
Show that the following four conditions are equivalent:
(i)\[A \subset B\]
(ii)\[A - B = \phi \]
(iii)\[A \cup B = B\]
(iv)\[A \cap B = A\]
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to show that condition (i) is equivalent to (ii), condition (ii) is equivalent to (iii) and condition (iii) is equivalent to (iv). Hence, all the four conditions are equivalent. We can also use the Venn diagrams for practical understanding of the question and prove that all the four conditions are equivalent.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, let us assume : \[ \subset \to shows\,{\rm{ a\, symbol\, of\, subset\,}}\]\[A \subset B \to shows\,{\rm{ all\, the\, elements\, of\, A\, are\, present\, in\, B\,}}\] \[U \to is\,{\rm{ the\, universal\, set\,}}{\rm{.}}\]
Here ,we will do this question in three steps:
step1 Here, we show condition \[A \subset B\] is equivalent to condition \[A - B = \phi \].
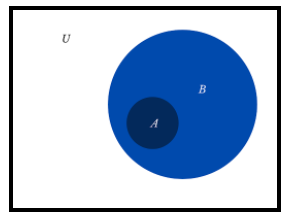
As we know, \[A \subset B\] means all the elements of A are present in B.
\[\therefore \] B consists of all the elements present in set A.
\[ \Rightarrow A - B = \phi \]
Step2 Here, we show condition \[A - B = \phi \] is equivalent to condition \[A \cup B = B\].
\[A - B = \phi \] means B consists of all the elements present in set A.
As, all the elements of A are present in B.
\[ \Rightarrow A \cup B = B\]
Step3: Here, we show condition \[A \cup B = B\] is equivalent to condition \[A \cap B = A\].
\[A \cup B = B\] means all the elements of A are present in B.
So, all the common elements of A and B must be present in A.
\[ \Rightarrow A \cap B = A\]
Thus, \[A \subset B \Leftrightarrow A - B = \phi \Leftrightarrow A \cup B = B \Leftrightarrow A \cap B = A\]
Hence, all the four conditions are equivalent to each other.
Additional Information: It is based on set theory which includes collection of unique sets of numbers. There are different types of set operations that are intersection, union, and difference. Based on these operations we draw Venn diagrams related to the need of the question.
Note: The Venn diagrams makes the question easier to understand as well as it helps us to know the concept in an efficient and practical manner. We can easily verify questions by using Venn diagrams as they can be overlapped to check multiple intersections and unions of sets.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, let us assume : \[ \subset \to shows\,{\rm{ a\, symbol\, of\, subset\,}}\]\[A \subset B \to shows\,{\rm{ all\, the\, elements\, of\, A\, are\, present\, in\, B\,}}\] \[U \to is\,{\rm{ the\, universal\, set\,}}{\rm{.}}\]
Here ,we will do this question in three steps:
step1 Here, we show condition \[A \subset B\] is equivalent to condition \[A - B = \phi \].

As we know, \[A \subset B\] means all the elements of A are present in B.
\[\therefore \] B consists of all the elements present in set A.
\[ \Rightarrow A - B = \phi \]
Step2 Here, we show condition \[A - B = \phi \] is equivalent to condition \[A \cup B = B\].
\[A - B = \phi \] means B consists of all the elements present in set A.
As, all the elements of A are present in B.
\[ \Rightarrow A \cup B = B\]
Step3: Here, we show condition \[A \cup B = B\] is equivalent to condition \[A \cap B = A\].
\[A \cup B = B\] means all the elements of A are present in B.
So, all the common elements of A and B must be present in A.
\[ \Rightarrow A \cap B = A\]
Thus, \[A \subset B \Leftrightarrow A - B = \phi \Leftrightarrow A \cup B = B \Leftrightarrow A \cap B = A\]
Hence, all the four conditions are equivalent to each other.
Additional Information: It is based on set theory which includes collection of unique sets of numbers. There are different types of set operations that are intersection, union, and difference. Based on these operations we draw Venn diagrams related to the need of the question.
Note: The Venn diagrams makes the question easier to understand as well as it helps us to know the concept in an efficient and practical manner. We can easily verify questions by using Venn diagrams as they can be overlapped to check multiple intersections and unions of sets.
Watch videos on
Show that the following four conditions are equivalent:
(i)\[A \subset B\]
(ii)\[A - B = \phi \]
(iii)\[A \cup B = B\]
(iv)\[A \cap B = A\]
(i)\[A \subset B\]
(ii)\[A - B = \phi \]
(iii)\[A \cup B = B\]
(iv)\[A \cap B = A\]

Class 11 MATHS Miscellaneous (Question - 4) | Sets Class 11 Chapter 1| NCERT | Ratan Kalra Sir
Subscribe
 Share
Share likes
34 Views
2 years ago
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE



 Watch Video
Watch Video
