
Siphonogamy is a reproductive process in plants that produce seeds. In this process, a pollen tube carries the sperm cells to the egg located within the integumented megasporangium. Which group of plants exhibits this process?
(a)Pteridophytes
(b)Bryophytes
(c)Thallophytes
(d)Gymnosperms
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: These flowerless plants produce cones and seeds. The seed of these types of plants is naked (whose ovule is not enclosed in the ovary of the flower). This is a vascular plant of the subkingdom Embyophyta and includes conifers, cycads, ginkgoes, and gnetophytes.
Complete answer:
Siphonogamy is exhibited by the gymnosperms. In siphonogamy, the pollen tubes are developed for the transfer of male cells to the eggs.
Additional Information: -The gymnosperms, also known as the Acrogymnospermae.
-The development of a vascular system capable of transporting water throughout the plant enabled the gymnosperm to colonize the land.
-The ovule is also known as the megasporangium.
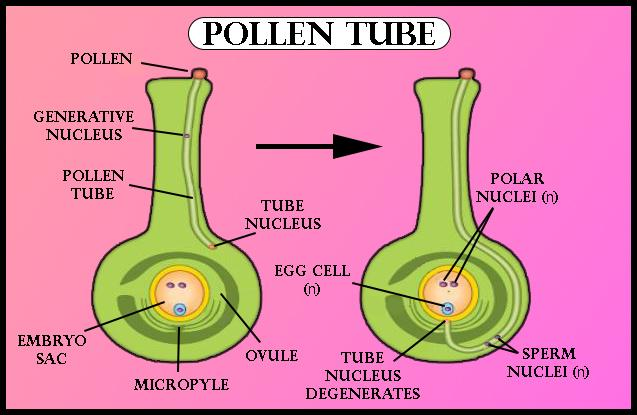
-A pollen tube is a tubular structure produced by the male gametophyte of the seed plants when it germinates.
-The growth of the pollen tube is stimulated by a sugary substance produced in the stigma of the flower.
-The length of the pollen tube depends upon the length of the styles.
-The pollen tube germinates after pollination from the intine layer of the pollen grain.
-When the pollen tube pierces through the integument of the ovule, such a process is called mesogamy.
-When the pollen tube enters the embryo sac through the base (chalaza) of the ovule, such a process is called chalazogamy.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Gymnosperms.’
Note: Gymnosperms are abundant in the temperate and boreal forest biomes with species that can tolerate moist or dry conditions. Gymnosperms are the first seed plants to have evolved. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones or exist alone as in yew, Torreya, Ginkgo.
Complete answer:
Siphonogamy is exhibited by the gymnosperms. In siphonogamy, the pollen tubes are developed for the transfer of male cells to the eggs.
Additional Information: -The gymnosperms, also known as the Acrogymnospermae.
-The development of a vascular system capable of transporting water throughout the plant enabled the gymnosperm to colonize the land.
-The ovule is also known as the megasporangium.
-A pollen tube is a tubular structure produced by the male gametophyte of the seed plants when it germinates.
-The growth of the pollen tube is stimulated by a sugary substance produced in the stigma of the flower.
-The length of the pollen tube depends upon the length of the styles.
-The pollen tube germinates after pollination from the intine layer of the pollen grain.
-When the pollen tube pierces through the integument of the ovule, such a process is called mesogamy.
-When the pollen tube enters the embryo sac through the base (chalaza) of the ovule, such a process is called chalazogamy.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Gymnosperms.’
Note: Gymnosperms are abundant in the temperate and boreal forest biomes with species that can tolerate moist or dry conditions. Gymnosperms are the first seed plants to have evolved. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones or exist alone as in yew, Torreya, Ginkgo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




