
Seed germination is the sprouting of a seed and growth of the embryo present inside the seed into a seedling or young plant capable of independent existence. Refer to the given figure showing seed germination and mark the incorrect option.
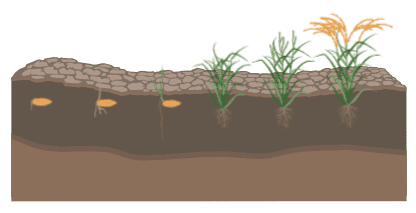
A. Cotyledons are brought out of the soil by the greater growth of hypocotyl.
B. Cotyledons become green and functional as the first leaves of the seedling.
C. The hypocotyl does not elongate much, instead, the epicotyl grows and takes the plumule above the soil.
D. This kind of germination is found in seeds of beans.

Answer
555k+ views
Hint: Germination typically includes the development of the plant within a seedling, which results in the creation of the seedling. Under proper conditions, the seed starts to germinate and the embryo begins to grow into a seedling.
Complete step by step answer:
The area between cotyledon attachment and plumule is epicotyl.
The axis region below cotyledons is the hypocotyl.
Each of them elongates at a time during germination.
The epicotyl elongates and cotyledons stay on the surface or below the layer, for example, gram during a hypogamic form of germination.
The hypocotyl elongates drive the cotyledons above the level, e.g., a bean in the epigeal form of germination.
This figure demonstrates the germination of epigeal seeds in bean seeds. Cotyledons are forced out of the soil with greater hypocotyl growth in this form of seed germination. Hypocotyl deliberately develops and is bent in order to avoid soil frictions from the plumule and cotyledons. The hypocotyl straightens after it falls out of the soil surface. The loosened seed coat falls down and cotyledons turn green to act as the first leaves of the seed.
The right answer is the hypocotyl does not extend much but grows and takes a plumule above the ground.
The answer the hypocotyl does not elongate much, instead, the epicotyl grows and takes the plumule above the soil then is correct.
Note: The bean seed absorbs water from the micropyle and becomes turgid, which allows the test to split. The radical is shaped and the root system develops downwards. The arched hypocotyl develops upwards so that the cotyledons come out of the soil and become an epigeal germ.
Complete step by step answer:
The area between cotyledon attachment and plumule is epicotyl.
The axis region below cotyledons is the hypocotyl.
Each of them elongates at a time during germination.
The epicotyl elongates and cotyledons stay on the surface or below the layer, for example, gram during a hypogamic form of germination.
The hypocotyl elongates drive the cotyledons above the level, e.g., a bean in the epigeal form of germination.
This figure demonstrates the germination of epigeal seeds in bean seeds. Cotyledons are forced out of the soil with greater hypocotyl growth in this form of seed germination. Hypocotyl deliberately develops and is bent in order to avoid soil frictions from the plumule and cotyledons. The hypocotyl straightens after it falls out of the soil surface. The loosened seed coat falls down and cotyledons turn green to act as the first leaves of the seed.
The right answer is the hypocotyl does not extend much but grows and takes a plumule above the ground.
The answer the hypocotyl does not elongate much, instead, the epicotyl grows and takes the plumule above the soil then is correct.
Note: The bean seed absorbs water from the micropyle and becomes turgid, which allows the test to split. The radical is shaped and the root system develops downwards. The arched hypocotyl develops upwards so that the cotyledons come out of the soil and become an epigeal germ.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




