
Ribosome is the site of
(a)Lipid synthesis
(b)Storage of food products
(c)Nutrient synthesis
(d)Protein synthesis
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Ribosome synthesizes a biomolecule or macronutrient which is essential for building muscle mass. Two diseases that are related to the deficiency of this substance are kwashiorkor and marasmus, seen in children.
Complete answer:
Ribosomes were first described in 1955 by a Romanian-American cell biologist George E. Palade, who found them associated with the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotic cells. Ribosomes are macromolecular machines found in large numbers in all living cells and serve as the site of protein synthesis. This process of formation of protein from mRNA is called translation.
Ribosomes occur as both freely in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and as particles which are attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells.
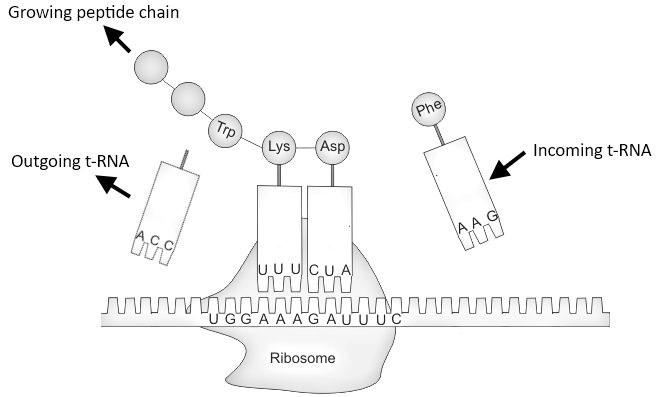
The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of amino acids in a protein, is transcribed into a special type of RNA chain called mRNA or messenger RNA. Ribosomes bind to the mRNA and Use the sequencing of mRNA to determine the correct sequence of amino acids for the generation of new protein.
The transfer of amino acids to the ribosome is facilitated by the tRNA to the transfer RNA molecule. Once the protein is produced it is folded in a functional three-dimensional structure.
So, the correct answer is,’ Protein synthesis.’
Note: Each ribosome is formed from two subunits, a larger one and a smaller one, each of which has a characteristic shape. The subunits are referred to with terms of their respective sedimentation rate, which is measured in Svedberg units (S), in a centrifugal field.
In eukaryotes, the small unit is designated as the 40S while the larger subunit by 60S respectively.
In prokaryotes, the smaller unit is referred with the 30S and the larger with 50S subunit.
Complete answer:
Ribosomes were first described in 1955 by a Romanian-American cell biologist George E. Palade, who found them associated with the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotic cells. Ribosomes are macromolecular machines found in large numbers in all living cells and serve as the site of protein synthesis. This process of formation of protein from mRNA is called translation.
Ribosomes occur as both freely in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and as particles which are attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells.
The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of amino acids in a protein, is transcribed into a special type of RNA chain called mRNA or messenger RNA. Ribosomes bind to the mRNA and Use the sequencing of mRNA to determine the correct sequence of amino acids for the generation of new protein.
The transfer of amino acids to the ribosome is facilitated by the tRNA to the transfer RNA molecule. Once the protein is produced it is folded in a functional three-dimensional structure.
So, the correct answer is,’ Protein synthesis.’
Note: Each ribosome is formed from two subunits, a larger one and a smaller one, each of which has a characteristic shape. The subunits are referred to with terms of their respective sedimentation rate, which is measured in Svedberg units (S), in a centrifugal field.
In eukaryotes, the small unit is designated as the 40S while the larger subunit by 60S respectively.
In prokaryotes, the smaller unit is referred with the 30S and the larger with 50S subunit.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




