
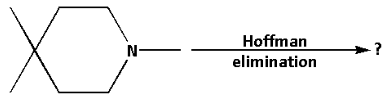
Repeated Hoffman elimination (exhaustive methylation followed by heating with ${\text{AgOH}}$) will often remove a nitrogen atom from an amine molecule.
Which of the following compounds is likely to be a product in this case?

Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: The elimination reactions of quaternary ammonium salts to produce tertiary amines and alkenes is known as Hoffman elimination. Hoffman elimination is also known as Hoffman exhaustive methylation or Hoffman degradation. The quaternary ammonium salt is heated with silver hydroxide to obtain the products.
Complete step-by-step answer:Hoffman elimination involves three steps. In the first step, ammonium iodide salt is formed. The ammonium iodide salt then reacts with silver oxide and gives a precipitate of silver iodide. Silver oxide causes deprotonation of water and produces hydroxide ions. On heating the mixture, elimination reaction occurs and tertiary amine and alkene are produced.
We are given a quaternary ammonium salt which is known as 1,4,4-tetramethylpiperidine. The 1,4,4-trimethyl pyridine reacts with methyl iodide and forms ammonium iodide salt. The iodide anion is then substituted by hydroxide anion which is formed by the deprotonation of water molecules. Then the reaction mixture is heated to start the elimination reaction.
Repeated Hoffman elimination suggests that the Hoffman elimination occurs twice. The reaction is as follows:
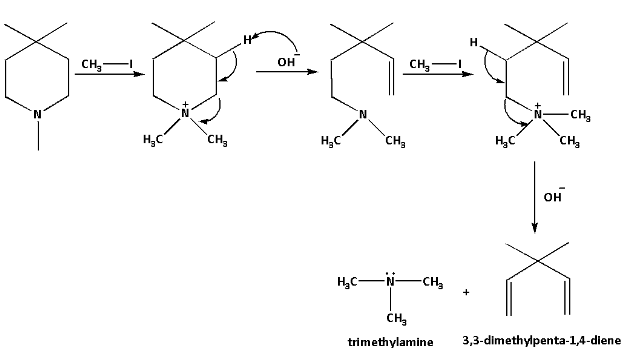
The products of the reaction are 3,3-methylpenta-1,4-diene and trimethylamine.
Trimethylamine is a tertiary amine and 3,3-dimethylpenta-1,4-diene is an alkene.
Thus, the products of repeated Hoffman elimination of 1,4,4-tetramethylpiperidine are 3,3-dimethylpenta-1,4-diene and trimethylamine.
Note:According to the Hoffman rule, the less stable alkene is the main product of the Hoffman elimination reaction. The most important use of Hoffman elimination reaction is to synthesize alkenes. Also, Hoffman elimination reaction is used in the formation of primary reactants that are involved in the production of benzene and its derivatives.
Complete step-by-step answer:Hoffman elimination involves three steps. In the first step, ammonium iodide salt is formed. The ammonium iodide salt then reacts with silver oxide and gives a precipitate of silver iodide. Silver oxide causes deprotonation of water and produces hydroxide ions. On heating the mixture, elimination reaction occurs and tertiary amine and alkene are produced.
We are given a quaternary ammonium salt which is known as 1,4,4-tetramethylpiperidine. The 1,4,4-trimethyl pyridine reacts with methyl iodide and forms ammonium iodide salt. The iodide anion is then substituted by hydroxide anion which is formed by the deprotonation of water molecules. Then the reaction mixture is heated to start the elimination reaction.
Repeated Hoffman elimination suggests that the Hoffman elimination occurs twice. The reaction is as follows:

The products of the reaction are 3,3-methylpenta-1,4-diene and trimethylamine.
Trimethylamine is a tertiary amine and 3,3-dimethylpenta-1,4-diene is an alkene.
Thus, the products of repeated Hoffman elimination of 1,4,4-tetramethylpiperidine are 3,3-dimethylpenta-1,4-diene and trimethylamine.
Note:According to the Hoffman rule, the less stable alkene is the main product of the Hoffman elimination reaction. The most important use of Hoffman elimination reaction is to synthesize alkenes. Also, Hoffman elimination reaction is used in the formation of primary reactants that are involved in the production of benzene and its derivatives.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




