
How do you sketch the graph of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$ ?
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: If we draw the graph of any function f(x) and shift the graph k units towards right , we will get the graph of f(x- k). If the function f(x) is ${{\log }_{2}}x$ the value of f(x –k) is equal to ${{\log }_{2}}\left( x-k \right)$. If we assume f(x) as ${{\log }_{2}}x$ and k as 1, to solve this question we will first draw the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ and then we will shift the graph 1 unit towards right we will get the graph of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to sketch $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$
We can draw the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ then we will shift the graph of 1 unit towards the right. We will get the graph of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$
The graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ will be same shape as graph of $\ln x$ we can write ${{\log }_{2}}x=\dfrac{\ln x}{\ln 2}$
So let’s draw the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ and shift the graph 1 unit towards right
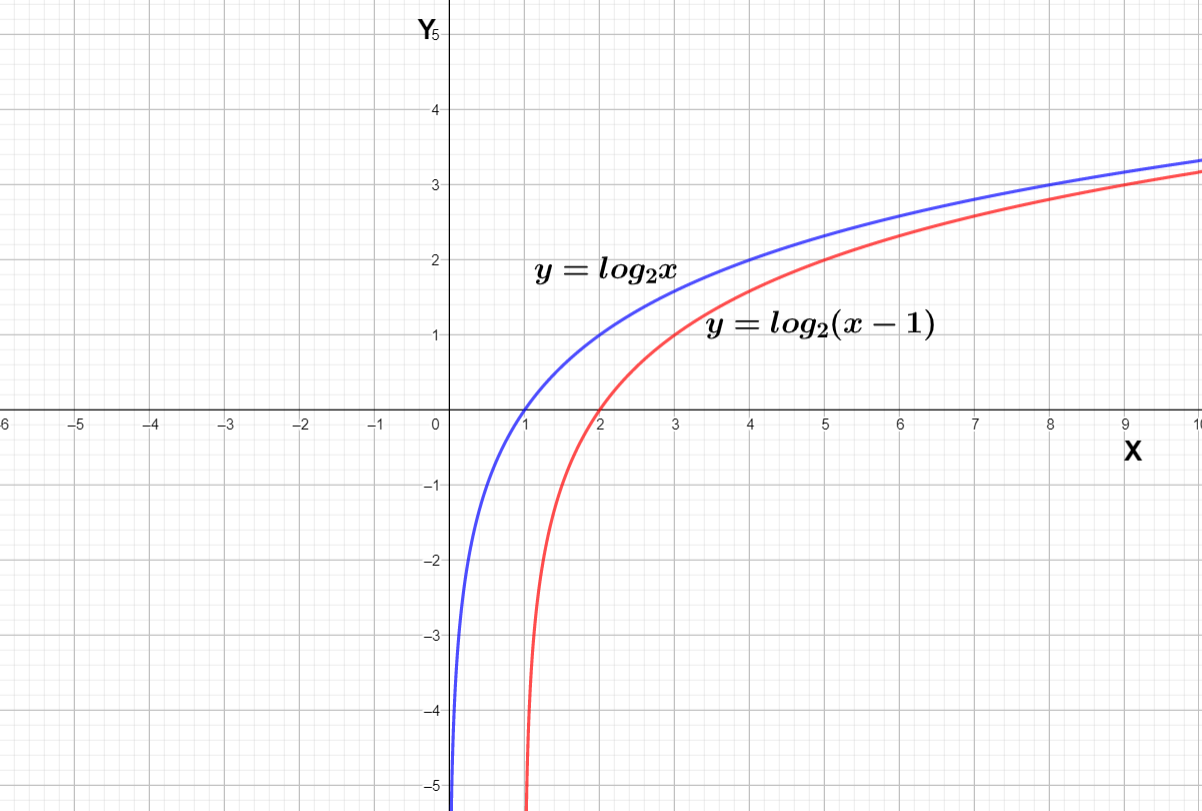
We can see the blue curve is the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ shifting the curve we get the red curve which is of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$
Note: We can see the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ does not exist when x is less equal to 0 that is because the domain of log x includes only positive real numbers . The domain of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$ is from 1 to infinity which does not include 1 because in $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$ the value of x – 1 should be positive real number and if we solve x – 1 > 0 we will get the solution $x\in \left( 1,\infty \right)$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to sketch $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$
We can draw the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ then we will shift the graph of 1 unit towards the right. We will get the graph of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$
The graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ will be same shape as graph of $\ln x$ we can write ${{\log }_{2}}x=\dfrac{\ln x}{\ln 2}$
So let’s draw the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ and shift the graph 1 unit towards right

We can see the blue curve is the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ shifting the curve we get the red curve which is of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$
Note: We can see the graph of ${{\log }_{2}}x$ does not exist when x is less equal to 0 that is because the domain of log x includes only positive real numbers . The domain of $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$ is from 1 to infinity which does not include 1 because in $y={{\log }_{2}}\left( x-1 \right)$ the value of x – 1 should be positive real number and if we solve x – 1 > 0 we will get the solution $x\in \left( 1,\infty \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




