
How many secondary carbon and hydrogen atoms are present in the given molecule below respectively?
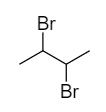
A.\[2,\,3\]
B.\[2,\,2\]
C.\[3,\,3\]
D.\[2,\,0\]

Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: Carbon atom which is attached to two different carbon atoms or bonded with two alkyl groups is known as secondary carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded to the secondary carbon are known as secondary hydrogen atoms.
Complete answer:
Carbon atoms are classified as the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon atom. There are majorly three classifications which are as follows:
Primary carbon: Also known as \[{1^o}\] carbon. It is the carbon atom which is bonded with three hydrogen atoms and one alkyl group. These are very reactive to give bimolecular nucleophilic reactions. Example: \[R - C{H_3}\].
Secondary carbon: Also known as \[{2^o}\] carbon. It is the carbon atom which is bonded with two hydrogen atoms and two alkyl groups. These can undergo both bimolecular as well as unimolecular nucleophilic reactions. Example: \[R - C{H_2} - R\].
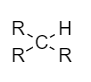
Tertiary carbon: Also known as \[{3^o}\] carbon. It is the carbon atom which is bonded with one hydrogen atom and three alkyl groups. These are very reactive to give unimolecular nucleophilic reactions. Example:
For the given molecule,
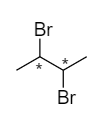
The carbon atoms marked with asterisk are the secondary carbon atoms because each of the marked carbon atoms is connected with two alkyl groups. Therefore, there are two secondary carbon atoms in the given molecule.
Now, as we know that a number of hydrogens attached to secondary carbon are termed as secondary hydrogen atoms. So, according to the given formula of the compound,
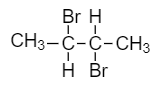
There are two hydrogen atoms attached to the secondary carbon. Therefore, two secondary hydrogen atoms are present in the molecule.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
Ensure that you are not counting the functional group bonded with the carbon atom while finding its degree because the functional group has no role to decide whether the compound is primary, secondary or tertiary. It can only be decided by the number of alkyl groups present.
Complete answer:
Carbon atoms are classified as the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon atom. There are majorly three classifications which are as follows:
Primary carbon: Also known as \[{1^o}\] carbon. It is the carbon atom which is bonded with three hydrogen atoms and one alkyl group. These are very reactive to give bimolecular nucleophilic reactions. Example: \[R - C{H_3}\].
Secondary carbon: Also known as \[{2^o}\] carbon. It is the carbon atom which is bonded with two hydrogen atoms and two alkyl groups. These can undergo both bimolecular as well as unimolecular nucleophilic reactions. Example: \[R - C{H_2} - R\].
Tertiary carbon: Also known as \[{3^o}\] carbon. It is the carbon atom which is bonded with one hydrogen atom and three alkyl groups. These are very reactive to give unimolecular nucleophilic reactions. Example:

For the given molecule,

The carbon atoms marked with asterisk are the secondary carbon atoms because each of the marked carbon atoms is connected with two alkyl groups. Therefore, there are two secondary carbon atoms in the given molecule.
Now, as we know that a number of hydrogens attached to secondary carbon are termed as secondary hydrogen atoms. So, according to the given formula of the compound,
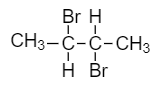
There are two hydrogen atoms attached to the secondary carbon. Therefore, two secondary hydrogen atoms are present in the molecule.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
Ensure that you are not counting the functional group bonded with the carbon atom while finding its degree because the functional group has no role to decide whether the compound is primary, secondary or tertiary. It can only be decided by the number of alkyl groups present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




