
Select the correct diagram for bonding molecular orbital which are formed by sideways overlapping.
A.

B.
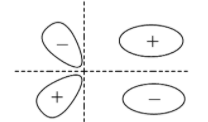
C.

D. None of these
This question has multiple correct options



Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Consider all the orbitals (s and p, since d and f are too complex to draw), and imagine their bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. What does a sideways overlap in these orbitals show?
Complete answer:
We know that $s$ orbitals are spherical in shape. So, no matter how they overlap, it can be considered that they undergo sideways overlapping.
Recall the 2 lobes of the dumbbell shaped $p$- orbitals. In order for both the lobes to overlap, the orbitals have to overlap in a sideways fashion.
When the p orbitals overlap, if the orbitals are in phase then the resultant orbital is the bonding molecular orbital. If the 2 orbitals are out of phase then the orbitals formed will be the anti-bonding molecular orbitals. Let us first look at the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals when 2 $s$ orbitals combine.
- Bonding molecular orbital for $s$
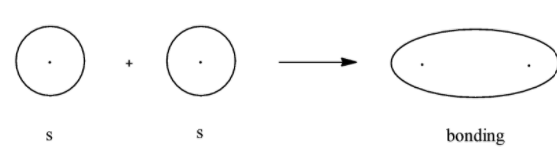
- Anti-bonding molecular orbital for $s$
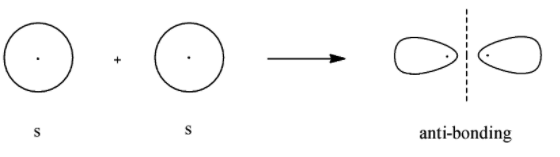
Here, we can see that the bonding molecular orbital mostly lies between the nuclei of the 2 atoms involved and the antibonding molecular orbitals lie in the space that is not between the 2 nuclei. Now we will look at the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals of the $p$- orbital.
- Bonding molecular orbital for $p$

- Anti-bonding molecular orbital for $p$
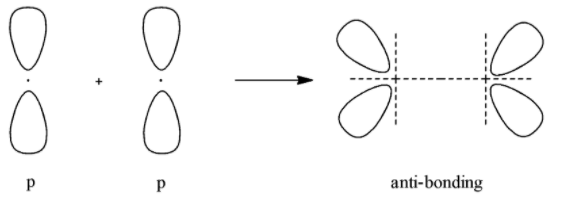
According to all these images, we can conclude that all the options given show the sideways overlap of the bonding orbitals of the $p$- orbital.
Hence the answers to this question are options ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’ .
Note:
Remember that although the options show bonding molecular orbitals, the options ‘B’ and ‘C’ also show anti-bonding molecular orbitals. They are shown partially in option ‘B’ and completely in option ‘C’. So, if the question asks for a diagram that shows only the bonding molecular orbitals then mark only ‘A’ as the correct option.
Complete answer:
We know that $s$ orbitals are spherical in shape. So, no matter how they overlap, it can be considered that they undergo sideways overlapping.
Recall the 2 lobes of the dumbbell shaped $p$- orbitals. In order for both the lobes to overlap, the orbitals have to overlap in a sideways fashion.
When the p orbitals overlap, if the orbitals are in phase then the resultant orbital is the bonding molecular orbital. If the 2 orbitals are out of phase then the orbitals formed will be the anti-bonding molecular orbitals. Let us first look at the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals when 2 $s$ orbitals combine.
- Bonding molecular orbital for $s$

- Anti-bonding molecular orbital for $s$

Here, we can see that the bonding molecular orbital mostly lies between the nuclei of the 2 atoms involved and the antibonding molecular orbitals lie in the space that is not between the 2 nuclei. Now we will look at the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals of the $p$- orbital.
- Bonding molecular orbital for $p$

- Anti-bonding molecular orbital for $p$

According to all these images, we can conclude that all the options given show the sideways overlap of the bonding orbitals of the $p$- orbital.
Hence the answers to this question are options ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’ .
Note:
Remember that although the options show bonding molecular orbitals, the options ‘B’ and ‘C’ also show anti-bonding molecular orbitals. They are shown partially in option ‘B’ and completely in option ‘C’. So, if the question asks for a diagram that shows only the bonding molecular orbitals then mark only ‘A’ as the correct option.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




