
Represent the reflex arc with the net flow chart.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Our brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system of our body which is held responsible for the coordination of movements in our body. Our body is always alarmed to the danger and also reacts to it.
Complete answer:
Reflex arc is a cycle or pathway which carries the stimulus from the organs to the central nervous system and from the central nervous system to the organs. Various nerve actions makes the transmission possible. It is a neural pathway that helps in generating a reflex to all the actions by our body.
Stimulus →Sense organ (Receptor) →Sensory neuron→ Spinal Cord (CNS) →Relay neuron → Motor Neuron→Effector→ Response
There are two types of reflexes: Automatic reflex arc and Somatic reflex arc Automatic will involve the spinal cord whereas somatic will include the brain mainly. In this pathway the sensory neurons will carry the information from the organ receptors to the spinal cord or central Nervous system. The response generated is given to the effector neurons which will carry the response to the organs from the spinal cord. This whole transmission forms the reflex arc. The involvement of one sensory and motor neuron makes the monosynaptic pathway. But in the polysynaptic pathway, there are more than one afferent and different signals. Mostly the signals are polysynaptic. Interneuron is the intermediate between sensory and motor neurons. Reflex action is the sudden response to a situation so it is done by reflex arc.
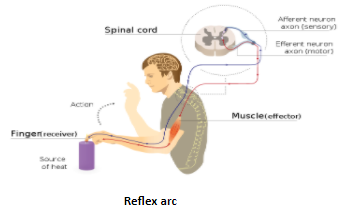
Note: Reflex arc is the involuntary movements of the body. Like when we touch a hot pan, our hands suddenly move off the pan to protect our body from harm. So this reflex generates an impulse which tells our body part in contact with danger to move away. Sensory and motor neurons are electrical impulses.
Complete answer:
Reflex arc is a cycle or pathway which carries the stimulus from the organs to the central nervous system and from the central nervous system to the organs. Various nerve actions makes the transmission possible. It is a neural pathway that helps in generating a reflex to all the actions by our body.
Stimulus →Sense organ (Receptor) →Sensory neuron→ Spinal Cord (CNS) →Relay neuron → Motor Neuron→Effector→ Response
There are two types of reflexes: Automatic reflex arc and Somatic reflex arc Automatic will involve the spinal cord whereas somatic will include the brain mainly. In this pathway the sensory neurons will carry the information from the organ receptors to the spinal cord or central Nervous system. The response generated is given to the effector neurons which will carry the response to the organs from the spinal cord. This whole transmission forms the reflex arc. The involvement of one sensory and motor neuron makes the monosynaptic pathway. But in the polysynaptic pathway, there are more than one afferent and different signals. Mostly the signals are polysynaptic. Interneuron is the intermediate between sensory and motor neurons. Reflex action is the sudden response to a situation so it is done by reflex arc.

Note: Reflex arc is the involuntary movements of the body. Like when we touch a hot pan, our hands suddenly move off the pan to protect our body from harm. So this reflex generates an impulse which tells our body part in contact with danger to move away. Sensory and motor neurons are electrical impulses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




