
What is the shape of $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion?
A. Trigonal planar
B. Octahedral
C. Trigonal pyramidal
D. Tetrahedral
Answer
534.3k+ views
Hint: Shape of any molecule depends upon the bonded pairs of electrons, as well as the non-bonded, free electrons. Shapes of various molecules are derived through VSEPR theory.
Complete step by step solution:
The shapes of molecules are widely discussed in the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. It consists of the prediction of the shape of covalent molecules. The fact that lone pairs are localized on central atom and occupy more space in comparison with bond pairs, which distorts the shape of the molecule, is one of the main postulates that will help us in identifying the shape of $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion.
$N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion consists of 4 bond pairs with a positive charge. We will take out the hybridization of $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion which will tell us about its shape.
Formula for hybrid state X is, $X={{S}_{A}}+\dfrac{1}{2}(G+V\pm E)$, where ${{S}_{A}}$ is number of surrounding atoms, G is number of electrons in valence shell of central atom, V is valence of surrounding atoms, and E is charge (negative charge is added, while positive subtracted)
So, for $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion, $X=4+\dfrac{1}{2}(5-4-1)$
X = 4 + 0
X = 4, which means $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization state.
Due to $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization state, the shape of this molecule is tetrahedral (according to VSEPR). The shape is,
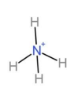
Hence, the shape of $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion is tetrahedral. So, option D is correct.
Note: The hybrid state X corresponds to sp = 2, $s{{p}^{2}}$= 3, $s{{p}^{3}}$= 4 and so on. The hybridization states with some shapes as in VSEPR theory are, linear for sp, bent and trigonal planar for $s{{p}^{2}}$, tetrahedral, pyramidal and bent for $s{{p}^{3}}$. These are for irregular geometry.
Complete step by step solution:
The shapes of molecules are widely discussed in the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. It consists of the prediction of the shape of covalent molecules. The fact that lone pairs are localized on central atom and occupy more space in comparison with bond pairs, which distorts the shape of the molecule, is one of the main postulates that will help us in identifying the shape of $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion.
$N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion consists of 4 bond pairs with a positive charge. We will take out the hybridization of $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion which will tell us about its shape.
Formula for hybrid state X is, $X={{S}_{A}}+\dfrac{1}{2}(G+V\pm E)$, where ${{S}_{A}}$ is number of surrounding atoms, G is number of electrons in valence shell of central atom, V is valence of surrounding atoms, and E is charge (negative charge is added, while positive subtracted)
So, for $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion, $X=4+\dfrac{1}{2}(5-4-1)$
X = 4 + 0
X = 4, which means $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization state.
Due to $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization state, the shape of this molecule is tetrahedral (according to VSEPR). The shape is,

Hence, the shape of $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$ ion is tetrahedral. So, option D is correct.
Note: The hybrid state X corresponds to sp = 2, $s{{p}^{2}}$= 3, $s{{p}^{3}}$= 4 and so on. The hybridization states with some shapes as in VSEPR theory are, linear for sp, bent and trigonal planar for $s{{p}^{2}}$, tetrahedral, pyramidal and bent for $s{{p}^{3}}$. These are for irregular geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




