
Segregation of Mendelian factors like no linkage or no crossing over occurs during
A. Anaphase I
B. Anaphase II
C. Diplotene
D. Metaphase I
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: The crossing over is a characteristic of meiosis or reductional division. In addition, it happens when the chromatids are moving towards the poles.
Complete answer: Mitosis is the equational division in which the daughter cells get the equal number of chromosomes as the parent cell carries. It is further divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. Meiosis is a reductional division in which the daughter cells carry half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell carries. This type of cell division occurs in a germ cell during gamete formation.
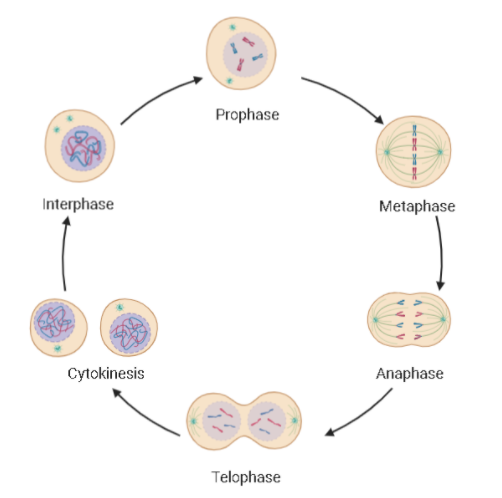
According to the options given:
In option A, Anaphase I is regarding the separation of whole chromosomes instead of the chromatids. In this step, the chromosomes divide half in number.
In option B, Anaphase II is regarded similar to Anaphase of mitosis. Here the chromosomes that are aligned on the metaphase plate are separated equally i.e. only the chromatids separate.
Option C, Diplotene is a subpart of prophase I, and actual crossing over occurs in this stage.
In option D, Metaphase I all the chromosomes arrange on the metaphase plate. In this step there is no chromosome separation occurring, just the chromosomes stay there.
Hence, option B Anaphase II is the correct answer.
Note: Meiosis and mitosis are important cell division cycles important for human survival. Crossing over is important during germ cell formation as it is the main step which leads to variation. Crossing over ensures the blending of characters and ensures a wide range of characters are expressed and checking offspring is not an exact copy of the parents.
Complete answer: Mitosis is the equational division in which the daughter cells get the equal number of chromosomes as the parent cell carries. It is further divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. Meiosis is a reductional division in which the daughter cells carry half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell carries. This type of cell division occurs in a germ cell during gamete formation.

According to the options given:
In option A, Anaphase I is regarding the separation of whole chromosomes instead of the chromatids. In this step, the chromosomes divide half in number.
In option B, Anaphase II is regarded similar to Anaphase of mitosis. Here the chromosomes that are aligned on the metaphase plate are separated equally i.e. only the chromatids separate.
Option C, Diplotene is a subpart of prophase I, and actual crossing over occurs in this stage.
In option D, Metaphase I all the chromosomes arrange on the metaphase plate. In this step there is no chromosome separation occurring, just the chromosomes stay there.
Hence, option B Anaphase II is the correct answer.
Note: Meiosis and mitosis are important cell division cycles important for human survival. Crossing over is important during germ cell formation as it is the main step which leads to variation. Crossing over ensures the blending of characters and ensures a wide range of characters are expressed and checking offspring is not an exact copy of the parents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




