
Sand is piled up on a horizontal ground in the form of a regular cone of a fixed base radius $R$. The coefficient of static friction between sand layers is $\mu $. The maximum volume of sand that can be pilled up, without the sand slipping on the surface is
A. $\dfrac{{\mu {R^3}}}{{3\pi }}$
B. $\dfrac{{\mu {R^3}}}{3}$
C. $\dfrac{{\pi {R^3}}}{{3\mu }}$
D. $\dfrac{{\mu \pi {R^3}}}{3}$
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: As the sand gets piled up as a circular cone, we will use the free body diagram to find the relation between forces. Using the angle of friction of the sand particles, we will formulate expressions and then compare them to get the result.
Complete step by step answer:
A circular cone of base radius $R$ is given. Let the height of the cone is $h$. Let $\theta $ be the angle between the slant height and radius. The free body diagram shows the force acting on a sand particle, say $P$.
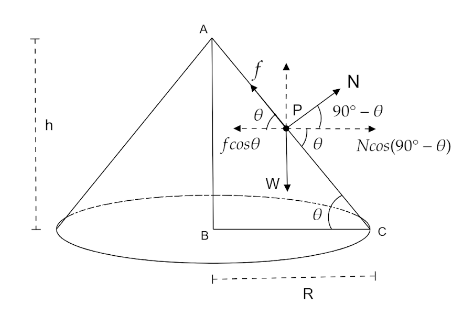
From the horizontal components of force we get,
$f\cos \theta = N\cos ({90^ \circ } - \theta ) = N\sin \theta $
Therefore, dividing both sides by $\cos \theta $ we get,
$f = N\tan \theta $
Now we know that friction is equal to the product of the coefficient of friction and normal.
Substituting $f = \mu N$ in the above equation we get,
$\mu N = N\tan \theta $
Eliminating $N$ from both sides of equation we get,
$\mu = \tan \theta - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
From geometry with the help from $\Delta $ABC we get,
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{h}{R} - - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
Comparing equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$\mu = \dfrac{h}{R}$
$ \Rightarrow h = \mu R - - - - - \left( 3 \right)$
Now the maximum volume of the cone $V = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {R^2}h - - - - \left( 4 \right)$
Substituting $\left( 3 \right)$ in equation $\left( 4 \right)$ we get,
$V = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {R^2} \times \mu R \\
\therefore V= \dfrac{{\mu \pi {R^3}}}{3}$
So, the correct option is D.
Note: It must be noted that when a particle on a horizontal plane is slipping then $\mu < \tan \theta $, but when it just slips then $\mu = \tan \theta $.This is also known as limiting value of coefficient of friction. The friction on the surface is the force which restricts the movement of the particles. We must neglect all the other frictional forces working on the sand like air resistance and others.
Complete step by step answer:
A circular cone of base radius $R$ is given. Let the height of the cone is $h$. Let $\theta $ be the angle between the slant height and radius. The free body diagram shows the force acting on a sand particle, say $P$.

From the horizontal components of force we get,
$f\cos \theta = N\cos ({90^ \circ } - \theta ) = N\sin \theta $
Therefore, dividing both sides by $\cos \theta $ we get,
$f = N\tan \theta $
Now we know that friction is equal to the product of the coefficient of friction and normal.
Substituting $f = \mu N$ in the above equation we get,
$\mu N = N\tan \theta $
Eliminating $N$ from both sides of equation we get,
$\mu = \tan \theta - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
From geometry with the help from $\Delta $ABC we get,
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{h}{R} - - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
Comparing equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$\mu = \dfrac{h}{R}$
$ \Rightarrow h = \mu R - - - - - \left( 3 \right)$
Now the maximum volume of the cone $V = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {R^2}h - - - - \left( 4 \right)$
Substituting $\left( 3 \right)$ in equation $\left( 4 \right)$ we get,
$V = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {R^2} \times \mu R \\
\therefore V= \dfrac{{\mu \pi {R^3}}}{3}$
So, the correct option is D.
Note: It must be noted that when a particle on a horizontal plane is slipping then $\mu < \tan \theta $, but when it just slips then $\mu = \tan \theta $.This is also known as limiting value of coefficient of friction. The friction on the surface is the force which restricts the movement of the particles. We must neglect all the other frictional forces working on the sand like air resistance and others.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




