
How can you say that glucose is a cyclic compound?
A. Glucose undergoes Tollens reaction
B. Glucose reacts with phenylhydrazine
C. Glucose fails to react with sodium hydrogen sulphite
D. Glucose reacts with nitric acid
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: We know that glucose is one of the six carbon-containing hexopyranose usually represented in the Haworth projection formula. It is also known that there is no free $ - {\rm{CHO}}$ group present in the cyclic structure of glucose.
Complete step by step answer:
The cyclic structure of carbohydrates or more specifically a monosaccharide is represented by using the general way of writing the structural formula that is called a Haworth projection formula. The Haworth projection formula specifies the hydrogen and the hydroxyl group arranged up and down of the carbon atom. The cyclic and straight chain structures of glucose are shown below.
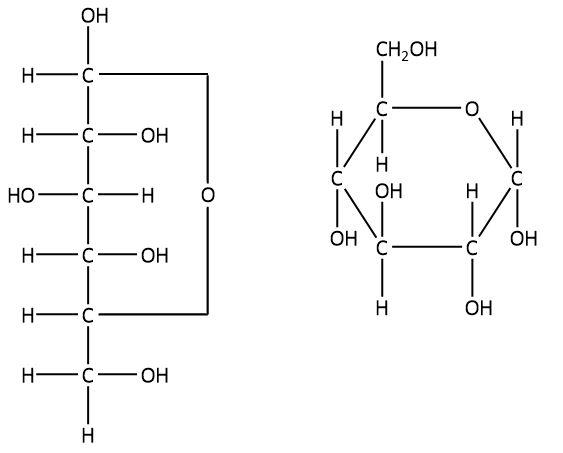
Glucose consists of an aldehyde group. However, it does not undergo reaction with sodium hydrogen sulphite in order to form bisulphite addition products. This is due to the fact that this reaction occurs in the presence of a free aldehyde group, but there is no free $ - {\rm{CHO}}$ group present in the structure of glucose. Therefore, we can say that sodium hydrogen sulphite is not able to cleave the cyclic ring $\left( {\delta {\rm{ - oxide}}\;{\rm{ring}}} \right)$ in glucose.
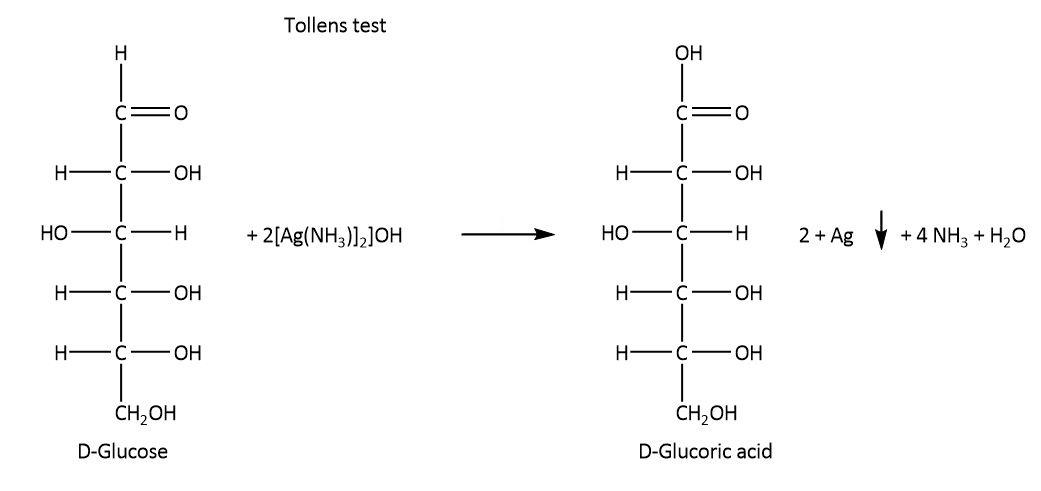
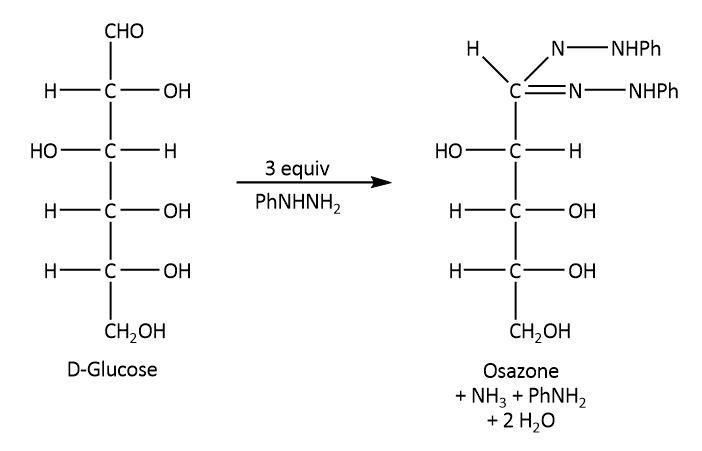
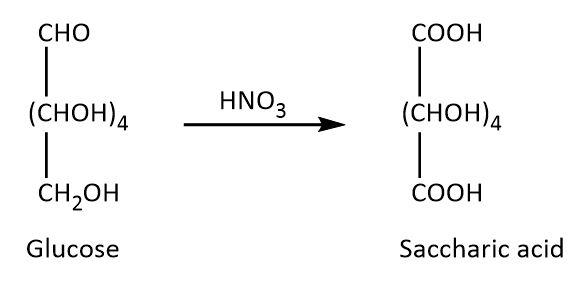
On the other hand, glucose undergoes Tollens reaction, it also reacts with phenyl hydrazine and nitric acid as these reactions require lower concentration of free aldehyde group. The respective reactions are shown below.
Hence, we can say that Glucose fails to react with sodium hydrogen sulphite.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
As we know that, hexopyranose is a six carbon-containing pyranose ring in the Haworth projection formula so it shows us that glucose has a cyclic structure. Also, Glucose X-ray analysis shows the presence of both the ring structure, as well as, the size of the ring.
Complete step by step answer:
The cyclic structure of carbohydrates or more specifically a monosaccharide is represented by using the general way of writing the structural formula that is called a Haworth projection formula. The Haworth projection formula specifies the hydrogen and the hydroxyl group arranged up and down of the carbon atom. The cyclic and straight chain structures of glucose are shown below.

Glucose consists of an aldehyde group. However, it does not undergo reaction with sodium hydrogen sulphite in order to form bisulphite addition products. This is due to the fact that this reaction occurs in the presence of a free aldehyde group, but there is no free $ - {\rm{CHO}}$ group present in the structure of glucose. Therefore, we can say that sodium hydrogen sulphite is not able to cleave the cyclic ring $\left( {\delta {\rm{ - oxide}}\;{\rm{ring}}} \right)$ in glucose.
On the other hand, glucose undergoes Tollens reaction, it also reacts with phenyl hydrazine and nitric acid as these reactions require lower concentration of free aldehyde group. The respective reactions are shown below.



Hence, we can say that Glucose fails to react with sodium hydrogen sulphite.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
As we know that, hexopyranose is a six carbon-containing pyranose ring in the Haworth projection formula so it shows us that glucose has a cyclic structure. Also, Glucose X-ray analysis shows the presence of both the ring structure, as well as, the size of the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




