
What is the relationship between the rectangle form of complex numbers and their corresponding polar form?
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this kind of problem we need to know the concept of rectangular form and polar form of coordinates. The polar form is where a complex number is denoted by the length and the angle of its vector. In the case of Rectangular form a complex number is denoted by its respective horizontal and vertical components.
Complete step by step solution:
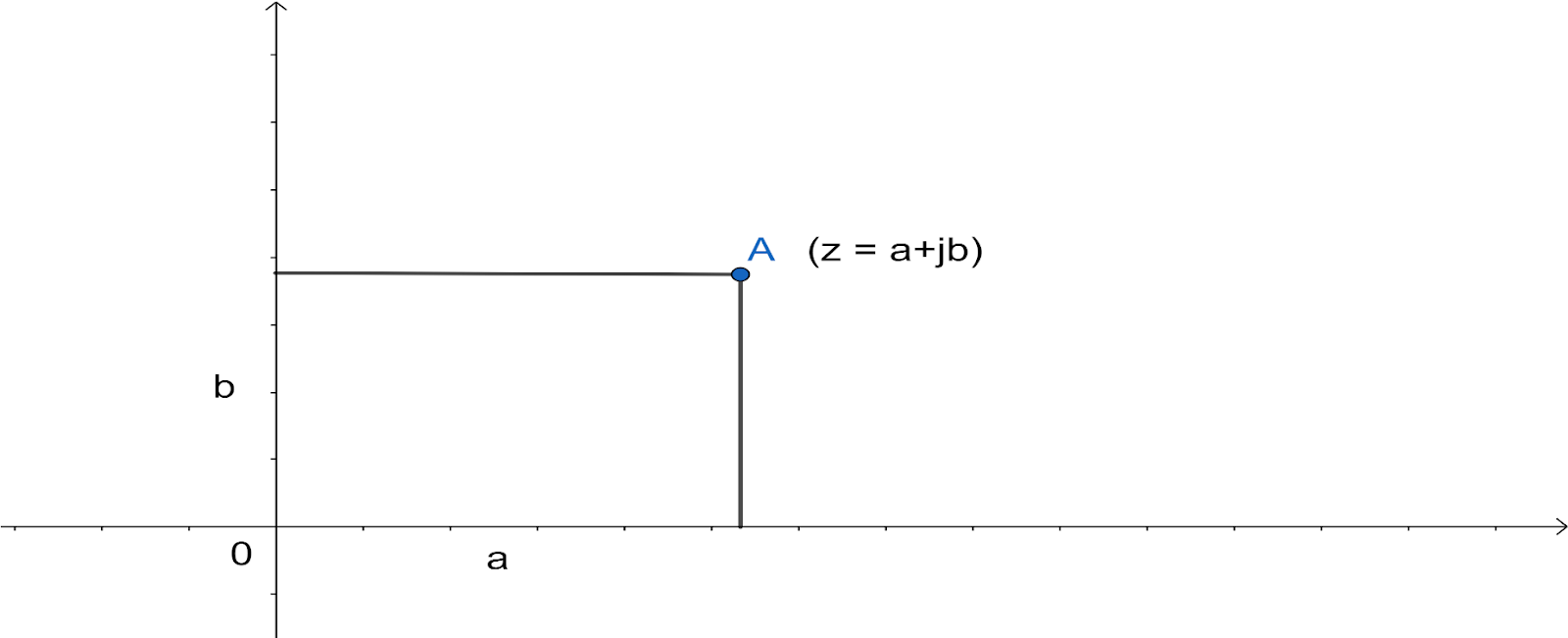
The question asks us to find the relation between the rectangular form of complex number and the polar form of complex number. To start with the definition of the rectangular form of complex number form of complex number which is written in the form of $z=a+jb$ where a and b are the real numbers.
“a” and “b” are the coordinates of a point representing the complex number on a special plane called (Argand-Gauss) where on the x axis we have the real part (the number a) and on the y axis the imaginary (the b number, associated with j). The above explanation could be much understandable with the graph shown below:
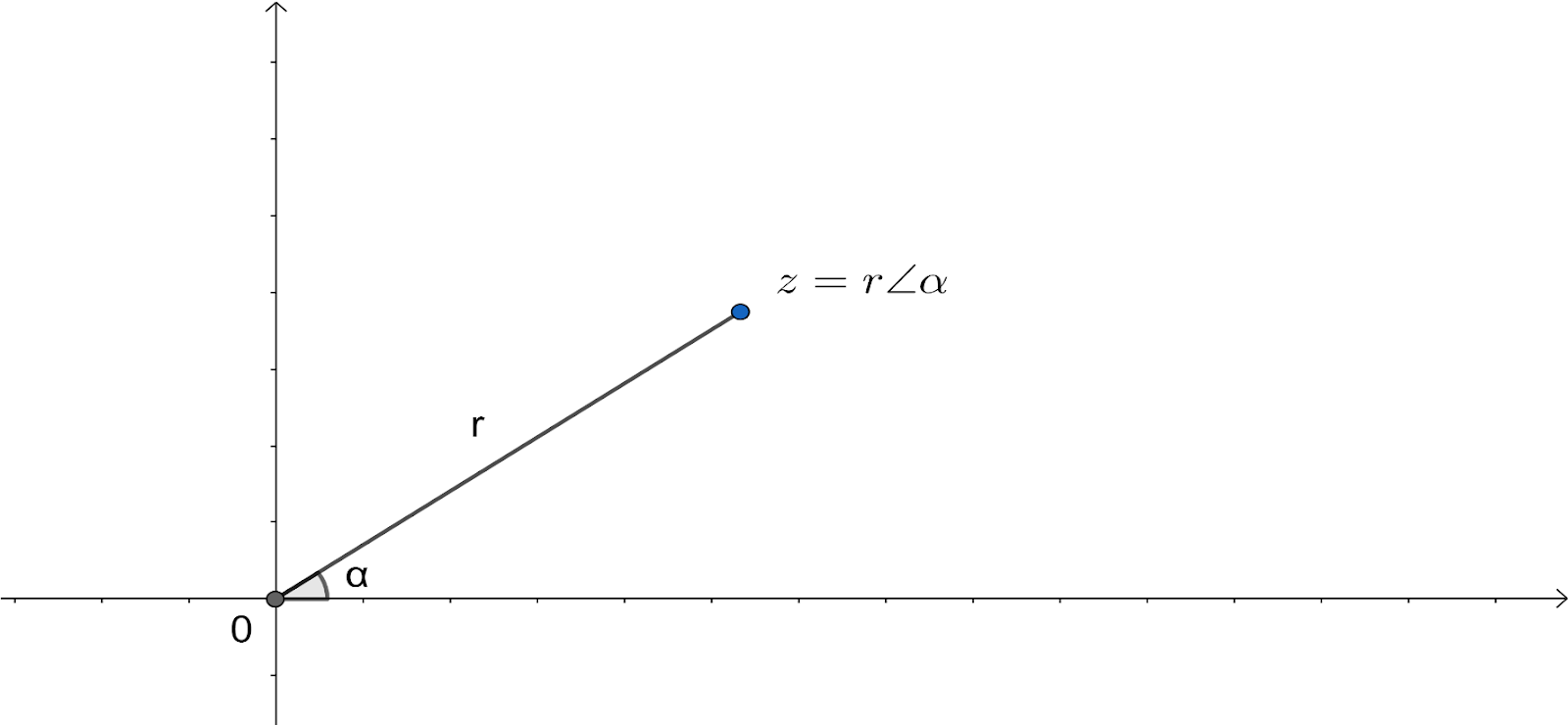
Taking the discussion towards the polar form of the coordinate for the given complex number. In the polar form for the representation of complex numbers the two independent variables are the magnitude $r$ and the argument $\alpha $. Now here the argument $\alpha $ is basically the angle between the magnitude and x-axis while $r$ is the magnitude of the complex number. The above statement will be much clear with the below diagram:
On combining the two coordinate system of the complex number, we get the following diagram of the representation of the complex number:
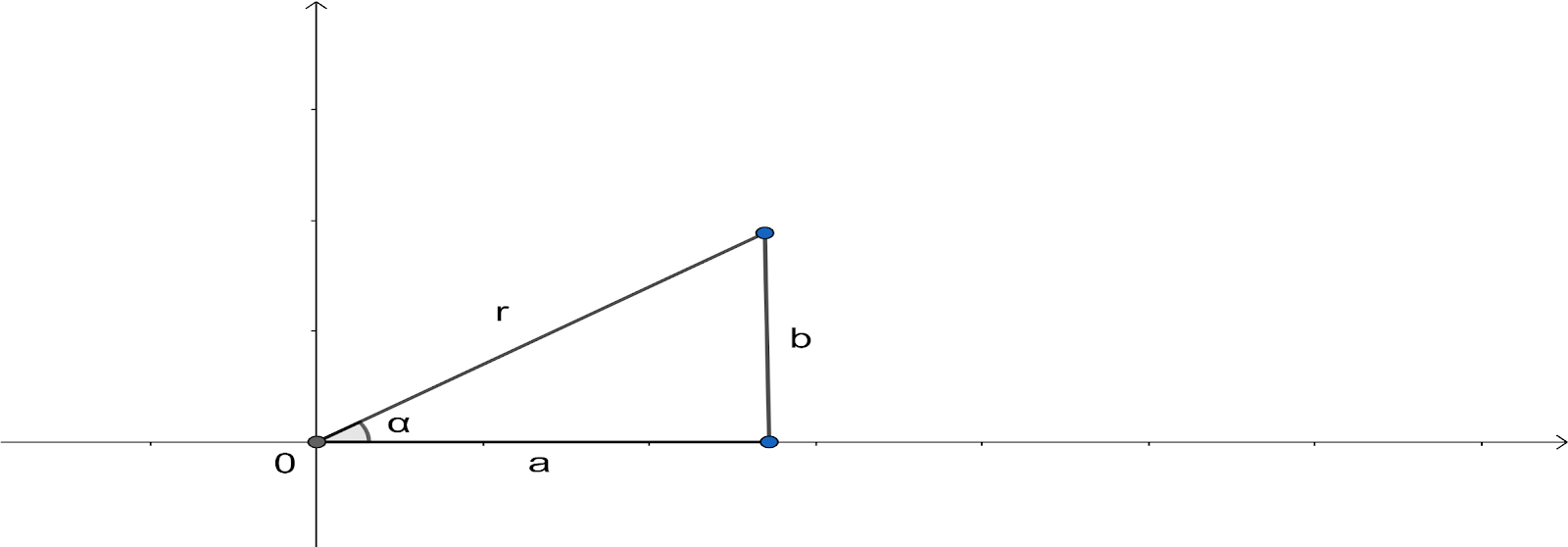
Some of the relationships between the two forms are:
1) Pythagoras Theorem: which is used to link the length r with a and b $r=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$ 2) Inverse trigonometric functions used to link the angle q with a and b $q=\arctan \left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
Note: The arctangent of x is defined as the inverse tangent function of x when x is real. When the tangent of y is equal to x: tan y = x. Then the arctangent of x is equal to the inverse tangent function of x, which is equal to y: \[\text{arctan }\!\!~\!\!\text{ x = ta}{{\text{n}}^{-1}}\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ x = y}\]
Complete step by step solution:
The question asks us to find the relation between the rectangular form of complex number and the polar form of complex number. To start with the definition of the rectangular form of complex number form of complex number which is written in the form of $z=a+jb$ where a and b are the real numbers.
“a” and “b” are the coordinates of a point representing the complex number on a special plane called (Argand-Gauss) where on the x axis we have the real part (the number a) and on the y axis the imaginary (the b number, associated with j). The above explanation could be much understandable with the graph shown below:

Taking the discussion towards the polar form of the coordinate for the given complex number. In the polar form for the representation of complex numbers the two independent variables are the magnitude $r$ and the argument $\alpha $. Now here the argument $\alpha $ is basically the angle between the magnitude and x-axis while $r$ is the magnitude of the complex number. The above statement will be much clear with the below diagram:

On combining the two coordinate system of the complex number, we get the following diagram of the representation of the complex number:

Some of the relationships between the two forms are:
1) Pythagoras Theorem: which is used to link the length r with a and b $r=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$ 2) Inverse trigonometric functions used to link the angle q with a and b $q=\arctan \left( \dfrac{b}{a} \right)$
Note: The arctangent of x is defined as the inverse tangent function of x when x is real. When the tangent of y is equal to x: tan y = x. Then the arctangent of x is equal to the inverse tangent function of x, which is equal to y: \[\text{arctan }\!\!~\!\!\text{ x = ta}{{\text{n}}^{-1}}\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ x = y}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




