
Sketch, label and describe zygotene.
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: This stage is a part of the stage prophase in meiosis, and is followed by leptotene, during which homologous chromosomes start to pair.
Complete answer:
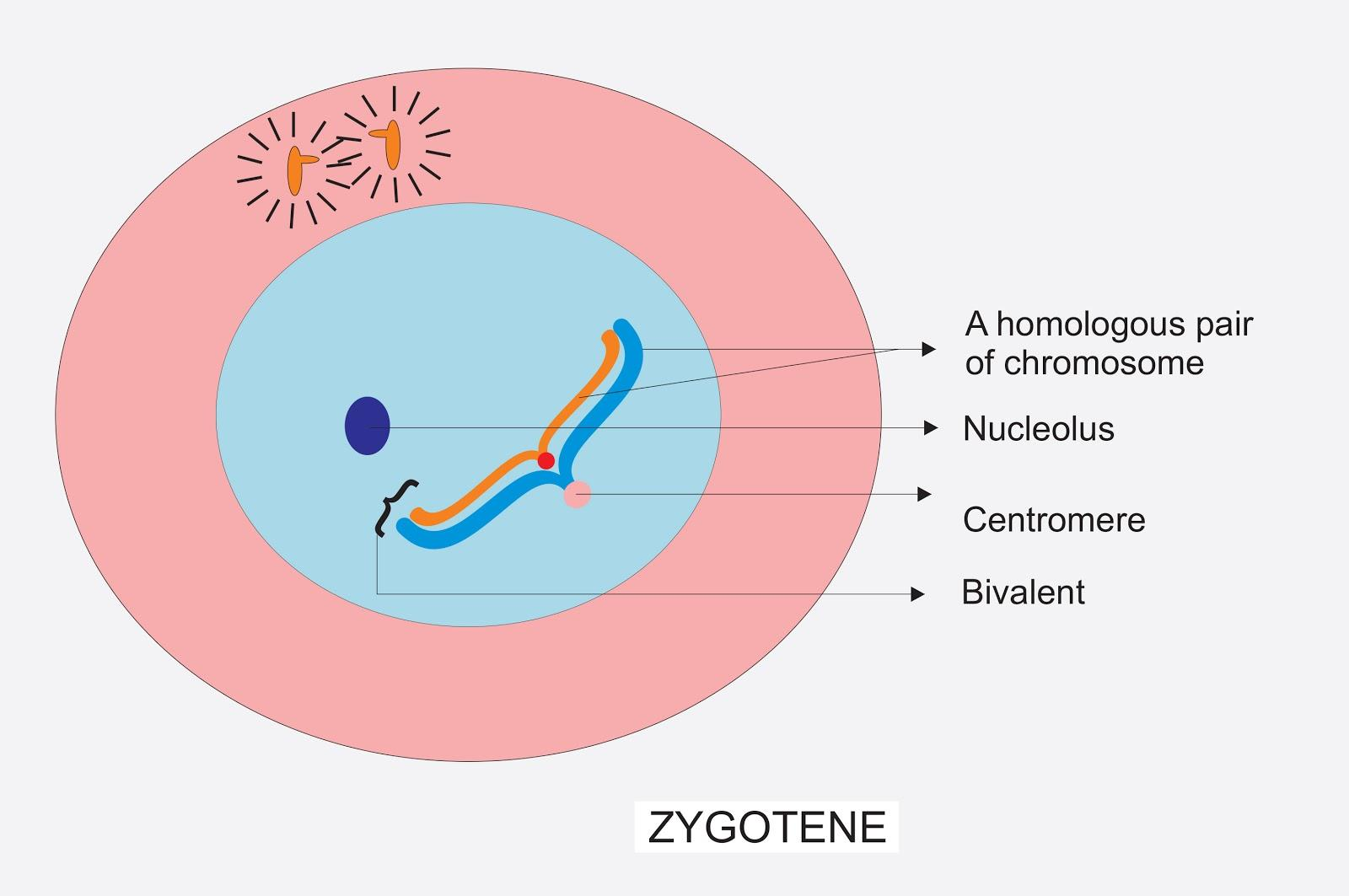
Zygotene is the second stage of the prophase of meiosis, following leptotene, during which homologous chromosomes start to pair. It is a substage of meiosis where synapsis between homologous chromosomes starts. This synapsis can form up and down the chromosomes to make various points of contact called 'synaptonemal complex', coiling of chromatin.
Meiosis is a form of cell division that gives rise to genetically diverse sex cells or gametes. It comprises two successive nuclear divisions namely meiosis l and meiosis ll.
Meiosis I comprises four stages: prophase l, metaphase l, anaphase l, and telophase l. Prophase l is the very first stage of meiosis I and it contains the following sub-stages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
The zygotene is the prophase I stage that follows after leptotene and then pachytene. Before zygotene, the chromosomes start to condense into long strands inside the nucleus and the chromosomes appear threadlike. Zygotene is that phase wherein the homologous chromosomes pair or come together in the synapse. The pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis and is facilitated by the synaptonemal complex.
The pairing is zipper-like in fashion. At any part of the chromosomes, the pairing may start, e.g., near the end of the centromere. The pairing is also particular, i.e., homologous chromosomes that come in pairs must be of equal length and have the same centromere position. The paired chromosomes are termed bivalent or tetrad chromosomes.
Note:
-The term zygotene is derived from Greek words that mean paired threads.
-The zygotene stage is also described as a bouquet stage since the telomeres cluster at one end of the nucleus. It is also known as zygonema.
Complete answer:
Zygotene is the second stage of the prophase of meiosis, following leptotene, during which homologous chromosomes start to pair. It is a substage of meiosis where synapsis between homologous chromosomes starts. This synapsis can form up and down the chromosomes to make various points of contact called 'synaptonemal complex', coiling of chromatin.

Meiosis is a form of cell division that gives rise to genetically diverse sex cells or gametes. It comprises two successive nuclear divisions namely meiosis l and meiosis ll.
Meiosis I comprises four stages: prophase l, metaphase l, anaphase l, and telophase l. Prophase l is the very first stage of meiosis I and it contains the following sub-stages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
The zygotene is the prophase I stage that follows after leptotene and then pachytene. Before zygotene, the chromosomes start to condense into long strands inside the nucleus and the chromosomes appear threadlike. Zygotene is that phase wherein the homologous chromosomes pair or come together in the synapse. The pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis and is facilitated by the synaptonemal complex.
The pairing is zipper-like in fashion. At any part of the chromosomes, the pairing may start, e.g., near the end of the centromere. The pairing is also particular, i.e., homologous chromosomes that come in pairs must be of equal length and have the same centromere position. The paired chromosomes are termed bivalent or tetrad chromosomes.
Note:
-The term zygotene is derived from Greek words that mean paired threads.
-The zygotene stage is also described as a bouquet stage since the telomeres cluster at one end of the nucleus. It is also known as zygonema.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




