
How many \[S{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}0{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}S\] linkages are there in dithionous acid?
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: In oxyacid of sulfur, sulfur is the central atom exhibiting a tetrahedral structure when coordinated with oxygen. This contains at least one \[S = O\] bond and one \[S - OH\] bond. In addition to these, a chain of \[{( - S - )_n}\] as in \[{H_2}{S_2}{O_6}\] . Such oxyacids with \[S - S\] linkages are called Thioacids.
Complete step by step answer:
The sulfur oxyacids are the acids that contain oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur. These are divided into four groups based on their structural similarities:
1.Sulphurous acid group- these are prepared by dissolving sulphur dioxide in water. Their structure is pyramidal with three oxygen atoms on a triangle i.e. tetrahedral structure is distorted by lone pair. These are strong reducing agents and have bleaching properties.
For example, sulphurous acid \[{H_2}S{O_3}\] .
2.Sulphuric acid group- these are also called oil of vitriol, produced by the lead chamber and contact processes by dissolving \[S{O_3}\] in water. For example, sulphuric acid \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] (oleum) and thiosulphuric acid.
3.Thionic acid group- these are a series of unstable acids with the general formula of \[{H_2}{S_n}{O_6}\] where n = 2 to 6. For example, Dithionic acid \[{H_2}{S_2}{O_6}\] .
4.Peroxo acid group- these are also called Marshall’s acid or Caro’s acid. The central atom sulphur has a +6-oxidation state with a peroxo group in it. These are derived from hydrogen peroxide by replacing hydrogen atoms. For example, peroxydisulfuric acid \[{H_2}{S_2}{O_8}\] .
From all these series, we saw that the \[S - S\] bond is present only one in the thionic acid series. For example, dithionic acid \[{H_2}{S_2}{O_6}\] . The structure is shown below,
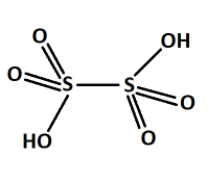
Note: All oxyacids have the acidic hydrogen bonded to an oxygen atom. i.e. \[ - OH\] bond. The electronegativity of the central atom and the number of O atoms are responsible for the oxyacid acidity.
Complete step by step answer:
The sulfur oxyacids are the acids that contain oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur. These are divided into four groups based on their structural similarities:
1.Sulphurous acid group- these are prepared by dissolving sulphur dioxide in water. Their structure is pyramidal with three oxygen atoms on a triangle i.e. tetrahedral structure is distorted by lone pair. These are strong reducing agents and have bleaching properties.
For example, sulphurous acid \[{H_2}S{O_3}\] .
2.Sulphuric acid group- these are also called oil of vitriol, produced by the lead chamber and contact processes by dissolving \[S{O_3}\] in water. For example, sulphuric acid \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] (oleum) and thiosulphuric acid.
3.Thionic acid group- these are a series of unstable acids with the general formula of \[{H_2}{S_n}{O_6}\] where n = 2 to 6. For example, Dithionic acid \[{H_2}{S_2}{O_6}\] .
4.Peroxo acid group- these are also called Marshall’s acid or Caro’s acid. The central atom sulphur has a +6-oxidation state with a peroxo group in it. These are derived from hydrogen peroxide by replacing hydrogen atoms. For example, peroxydisulfuric acid \[{H_2}{S_2}{O_8}\] .
From all these series, we saw that the \[S - S\] bond is present only one in the thionic acid series. For example, dithionic acid \[{H_2}{S_2}{O_6}\] . The structure is shown below,

Note: All oxyacids have the acidic hydrogen bonded to an oxygen atom. i.e. \[ - OH\] bond. The electronegativity of the central atom and the number of O atoms are responsible for the oxyacid acidity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




