
What is the resonance structure for benzyl alcohol ( $ {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}OH $ ) $ ? $
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: First we have to know that resonance structures are sets of Lewis structures that describe the delocalization of electrons in a molecule. Benzyl alcohol is an organic compound and it is a colourless, slightly aromatic liquid at standard conditions.
Complete answer:
In resonance structures, the electrons are able to move to help stabilize the molecule. This movement of the electrons is called delocalization. All resonance structures must follow the rules of writing Lewis-structure. The hybridization of the structure must stay the same. The skeleton of the structure cannot be changed (only the electrons move).
Benzyl alcohol is a compound consisting of a hydroxyl group attached to a methyl group by replacing one of the hydrogens by a hydroxyl group. The resonance structure of a $ {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}OH $ molecule is illustrated below.
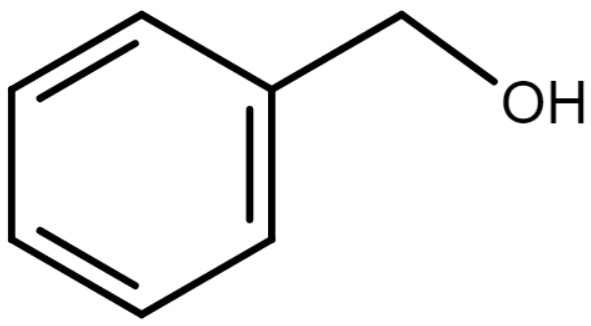
Here, the pi electrons in the benzene ring are delocalized due to resonance.
Additional Information:
Benzyl alcohol is prepared by using sodium hydroxide in the hydrolysis of benzyl chloride which gives benzyl alcohol and sodium chloride as the products. The chemical equation for this reaction written as follows
$ NaOH + {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl \to NaCl + {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}OH $
Note:
In many cases, a single Lewis structure fails to explain the bonding in a molecule due to the presence of partial charges and fractional bonds in it. In such cases, resonance structures are used to describe chemical bonding. Also note that resonance structures should have the same number of electrons, do not add or subtract any electrons.
Complete answer:
In resonance structures, the electrons are able to move to help stabilize the molecule. This movement of the electrons is called delocalization. All resonance structures must follow the rules of writing Lewis-structure. The hybridization of the structure must stay the same. The skeleton of the structure cannot be changed (only the electrons move).
Benzyl alcohol is a compound consisting of a hydroxyl group attached to a methyl group by replacing one of the hydrogens by a hydroxyl group. The resonance structure of a $ {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}OH $ molecule is illustrated below.

Here, the pi electrons in the benzene ring are delocalized due to resonance.
Additional Information:
Benzyl alcohol is prepared by using sodium hydroxide in the hydrolysis of benzyl chloride which gives benzyl alcohol and sodium chloride as the products. The chemical equation for this reaction written as follows
$ NaOH + {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl \to NaCl + {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}OH $
Note:
In many cases, a single Lewis structure fails to explain the bonding in a molecule due to the presence of partial charges and fractional bonds in it. In such cases, resonance structures are used to describe chemical bonding. Also note that resonance structures should have the same number of electrons, do not add or subtract any electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




