
How do you sketch the graph of the polar equation and find the tangents at the pole of $r=3\sin \theta $?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: We explain the number of ways position of a point or equation can be expressed in different forms. We also explain the ways the representation works for polar and cartesian form. Then we convert the given equation into rectangular form using the relations $x=r\cos \theta ;y=r\sin \theta $.
Complete step by step solution:
In case of polar form, we use the distance and the angle from the origin to get the position of the point or curve.
The given equation $r=3\sin \theta $ is a representation of the polar form. r represents the distance and $\theta $ represents the angle.
We need to convert the given equation $r=3\sin \theta $ into the rectangular form.
The relation between these two forms in two-dimensional is
$x=r\cos \theta ;y=r\sin \theta ;{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$.
From the relations we get $\sin \theta =\dfrac{y}{r}$.
We now replace the value of $\sin \theta =\dfrac{y}{r}$ in the equation $r=3\sin \theta $ to get
\[\begin{align}
& r=3\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow r=3\left( \dfrac{y}{r} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{3y}{r} \\
& \Rightarrow 3y={{r}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We now replace the value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$ for the equation \[3y={{r}^{2}}\]. The revised equation becomes \[3y={{r}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}\].
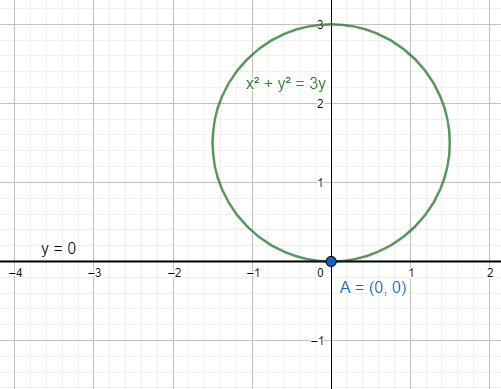
The equation is an equation of circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=3y\].
Now we have to find the tangent of the circle at the pole $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
Doing differentiation, we get $x{{x}_{1}}+y{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{3}{2}\left( y+{{y}_{1}} \right)$ at point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$.
Putting the value of $\left( 0,0 \right)$, we get
$0=\dfrac{3}{2}\left( y \right)\Rightarrow y=0$.
The tangent is $y=0$.
Note:In case of points for cartesian form we use x and y coordinates as $\left( x,y \right)$ to express their position in the cartesian plane. The distance from origin is $r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}$. This r represents the distance in polar form.
Complete step by step solution:
In case of polar form, we use the distance and the angle from the origin to get the position of the point or curve.
The given equation $r=3\sin \theta $ is a representation of the polar form. r represents the distance and $\theta $ represents the angle.
We need to convert the given equation $r=3\sin \theta $ into the rectangular form.
The relation between these two forms in two-dimensional is
$x=r\cos \theta ;y=r\sin \theta ;{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$.
From the relations we get $\sin \theta =\dfrac{y}{r}$.
We now replace the value of $\sin \theta =\dfrac{y}{r}$ in the equation $r=3\sin \theta $ to get
\[\begin{align}
& r=3\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow r=3\left( \dfrac{y}{r} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{3y}{r} \\
& \Rightarrow 3y={{r}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We now replace the value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$ for the equation \[3y={{r}^{2}}\]. The revised equation becomes \[3y={{r}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}\].
The equation is an equation of circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=3y\].
Now we have to find the tangent of the circle at the pole $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
Doing differentiation, we get $x{{x}_{1}}+y{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{3}{2}\left( y+{{y}_{1}} \right)$ at point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$.
Putting the value of $\left( 0,0 \right)$, we get
$0=\dfrac{3}{2}\left( y \right)\Rightarrow y=0$.
The tangent is $y=0$.

Note:In case of points for cartesian form we use x and y coordinates as $\left( x,y \right)$ to express their position in the cartesian plane. The distance from origin is $r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}$. This r represents the distance in polar form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




