
Sketch and label the organelle known as a powerhouse of cells.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint:Cell is the basic structural and function unit of life. The term cell was introduced by Robert Hooke and various organelles are present in the cell. The organelles are organized structures in the cytoplasm having specific functions necessary for the metabolism of the cell.
Complete answer:
Various cell organelles are plasma membrane, cell wall, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, plastids, ribosomes, vacuoles etc out of these cell walls, plastids (chloroplast) are found only in plant cells.
Mitochondria is known as the “powerhouse of the cell”. It has two membranes, the outer membrane is smooth and has porin proteins, and the inner membrane is semipermeable and regulates the passage of materials into and out of the mitochondria. It usually produces numerous infolds called cristae. They are semiautonomous organelles and are capable of self-duplication.
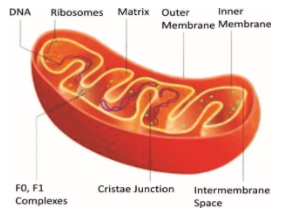
The cristae and the inner face of the inner membrane is studded with oxysomes.Mitochondria are the main site of cellular respiration. Thus, they help in oxidation of food, due to which they release energy in the form of ATP. ATP is the “energy currency” of the cell and required for all cellular activities. Hence, mitochondria are known as “power-house” of the cell.
Mitochondria regulate the calcium ion concentration in the cell by storing and releasing $Ca^{2+}$
Note:The function of mitochondria is as follows,
>It promotes growth of new cells and also in cell multiplication.
>It helps in regulation of a cell's metabolic activities.
>It plays an important role in apoptosis of the cell or programmed cell death.
>It is involved in cellular activities like - cell signalling, cell senescence, cell growth, cellular differentiation, etc
Complete answer:
Various cell organelles are plasma membrane, cell wall, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, plastids, ribosomes, vacuoles etc out of these cell walls, plastids (chloroplast) are found only in plant cells.
Mitochondria is known as the “powerhouse of the cell”. It has two membranes, the outer membrane is smooth and has porin proteins, and the inner membrane is semipermeable and regulates the passage of materials into and out of the mitochondria. It usually produces numerous infolds called cristae. They are semiautonomous organelles and are capable of self-duplication.

The cristae and the inner face of the inner membrane is studded with oxysomes.Mitochondria are the main site of cellular respiration. Thus, they help in oxidation of food, due to which they release energy in the form of ATP. ATP is the “energy currency” of the cell and required for all cellular activities. Hence, mitochondria are known as “power-house” of the cell.
Mitochondria regulate the calcium ion concentration in the cell by storing and releasing $Ca^{2+}$
Note:The function of mitochondria is as follows,
>It promotes growth of new cells and also in cell multiplication.
>It helps in regulation of a cell's metabolic activities.
>It plays an important role in apoptosis of the cell or programmed cell death.
>It is involved in cellular activities like - cell signalling, cell senescence, cell growth, cellular differentiation, etc
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




