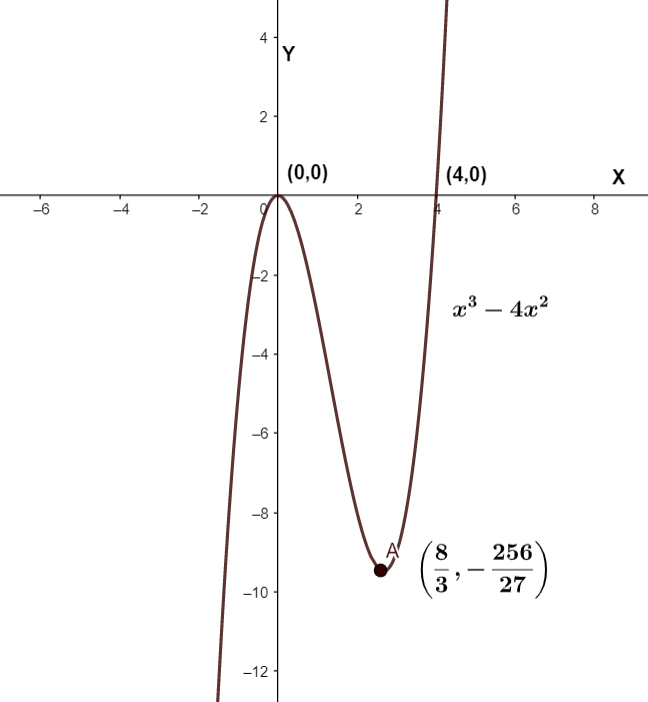
Note: The method to graph the function using their first and second derivative is very useful. We can describe the nature of a function in a range by looking at its graph. The graph of the function also tells us about the local and global maxima or minima, also the roots of the function.
Complete step by step solution:
The given equation is \[y={{x}^{3}}-4{{x}^{2}}\]. We know the steps to follow to graph an equation using its derivatives. First, let’s find the roots of the equation. As the constant term of the equation is zero, one root must be \[x=0\]. Factoring the equation, we get \[y=x\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x \right)\]. We can factorize this quadratic equation to further factorize equation as \[y={{x}^{2}}\left( x-4 \right)\]
We can say that this cubic equation has three roots, one of them is a repeated root. So together the given equation has two real roots.
Differentiating the equation, we get
\[\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( {{x}^{3}}-4{{x}^{2}} \right)}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( {{x}^{3}} \right)}{dx}-\dfrac{d\left( 4{{x}^{2}} \right)}{dx}\]
\[\dfrac{dy}{dx}=3{{x}^{2}}-8x\]
We can easily find the roots of the above quadratic equation as \[x=0\And x=\dfrac{8}{3}\].
Further factoring the derivative to get second derivative, we get \[\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}y}{d{{x}^{2}}}=6x-8\]. This linear equation has only one real root, \[x=\dfrac{8}{6}=\dfrac{4}{3}\].
Now, we have the first and second derivative of the function, and their roots. We can use this information to plot the given equation as follows,

Note: The method to graph the function using their first and second derivative is very useful. We can describe the nature of a function in a range by looking at its graph. The graph of the function also tells us about the local and global maxima or minima, also the roots of the function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




