
How do you read the phase diagram of water?
Answer
549.9k+ views
Hint The answer is based on the concept of the physical chemistry where the phase diagram is the one in which the pressure is plotted against temperature and phase of water under different conditions of temperature and pressure is examined.
Complete step by step answer:
In the lower classes of chemistry, we have dealt with the concept of phase diagrams for different compounds where the phase of that substance can be determined under different pressure and temperature.
- Firstly let us see the phase diagram of water and then decide the conditions of temperature and pressure.
- The phase diagram of water is shown below,
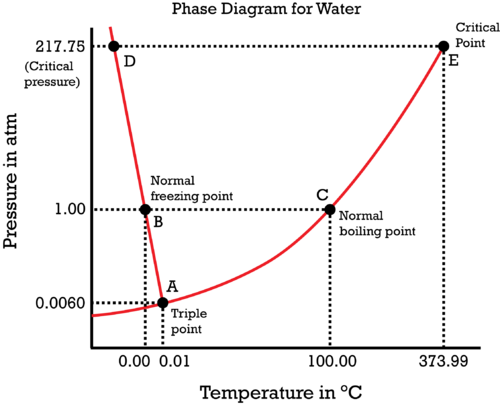
Now, here we can draw the coordinate at P = 1atm and also we can see that phase transitions of water at 1 atm that is at ${{0}^{0}}C$ and ${{100}^{0}}C$.
- In this diagram, we can see that at ${{0}^{0}}C$, the point will be the freezing point of water and it becomes solid.
- At ${{100}^{0}}C$, the point is called the boiling point of water where the liquid form of water changes to vapour form.
- In between these there is a liquid form at room temperature and at one phase there exists a point called triple point where all the three states of water are in equilibrium.
- The critical point is where it occurs at non-standard conditions of temperature and pressure and here the densities of the liquid and gaseous phase become equal and no longer can we distinguish between these phases.
Thus, the phase diagram gives information on the different states of matter at which the compound exists.
Note: Note that phase diagrams can be used to predict the phase changes that have occurred in an alloy which has been exposed to particular heat treatment and this is important because the properties of metal components depend upon the phases present in the metal.
Complete step by step answer:
In the lower classes of chemistry, we have dealt with the concept of phase diagrams for different compounds where the phase of that substance can be determined under different pressure and temperature.
- Firstly let us see the phase diagram of water and then decide the conditions of temperature and pressure.
- The phase diagram of water is shown below,

Now, here we can draw the coordinate at P = 1atm and also we can see that phase transitions of water at 1 atm that is at ${{0}^{0}}C$ and ${{100}^{0}}C$.
- In this diagram, we can see that at ${{0}^{0}}C$, the point will be the freezing point of water and it becomes solid.
- At ${{100}^{0}}C$, the point is called the boiling point of water where the liquid form of water changes to vapour form.
- In between these there is a liquid form at room temperature and at one phase there exists a point called triple point where all the three states of water are in equilibrium.
- The critical point is where it occurs at non-standard conditions of temperature and pressure and here the densities of the liquid and gaseous phase become equal and no longer can we distinguish between these phases.
Thus, the phase diagram gives information on the different states of matter at which the compound exists.
Note: Note that phase diagrams can be used to predict the phase changes that have occurred in an alloy which has been exposed to particular heat treatment and this is important because the properties of metal components depend upon the phases present in the metal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




