
Represents the shaded part of the Venn diagram in terms of union and intersection of sets \[P\] and \[Q\] their complements:
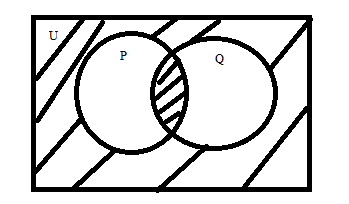

Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Here we will use the property of Venn diagrams where Union symbol (\[ \cup \]) represents the set that contains every element of any two or more sets and Intersection represents (\[ \cap \]) represents the new set that contains every element that is in both of the inputs sets or we can say common in two or more sets.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: From the diagram below, the universal set U is the complete set along with sets \[P\] and \[Q\].
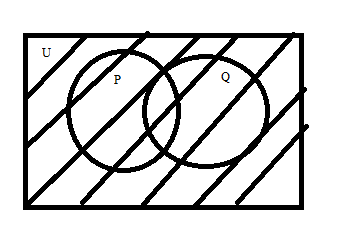
Step 2: From the below diagram \[P \cup Q\] is the set contains all the shaded area of both the sets as shown below:
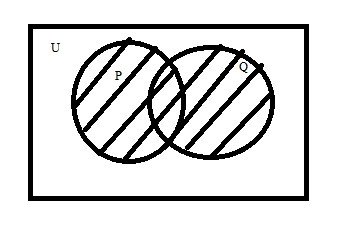
Step 3: Similarly, the intersection is that area which is common in two or more sets. So, \[P \cap Q\] is that shaded area which is common in both sets as shown below:
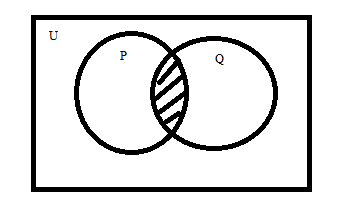
Step 4: Now, for finding the shaded area from the below diagram, we need to subtract \[P \cup Q\] from the universal set and after that, we will add the shaded area which is common in the set \[P\] and \[Q\] as shown below:
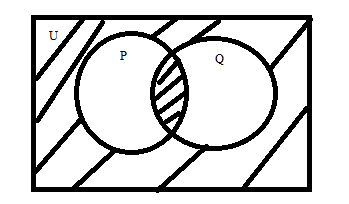
$\therefore $ The Shaded area = \[U - P \cup Q + P \cap Q\].
Note:
Students need to remember the below formulas for these types of questions:
If there are two sets \[A = \left\{ {1,2} \right\}\] and \[B = \left\{ {1,2,3} \right\}\], then:
> \[A \cup B\] consists of all the elements that are in at least one of the sets:
> \[ \Rightarrow A \cup B = \left\{ {1,2,3} \right\}\]
> \[A \cap B\] consists of all the elements that are common in both the sets:
> \[ \Rightarrow A \cup B = \left\{ {1,2} \right\}\]
> The complement of any set is denoted by the symbol bar on top of the set as shown below:
> The complement of a set A will be equal to \[\bar A\] is the set of all elements that are in the universal set but are not in A set.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: From the diagram below, the universal set U is the complete set along with sets \[P\] and \[Q\].

Step 2: From the below diagram \[P \cup Q\] is the set contains all the shaded area of both the sets as shown below:

Step 3: Similarly, the intersection is that area which is common in two or more sets. So, \[P \cap Q\] is that shaded area which is common in both sets as shown below:

Step 4: Now, for finding the shaded area from the below diagram, we need to subtract \[P \cup Q\] from the universal set and after that, we will add the shaded area which is common in the set \[P\] and \[Q\] as shown below:

$\therefore $ The Shaded area = \[U - P \cup Q + P \cap Q\].
Note:
Students need to remember the below formulas for these types of questions:
If there are two sets \[A = \left\{ {1,2} \right\}\] and \[B = \left\{ {1,2,3} \right\}\], then:
> \[A \cup B\] consists of all the elements that are in at least one of the sets:
> \[ \Rightarrow A \cup B = \left\{ {1,2,3} \right\}\]
> \[A \cap B\] consists of all the elements that are common in both the sets:
> \[ \Rightarrow A \cup B = \left\{ {1,2} \right\}\]
> The complement of any set is denoted by the symbol bar on top of the set as shown below:
> The complement of a set A will be equal to \[\bar A\] is the set of all elements that are in the universal set but are not in A set.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




