
What is refraction? Give two examples.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: To understand what is refraction we need to know where refraction occurs, and in which conditions, what are its limitations. Then we have to draw two figures to understand what are the examples for refraction.
Complete answer:
To understand the phenomenon of refraction we at first need to know about the definition of refraction.
So, the definition of refraction states that the bending of a light wave when it is moving from one medium to another the light wave tends to go towards the normal or away from the normal, this phenomenon is known as refraction.
This bending of light is due to the density of the medium.
Because of the change in density of the medium, the speed of light in those medium changes and hence the light ray bends.
So, now let’s see some examples of this phenomenon.
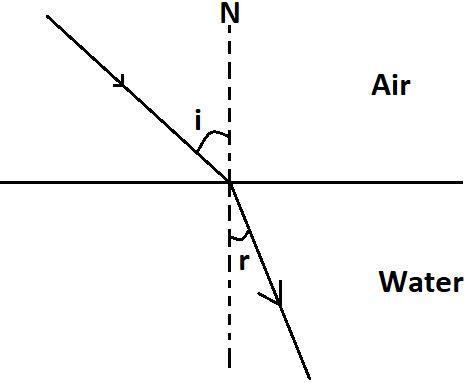
In the above diagram we see a ray of light is moving from one medium that is air to another medium that is water, ‘i’ is the angle of incidence and ‘r’ is the angle of refraction, and ‘N’ is normal, we see that when the light is passing from the air which is a less dense medium compared to water, the light ray bends towards the normal.
Now, let us see another example,
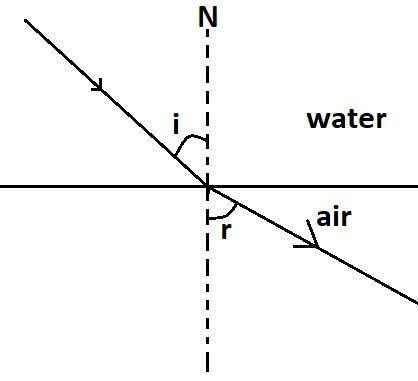
In the above diagram we see a ray of light is moving from one medium that is water to another medium that is air, ‘i’ is the angle of incidence and ‘r’ is the angle of refraction, and ‘N’ is normal, we see that when the light is passing from water which is a denser medium as compared to air, the light ray bends away from the normal.
Other examples in real life are,
- The twinkling of the stars is actually due to the refraction of light.
- A swimming pool always looks shorter in-depth than it actually is, it is due to the light rays coming down from the pool bends at the surface when the medium changes.
- The formation of the rainbow is also an example of refraction.
Note:
There are some laws that the phenomenon of refraction follows those are,
- The incident ray, normal, and the refracted ray all lie on the same plane.
- According to Snell’s laws of refraction, the ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to the ratio of the angle of refraction is a constant value which is fixed for any two given mediums.
$\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\text{constant}$.
Complete answer:
To understand the phenomenon of refraction we at first need to know about the definition of refraction.
So, the definition of refraction states that the bending of a light wave when it is moving from one medium to another the light wave tends to go towards the normal or away from the normal, this phenomenon is known as refraction.
This bending of light is due to the density of the medium.
Because of the change in density of the medium, the speed of light in those medium changes and hence the light ray bends.
So, now let’s see some examples of this phenomenon.

In the above diagram we see a ray of light is moving from one medium that is air to another medium that is water, ‘i’ is the angle of incidence and ‘r’ is the angle of refraction, and ‘N’ is normal, we see that when the light is passing from the air which is a less dense medium compared to water, the light ray bends towards the normal.
Now, let us see another example,

In the above diagram we see a ray of light is moving from one medium that is water to another medium that is air, ‘i’ is the angle of incidence and ‘r’ is the angle of refraction, and ‘N’ is normal, we see that when the light is passing from water which is a denser medium as compared to air, the light ray bends away from the normal.
Other examples in real life are,
- The twinkling of the stars is actually due to the refraction of light.
- A swimming pool always looks shorter in-depth than it actually is, it is due to the light rays coming down from the pool bends at the surface when the medium changes.
- The formation of the rainbow is also an example of refraction.
Note:
There are some laws that the phenomenon of refraction follows those are,
- The incident ray, normal, and the refracted ray all lie on the same plane.
- According to Snell’s laws of refraction, the ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to the ratio of the angle of refraction is a constant value which is fixed for any two given mediums.
$\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\text{constant}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




