
Reduction of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NC}}$ with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as catalyst gives:
A.${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
B.${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NHC}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
C.${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
D. ${\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_3}{\text{N}}$
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint:We should know the structure of the isonitrile group and the reduction mechanism of isonitrile to answer this question. In isonitrile, nitrogen forms four bonds, so it has a positive charge and carbon has a negative change. It gets protonated. The${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NC}}$ itself indicates the type of amine formed.
Complete step-by-step answer:The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt is known as catalytic hydrogenation. The $ - {\text{NC}}$ is known as isonitrile. The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as a catalyst is shown as follows:
In isonitrile, the negative changed carbon work as a nucleophile. It attacks hydrogen and gets protonated. The triple bond shifts to the nitrogen and the lone pair of the nitrogen attacks on another hydrogen. Again the breaking of the N=C bond results in the secondary amine.
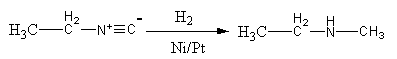
The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt gives secondary amine.
So, the reduction of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NC}}$ with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as catalyst gives ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NHC}}{{\text{H}}_3}$.
Therefore, option (B) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NHC}}{{\text{H}}_3}$, is correct.
Note: The $ - {\text{NC}}$ is isonitrile. It is also known as isocyanide and $ - {\text{CN}}$ is known as nitrile. The reduction of isonitrile gives secondary amine. The reduction of nitrile gives the primary amine. The isonitrile can also be reduced by using strong reducing agents like lithium aluminium hydride ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ . The amine produced by the reduction has one carbon more than the reactant. The isonitrile test is used for the detection of primary amine. In this test, primary amine is treated with potassium hydroxide and trichloromethane. The isocyanide or isonitrile is formed as a product which has an unpleasant odour.
Complete step-by-step answer:The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt is known as catalytic hydrogenation. The $ - {\text{NC}}$ is known as isonitrile. The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as a catalyst is shown as follows:
In isonitrile, the negative changed carbon work as a nucleophile. It attacks hydrogen and gets protonated. The triple bond shifts to the nitrogen and the lone pair of the nitrogen attacks on another hydrogen. Again the breaking of the N=C bond results in the secondary amine.
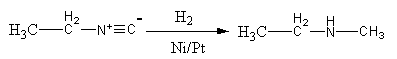
The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt gives secondary amine.
So, the reduction of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NC}}$ with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as catalyst gives ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NHC}}{{\text{H}}_3}$.
Therefore, option (B) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NHC}}{{\text{H}}_3}$, is correct.
Note: The $ - {\text{NC}}$ is isonitrile. It is also known as isocyanide and $ - {\text{CN}}$ is known as nitrile. The reduction of isonitrile gives secondary amine. The reduction of nitrile gives the primary amine. The isonitrile can also be reduced by using strong reducing agents like lithium aluminium hydride ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ . The amine produced by the reduction has one carbon more than the reactant. The isonitrile test is used for the detection of primary amine. In this test, primary amine is treated with potassium hydroxide and trichloromethane. The isocyanide or isonitrile is formed as a product which has an unpleasant odour.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




