
Root hair develop from
A. Zone of cell maturation
B. Zone of cell elongation
C Zone of mature cells
D. Zone of cell maturation
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: A root hair is a tubular extension of a trichoblast, a hair-forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root, the rhizoid of a vascular plant. Because they are single cell lateral extensions and are rarely branched. Their differing lateral elongation increases the exchange area between the root system of the plant and the soil.
Complete answer:
They are not found only in the elongation zone and in the maturation zone, possibly because as the root elongates and moves through the soil, any root hair that occurs is sheared off.
At the top of the root, or nearest to the plant, the maturation region is located. The root cap is known as the end of the root. In the region of cell division, a plant cell will begin and then travel to the area of elongation. A cell will elongate in this zone and then travel to the zone of maturation. The extended version at the tip of the plant's roots is root hair cells.
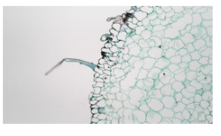
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Under stressful circumstances, the density and/or length of the root hairs (RHS) that are produced is thought to have a significant influence on the production of the plant. Any effort to enhance the root system of a crop would require a thorough understanding of the RH differentiation processes. Recent progress has been documented in the grasses in uncovering the molecular basis of root epidermis specialization. The purpose of this analysis is to present the current view of the differentiation of RH in grass species.
Complete answer:
They are not found only in the elongation zone and in the maturation zone, possibly because as the root elongates and moves through the soil, any root hair that occurs is sheared off.
At the top of the root, or nearest to the plant, the maturation region is located. The root cap is known as the end of the root. In the region of cell division, a plant cell will begin and then travel to the area of elongation. A cell will elongate in this zone and then travel to the zone of maturation. The extended version at the tip of the plant's roots is root hair cells.

Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Under stressful circumstances, the density and/or length of the root hairs (RHS) that are produced is thought to have a significant influence on the production of the plant. Any effort to enhance the root system of a crop would require a thorough understanding of the RH differentiation processes. Recent progress has been documented in the grasses in uncovering the molecular basis of root epidermis specialization. The purpose of this analysis is to present the current view of the differentiation of RH in grass species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




