
Representing $P,V$ and $T$ as pressure, volume and temperature respectively ,which of the following is the correct representation of Boyle’s Law?
A. $V \propto \dfrac{1}{T}$ $ (P$ constant $)$
B. $V \propto \dfrac{1}{P}$ $(T$ constant $)$
C. $PV = RT$
D. $PV = nRT$
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: We have studied that Boyle’s Law is concerning the compression and expansion of a gas at constant temperature. Robert Boyle’s states that the pressure of a quantity of gas varies inversely with its volume at constant temperature.
Complete answer:
This law can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases. It is a law for ideal gases (Ideal gas helps in prediction of real gases). In simple terms we can say that the volume of an ideal gas at constant temperature is inversely proportional to the pressure applied on it. The relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature is expressed as follows,
$ \Rightarrow P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}$, where P is the pressure and V is the volume of the gas. Now to remove the proportionality sign we will convert it into an equation by adding a constant.
$ \Rightarrow P = k \times (\dfrac{1}{V})$
$ \Rightarrow PV = k = $ constant
The above equation can also be shown in graph ,the relation between pressure and volume can be shown in graph,
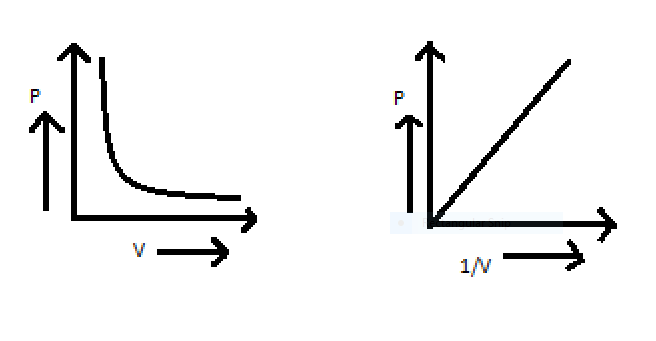 To get the answer of the problem we will take help of ideal gas equation that is $PV = nRT$
To get the answer of the problem we will take help of ideal gas equation that is $PV = nRT$
$ \Rightarrow PV = $ constant =k
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{k}{P}$
$ \Rightarrow V \propto \dfrac{1}{p}$ so option B that is $V \propto \dfrac{1}{P}$ (T constant) is the correct representation of Boyle’s Law.
Note: Now we know that in Boyle’s Law ,’’ Any change in the volume of the gas at constant temperature will result in change in the pressure applied by it”. Mathematically this law is expressed as ${P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$ where ${P_1},{P_2},{V_1},{V_2}$ are respectively initial pressure, final pressure , initial volume, final volume. We should remember that this law holds true only when the number of moles and temperature both are constant.
Complete answer:
This law can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases. It is a law for ideal gases (Ideal gas helps in prediction of real gases). In simple terms we can say that the volume of an ideal gas at constant temperature is inversely proportional to the pressure applied on it. The relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature is expressed as follows,
$ \Rightarrow P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}$, where P is the pressure and V is the volume of the gas. Now to remove the proportionality sign we will convert it into an equation by adding a constant.
$ \Rightarrow P = k \times (\dfrac{1}{V})$
$ \Rightarrow PV = k = $ constant
The above equation can also be shown in graph ,the relation between pressure and volume can be shown in graph,

$ \Rightarrow PV = $ constant =k
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{k}{P}$
$ \Rightarrow V \propto \dfrac{1}{p}$ so option B that is $V \propto \dfrac{1}{P}$ (T constant) is the correct representation of Boyle’s Law.
Note: Now we know that in Boyle’s Law ,’’ Any change in the volume of the gas at constant temperature will result in change in the pressure applied by it”. Mathematically this law is expressed as ${P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$ where ${P_1},{P_2},{V_1},{V_2}$ are respectively initial pressure, final pressure , initial volume, final volume. We should remember that this law holds true only when the number of moles and temperature both are constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




