
Ribosome of bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are
(a)50S type
(b)80S type
(c)70S type
(d)30S type
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: Even though mitochondria and chloroplast are present in eukaryotic cells they show prokaryotic characteristics. Their ribosome is also similar to that of prokaryotic bacteria.
Complete answer:
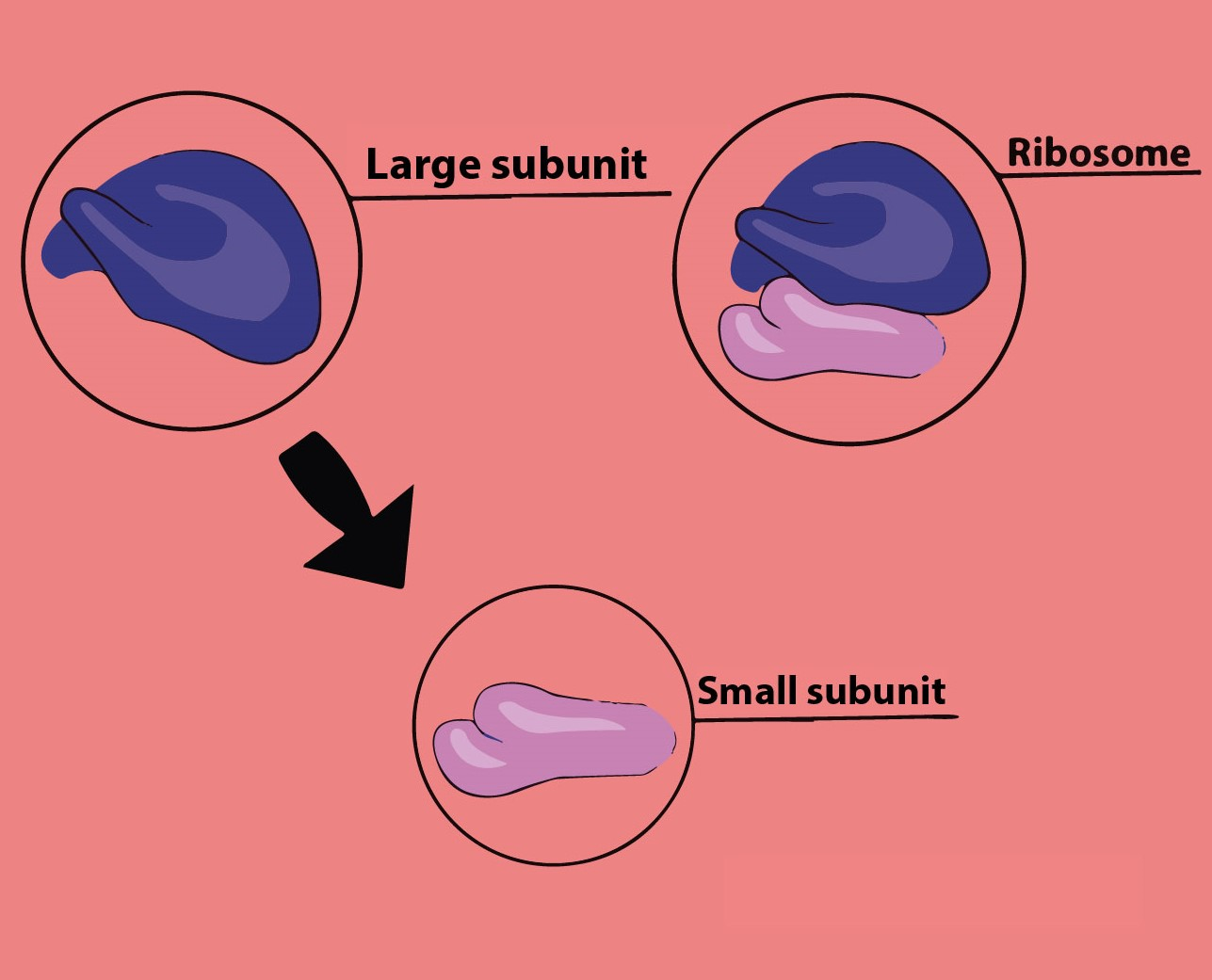
The ribosome of bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have a 70S type of ribosome. They all have their own nucleic acid. The bacterial ribosome is made of two subunits, the 50S, and 30S. Together they form a 70S ribosome. The main function of this is to synthesize proteins by translation of rRNA to form specific proteins required for the functioning of the cell organelles.
Additional Information: Ribosomes are the cell organelles found in living cells that produce protein from amino acids. This process is called protein synthesis or translation. It is found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. However, the eukaryotic cell contains 70S ribosomes and prokaryotic contains 80S.
Here's an explanation of each one of them:
Bacterial ribosome- This is a cytoplasmic nucleoprotein particle that serves the function of protein synthesis and mRNA translation in the bacterial cells. The two subunits are 30S(smaller) and 50S(larger). During protein synthesis, the ribosome moves along an mRNA molecule, reads the codon, and adds amino acid to the growing protein. The mRNA and protein are released at the end when the stop codon is reached and translation ceases.
Mitochondrial and chromosomal ribosome- Even though mitochondria and chromosomes are found in eukaryotic cells and should contain the 80S ribosome, they don’t follow that rule. The ribosomes of each of them contain two subunits of the 30S and 50S and make the 70S ribosome. The reason is believed to be that these organelles are descendants of bacteria itself.
Therefore, bacterial cells, mitochondria, and chloroplast all contain the 70S ribosome.
So, the correct answer is '70 S type'.
Note: 70S ribosomes are present in prokaryotic cells and all eukaryotic cells only contain 80S ribosomes. The only two exceptions are Mitochondrial and chromosomal ribosomes since they evolved from prokaryotic bacteria and developed a symbiotic relationship with the cell.
Complete answer:
The ribosome of bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have a 70S type of ribosome. They all have their own nucleic acid. The bacterial ribosome is made of two subunits, the 50S, and 30S. Together they form a 70S ribosome. The main function of this is to synthesize proteins by translation of rRNA to form specific proteins required for the functioning of the cell organelles.
Additional Information: Ribosomes are the cell organelles found in living cells that produce protein from amino acids. This process is called protein synthesis or translation. It is found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. However, the eukaryotic cell contains 70S ribosomes and prokaryotic contains 80S.
Here's an explanation of each one of them:
Bacterial ribosome- This is a cytoplasmic nucleoprotein particle that serves the function of protein synthesis and mRNA translation in the bacterial cells. The two subunits are 30S(smaller) and 50S(larger). During protein synthesis, the ribosome moves along an mRNA molecule, reads the codon, and adds amino acid to the growing protein. The mRNA and protein are released at the end when the stop codon is reached and translation ceases.
Mitochondrial and chromosomal ribosome- Even though mitochondria and chromosomes are found in eukaryotic cells and should contain the 80S ribosome, they don’t follow that rule. The ribosomes of each of them contain two subunits of the 30S and 50S and make the 70S ribosome. The reason is believed to be that these organelles are descendants of bacteria itself.
Therefore, bacterial cells, mitochondria, and chloroplast all contain the 70S ribosome.
So, the correct answer is '70 S type'.
Note: 70S ribosomes are present in prokaryotic cells and all eukaryotic cells only contain 80S ribosomes. The only two exceptions are Mitochondrial and chromosomal ribosomes since they evolved from prokaryotic bacteria and developed a symbiotic relationship with the cell.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




