
Relative stability among conjugated dienes(i), alkenes(ii), alkynes(iii) towards electrophilic addition reaction is in the order
A) (i)> (ii)> (iii)
B) (i)>(iii)>(ii)
C) (iii)>(ii)>(i)
D) (ii)>(iii)>(i)
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint:In electrophilic addition reaction electrophile is added across the double or triple bond of the substrate leads to form a new sigma bond between added electrophile and substrate. The order of reactivity of the substrate molecule depends on the stability of the intermediate formed in the reaction. The higher the stability of the intermediate, the higher will be the reactivity of the substrate.
Complete solution:
The general mechanism for the electrophilic addition reaction is as follows:
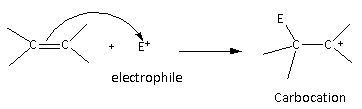
Here, we can see that in the first step of the reaction, carbocation is formed as an intermediate more substituted carbocation is favourable because of the stability.
The second step of the reaction is as follows:
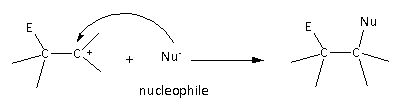
Here, we can see that the nucleophile attacks the carbocation and gives the product molecule.
If the substrate molecule is conjugated diene, then the intermediate formed is allylic carbocation which is resonance stabilized. Therefore, the conjugated dienes are more reactive toward the electrophilic addition reaction than alkene and alkynes.
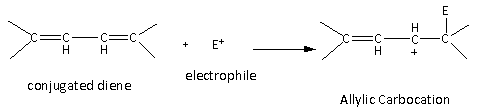
Here, the allylic carbocation formed is resonance stabilized. The resonating structures are as follows:
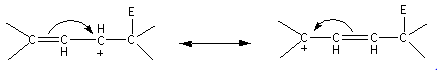
In the case of the alkenes, the carbocation formed are primary, secondary, tertiary carbocation are formed which are less stable than the allylic carbocation. Therefore, the alkenes are less reactive than conjugated dienes.
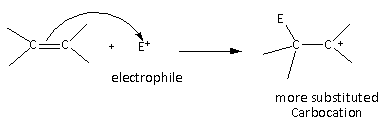
In the case of the alkynes, vinyl carbocation is formed as an intermediate.
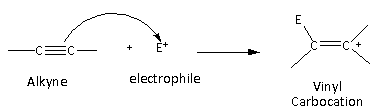
Here, we can see that the vinyl carbocation is formed which is least stable than the primary, secondary, tertiary, and allylic carbocation. Therefore, alkynes are least reactive toward the electrophilic addition reaction.
In option (a) the order given is (i)>(ii)>(iii) indicates dienes are more reactive than alkenes which are more reactive than the alkynes. This is correct as per our result. Hence, option (a)(i)>(ii)>(iii) is the correct answer for the given question.
In option (b) the order given is (i)>(iii)>(ii) indicates dienes are more reactive than alkenes which are more reactive than the alkenes. Hence, option (b) incorrect answer for the given question.
In option (c) the order given is (iii)>(ii)>(i) indicates alkynes are more reactive than alkenes which are more reactive than the dienes. Hence, option (c) incorrect answer for the given question.
In option (d) the order given is (ii)>(iii)>(i) indicates alkenes are more reactive than alkynes which are more reactive than the dienes. Hence, option (d) incorrect answer for the given question.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (A).
Note: Electrophile is a chemical species that is electron deficient therefore in a chemical reaction the electron-rich centre that is nucleophile attacks on the electrophile to satisfy their electron need. In the case of the electrophilic addition reactions, carbocation is formed as intermediate. The stability of the formed carbocation decided the reactivity of the substrate used in the reaction. If any intermediate is resonance stabilized then the respective substrate is more reactive in an electrophilic addition reaction.
Complete solution:
The general mechanism for the electrophilic addition reaction is as follows:

Here, we can see that in the first step of the reaction, carbocation is formed as an intermediate more substituted carbocation is favourable because of the stability.
The second step of the reaction is as follows:

Here, we can see that the nucleophile attacks the carbocation and gives the product molecule.
If the substrate molecule is conjugated diene, then the intermediate formed is allylic carbocation which is resonance stabilized. Therefore, the conjugated dienes are more reactive toward the electrophilic addition reaction than alkene and alkynes.

Here, the allylic carbocation formed is resonance stabilized. The resonating structures are as follows:

In the case of the alkenes, the carbocation formed are primary, secondary, tertiary carbocation are formed which are less stable than the allylic carbocation. Therefore, the alkenes are less reactive than conjugated dienes.

In the case of the alkynes, vinyl carbocation is formed as an intermediate.

Here, we can see that the vinyl carbocation is formed which is least stable than the primary, secondary, tertiary, and allylic carbocation. Therefore, alkynes are least reactive toward the electrophilic addition reaction.
In option (a) the order given is (i)>(ii)>(iii) indicates dienes are more reactive than alkenes which are more reactive than the alkynes. This is correct as per our result. Hence, option (a)(i)>(ii)>(iii) is the correct answer for the given question.
In option (b) the order given is (i)>(iii)>(ii) indicates dienes are more reactive than alkenes which are more reactive than the alkenes. Hence, option (b) incorrect answer for the given question.
In option (c) the order given is (iii)>(ii)>(i) indicates alkynes are more reactive than alkenes which are more reactive than the dienes. Hence, option (c) incorrect answer for the given question.
In option (d) the order given is (ii)>(iii)>(i) indicates alkenes are more reactive than alkynes which are more reactive than the dienes. Hence, option (d) incorrect answer for the given question.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (A).
Note: Electrophile is a chemical species that is electron deficient therefore in a chemical reaction the electron-rich centre that is nucleophile attacks on the electrophile to satisfy their electron need. In the case of the electrophilic addition reactions, carbocation is formed as intermediate. The stability of the formed carbocation decided the reactivity of the substrate used in the reaction. If any intermediate is resonance stabilized then the respective substrate is more reactive in an electrophilic addition reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




