
Show that the function $f:R\to R:f(x)=\left| x \right|$ is neither one-one nor onto.
Answer
610.8k+ views
Hint: To check whether the given function is one-one or not, assume two elements ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ in the set of the domain of the given function and substitute $f({{x}_{1}})=f({{x}_{2}})$. If ${{x}_{1}}={{x}_{2}}$, then $f(x)$ is one-one and if there is any more relation between ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ other than ${{x}_{1}}={{x}_{2}}$ then $f(x)$ is not one-one. To check whether the given function is onto or not, check if the range of $f(x)$ is equal to co-domain or not. Here, co-domain is the set of all values of $f(x)$ in which the range of the function is constrained.
Complete step-by-step solution -
It is given that function is defined for all real numbers and over all real numbers. Therefore, both domain and co-domain of the given function consists of the set of all real numbers.
First let us show that the function is not one-one.
Assume two elements ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ in the set of the domain of the given function. Therefore,
\[f({{x}_{1}})=f({{x}_{2}})\]
Substituting, ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ in the function, we get,
\[\left| {{x}_{1}} \right|=\left| {{x}_{2}} \right|\]
On squaring both sides, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left| {{x}_{1}} \right|}^{2}}={{\left| {{x}_{2}} \right|}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| {{x}_{1}}^{2} \right|=\left| {{x}_{2}}^{2} \right| \\
\end{align}\]
Removing modulus from both sides, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}_{1}}^{2}={{x}_{2}}^{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}^{2}-{{x}_{2}}^{2}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}^{2}-{{x}_{2}}^{2}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow ({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})({{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}})=0 \\
& \Rightarrow ({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})=0\text{ or }({{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}})=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}={{x}_{2}}\text{ or }{{x}_{1}}=-{{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Clearly, we can see that, when \[f({{x}_{1}})=f({{x}_{2}})\] then, there is more than one relation between ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$. Therefore, $f(x)$ is not one-one.
Now, let us show that the given function is not onto.
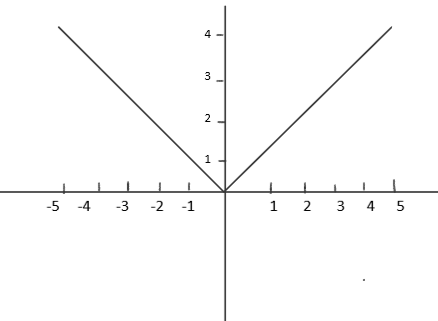
Clearly, we can see that the co-domain of the function contains the set of real numbers. Since, $f(x)=\left| x \right|$, therefore, the range of $f(x)$ will be only positive real numbers because the modulus of any real number will always be positive. So, here range and co-domain are not equal.
Therefore, it is proved that $f(x)$ is not onto.
Note: One may note that we do not have to cancel the common terms while checking whether the function is one-one. Consider all the possible relations between ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ and then only come to the conclusion just as we did in the above solution. Also, there is another method to check whether the given function is onto or not. We have to draw the graph of $f(x)=\left| x \right|$ for all real values of ‘x’. If the graph of $f(x)=\left| x \right|$ extends from $-\infty \text{ to }\infty $, that is it extends over all real numbers, then the function is onto otherwise not.
Complete step-by-step solution -
It is given that function is defined for all real numbers and over all real numbers. Therefore, both domain and co-domain of the given function consists of the set of all real numbers.
First let us show that the function is not one-one.
Assume two elements ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ in the set of the domain of the given function. Therefore,
\[f({{x}_{1}})=f({{x}_{2}})\]
Substituting, ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ in the function, we get,
\[\left| {{x}_{1}} \right|=\left| {{x}_{2}} \right|\]
On squaring both sides, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left| {{x}_{1}} \right|}^{2}}={{\left| {{x}_{2}} \right|}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| {{x}_{1}}^{2} \right|=\left| {{x}_{2}}^{2} \right| \\
\end{align}\]
Removing modulus from both sides, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}_{1}}^{2}={{x}_{2}}^{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}^{2}-{{x}_{2}}^{2}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}^{2}-{{x}_{2}}^{2}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow ({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})({{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}})=0 \\
& \Rightarrow ({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})=0\text{ or }({{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}})=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}={{x}_{2}}\text{ or }{{x}_{1}}=-{{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Clearly, we can see that, when \[f({{x}_{1}})=f({{x}_{2}})\] then, there is more than one relation between ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$. Therefore, $f(x)$ is not one-one.
Now, let us show that the given function is not onto.

Clearly, we can see that the co-domain of the function contains the set of real numbers. Since, $f(x)=\left| x \right|$, therefore, the range of $f(x)$ will be only positive real numbers because the modulus of any real number will always be positive. So, here range and co-domain are not equal.
Therefore, it is proved that $f(x)$ is not onto.
Note: One may note that we do not have to cancel the common terms while checking whether the function is one-one. Consider all the possible relations between ${{x}_{1}}\text{ and }{{x}_{2}}$ and then only come to the conclusion just as we did in the above solution. Also, there is another method to check whether the given function is onto or not. We have to draw the graph of $f(x)=\left| x \right|$ for all real values of ‘x’. If the graph of $f(x)=\left| x \right|$ extends from $-\infty \text{ to }\infty $, that is it extends over all real numbers, then the function is onto otherwise not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

India is a sovereign socialist secular democratic republic class 12 social science CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

What are the advantages of vegetative propagation class 12 biology CBSE

Suicide bags of cells are aEndoplasmic reticulum bLysosome class 12 biology CBSE

What is the Full Form of PVC, PET, HDPE, LDPE, PP and PS ?




