
Salicylic acid on heating with soda lime forms:
A.Benzene.
B.Phenol.
C.Benzyl Alcohol.
D.Benzoic Acid.
Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: We know that Salicylic Acid is a small aromatic acid whose chemical name is mono hydroxybenzoic acid. It is lipophilic in nature. All carbon atoms present in the benzene ring of Salicylic Acid are sp hybridized. Salicylic Acid forms an intermolecular hydrogen bond. In aqueous solution, Salicylic Acid, being an organic acid, dissociates to lose a proton from the carboxylic acid functional group.
Complete answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts. The preparation of salicylic acid is done via a process known as Kolbe’s Reaction. This reaction involves phenol as the major reactant. The mechanism of this reaction can be discussed as follows: We need to first increase the reactivity of the phenol functional group. For this purpose, we make the phenol molecule react with sodium hydroxide, which is a strong base. This causes the displacement of the hydrogen atom in the hydroxyl group, with the sodium atom. The compound thus formed is known as a phenoxide ion. We now carry out electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide.
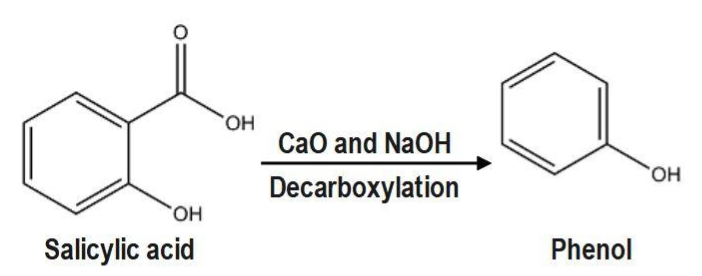
This results in the formation of a salicylate compound. In the end, we react with a strong acid line sulphuric acid to substitute the sodium atoms with hydrogen atoms, which results in the formation of salicylic acid. Salicylic acid will give phenol with \[CaO\] and \[NaOH.\]When carboxylic acids are heated with sodalite, they undergo decarboxylation.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that Salicylic Acid is a small aromatic acid whose chemical name is mono hydroxy benzoic acid. It is lipophilic in nature. It was first derived from the bark of the Willow Tree. It derives its common name from a variety of sources related to it with a similar name.
Complete answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts. The preparation of salicylic acid is done via a process known as Kolbe’s Reaction. This reaction involves phenol as the major reactant. The mechanism of this reaction can be discussed as follows: We need to first increase the reactivity of the phenol functional group. For this purpose, we make the phenol molecule react with sodium hydroxide, which is a strong base. This causes the displacement of the hydrogen atom in the hydroxyl group, with the sodium atom. The compound thus formed is known as a phenoxide ion. We now carry out electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide.

This results in the formation of a salicylate compound. In the end, we react with a strong acid line sulphuric acid to substitute the sodium atoms with hydrogen atoms, which results in the formation of salicylic acid. Salicylic acid will give phenol with \[CaO\] and \[NaOH.\]When carboxylic acids are heated with sodalite, they undergo decarboxylation.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that Salicylic Acid is a small aromatic acid whose chemical name is mono hydroxy benzoic acid. It is lipophilic in nature. It was first derived from the bark of the Willow Tree. It derives its common name from a variety of sources related to it with a similar name.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




