
Show that (-2,3)(8,3)(6,7) are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: In every right triangle Pythagoras theorem is applicable.
Pythagoras theorem, states that the square of the longest side is equal to the square of the other two smaller sides.
If we prove Pythagoras theorem in any triangle, then that triangle is said to be the right triangle.
Also the length of the sides will be calculated from the points which are provided in the question using distance formula, which is given by:
$\sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $ ($x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ are coordinates of the two points between which we need to calculate the distance).
Using the above concepts we will solve the equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let's mark the points given in the question in the right triangle.
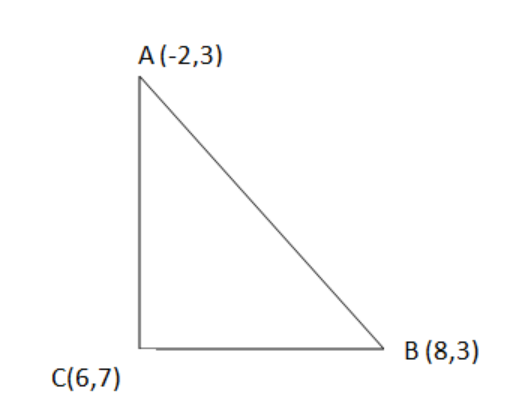
Now, we will calculate the length of each side using distance formula and then we will apply Pythagoras theorem with detailed explanation to show that the triangle is the right triangle.
Using the distance formula:
$\sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $
Side AB is given as:
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(8 - ( - 2))}^2} + {{(3 - 3)}^2}} $ (We have assumed the points given in the side as $x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ respectively)
$\Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(8 + 2)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{10}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow 10$
Side BC is given as:
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(6 - 8)}^2} + {{(7 - 3)}^2}} $(We have assumed the points given in the side as $x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ respectively)
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{( - 2)}^2} + {{(4)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {20} $
Side CA is given as:
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(6 - ( - 2))}^2} + {{(7 - 3)}^2}} $(We have assumed the points given in the side as $x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ respectively)
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{8^2} + {4^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {80} $
We have got the values of all the sides, now we will apply Pythagoras theorem to prove the given triangle as the right triangle.
Pythagoras Theorem states that, in a right triangle the sum of the two sides of the triangle is equal to the square of the longest side.
${\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BC} \right)^2} + {\left( {CA} \right)^2}$ ..............(1)
On substituting the value of each side in equation 1
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {10} \right)^2} = {\left( {\sqrt {20} } \right)^2} + {\left( {\sqrt {80} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 100 = 20 + 80 $
$ \Rightarrow 100 = 100 $
(On removing the square root from the numerical values)
We have seen that the Pythagoras theorem is satisfied and hence the triangle is the Right triangle.
Note: Pythagoras Theorem has many applications in our day to day life as well, with the concept that the two straight lines are joined diagonally with third line, this concept is generally used in woodworking and other physically constructional architectures, Navigation and Surveying.
Pythagoras theorem, states that the square of the longest side is equal to the square of the other two smaller sides.
If we prove Pythagoras theorem in any triangle, then that triangle is said to be the right triangle.
Also the length of the sides will be calculated from the points which are provided in the question using distance formula, which is given by:
$\sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $ ($x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ are coordinates of the two points between which we need to calculate the distance).
Using the above concepts we will solve the equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let's mark the points given in the question in the right triangle.
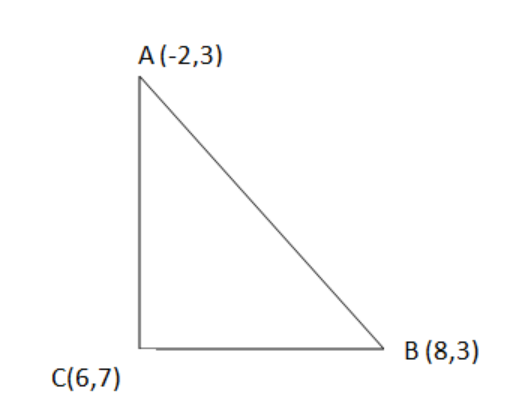
Now, we will calculate the length of each side using distance formula and then we will apply Pythagoras theorem with detailed explanation to show that the triangle is the right triangle.
Using the distance formula:
$\sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $
Side AB is given as:
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(8 - ( - 2))}^2} + {{(3 - 3)}^2}} $ (We have assumed the points given in the side as $x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ respectively)
$\Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(8 + 2)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{10}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow 10$
Side BC is given as:
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(6 - 8)}^2} + {{(7 - 3)}^2}} $(We have assumed the points given in the side as $x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ respectively)
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{( - 2)}^2} + {{(4)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {20} $
Side CA is given as:
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(6 - ( - 2))}^2} + {{(7 - 3)}^2}} $(We have assumed the points given in the side as $x_1$, $x_2$, $y_1$, $y_2$ respectively)
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{8^2} + {4^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {80} $
We have got the values of all the sides, now we will apply Pythagoras theorem to prove the given triangle as the right triangle.
Pythagoras Theorem states that, in a right triangle the sum of the two sides of the triangle is equal to the square of the longest side.
${\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BC} \right)^2} + {\left( {CA} \right)^2}$ ..............(1)
On substituting the value of each side in equation 1
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {10} \right)^2} = {\left( {\sqrt {20} } \right)^2} + {\left( {\sqrt {80} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 100 = 20 + 80 $
$ \Rightarrow 100 = 100 $
(On removing the square root from the numerical values)
We have seen that the Pythagoras theorem is satisfied and hence the triangle is the Right triangle.
Note: Pythagoras Theorem has many applications in our day to day life as well, with the concept that the two straight lines are joined diagonally with third line, this concept is generally used in woodworking and other physically constructional architectures, Navigation and Surveying.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




