
Read the following statements regarding ecological pyramids and choose the correct answer.
(a) Relationship between organisms at the different trophic levels is expressed in terms of number, biomass, and energy.
(b) Any calculations of energy content, biomass or number has to include one group of organisms at that trophic level.
(c) All the pyramids of number, biomass, and energy are upright in most ecosystems.
(d) The pyramid of biomass in the sea is generally inverted.
(e) The pyramid of energy is always inverted and can never be upright.
(i) a, c and d are wrong
(ii) a is wrong
(iii) b and e are wrong
(iv) a and e are wrong
(v) d and e are wrong
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Ecological pyramid is a graphical representation indicating the relationship between organisms at different trophic levels. Based on expression in terms of number, biomass, and energy. This is of 3 types, pyramid of the number, pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy which include all groups of organisms at that trophic level.
Complete answer:
Ecological pyramids provide an intuitive, visual picture of how the trophic levels in an ecosystem compare for a feature of interest, such as energy flow, biomass, or several organisms.
Energy pyramid: it represents energy flow through trophic levels. This usually shows rates of energy flow through trophic levels, not absolute amounts of energy stored. Energy pyramids are always upright, that is, narrower at each successive level—unless organisms enter the ecosystem from elsewhere.
Biomass pyramids: Another way to visualize ecosystem structure is with biomass pyramids. The amount of energy that's stored in living tissue is represented by these pyramids at the different trophic levels. Unlike energy pyramids, biomass pyramids show how much biomass is present at a level, not the rate at which it's added. This pyramid, like many biomass pyramids, is upright.
Numbers pyramids: Numbers pyramids show how many individual organisms there are in each trophic level. Depending on the ecosystem, they can be upright, inverted, or kind of lumpy.
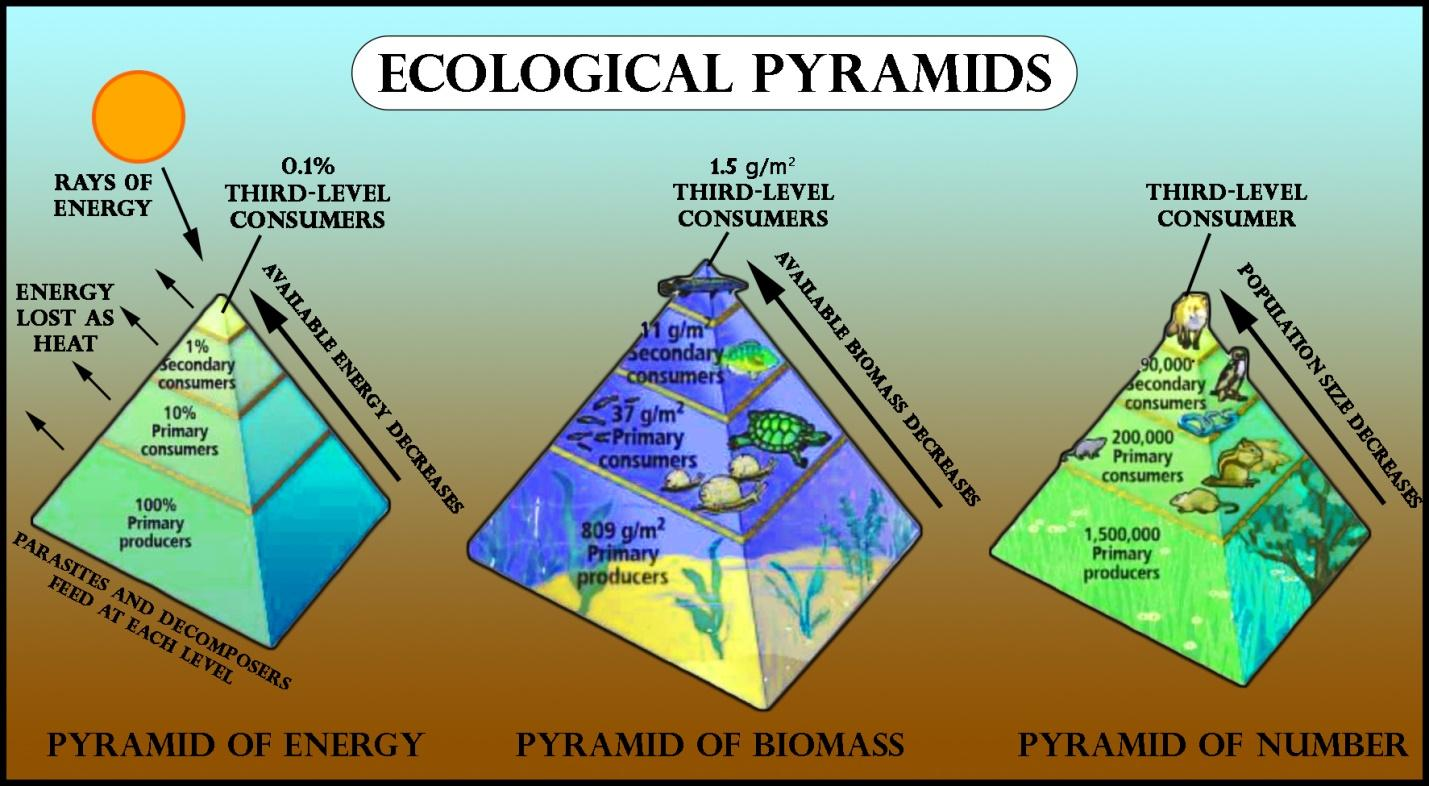
Additional Information:
1) The overall rate of energy capture is called gross productivity. Net productivity is lower, adjusted for energy used by organisms in respiration/metabolism.
2) Energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient. Only about 10% of the net productivity of one level ends up as net productivity at the next level.
3) The pattern of the energy pyramid reflects the laws of thermodynamics, which tell us that new energy can't be created and that some energy must be converted to a not-useful form—heat—in each transfer.
4) the biomass pyramid is shown on the right—from a marine ecosystem in the English Channel—is upside-down, or inverted.
So, the correct answer is,’b and e are wrong.’
Note: The feeding patterns of organisms in different ecosystems can be seen with help of an ecological pyramid. It can also give us an insight into how inefficient energy transfer is, also the influence that a change in numbers at one trophic level can have on the trophic levels above and below it. Also, the effects of the changes that take place in the environment on the organisms can be studied after collecting and comparing the data over the years. Because of pollution or overhunting by humans, If an ecosystem’s conditions are found to be worsening over the years, action can be taken to prevent further damage and possibly reverse some of the present damage.
Complete answer:
Ecological pyramids provide an intuitive, visual picture of how the trophic levels in an ecosystem compare for a feature of interest, such as energy flow, biomass, or several organisms.
Energy pyramid: it represents energy flow through trophic levels. This usually shows rates of energy flow through trophic levels, not absolute amounts of energy stored. Energy pyramids are always upright, that is, narrower at each successive level—unless organisms enter the ecosystem from elsewhere.
Biomass pyramids: Another way to visualize ecosystem structure is with biomass pyramids. The amount of energy that's stored in living tissue is represented by these pyramids at the different trophic levels. Unlike energy pyramids, biomass pyramids show how much biomass is present at a level, not the rate at which it's added. This pyramid, like many biomass pyramids, is upright.
Numbers pyramids: Numbers pyramids show how many individual organisms there are in each trophic level. Depending on the ecosystem, they can be upright, inverted, or kind of lumpy.

Additional Information:
1) The overall rate of energy capture is called gross productivity. Net productivity is lower, adjusted for energy used by organisms in respiration/metabolism.
2) Energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient. Only about 10% of the net productivity of one level ends up as net productivity at the next level.
3) The pattern of the energy pyramid reflects the laws of thermodynamics, which tell us that new energy can't be created and that some energy must be converted to a not-useful form—heat—in each transfer.
4) the biomass pyramid is shown on the right—from a marine ecosystem in the English Channel—is upside-down, or inverted.
So, the correct answer is,’b and e are wrong.’
Note: The feeding patterns of organisms in different ecosystems can be seen with help of an ecological pyramid. It can also give us an insight into how inefficient energy transfer is, also the influence that a change in numbers at one trophic level can have on the trophic levels above and below it. Also, the effects of the changes that take place in the environment on the organisms can be studied after collecting and comparing the data over the years. Because of pollution or overhunting by humans, If an ecosystem’s conditions are found to be worsening over the years, action can be taken to prevent further damage and possibly reverse some of the present damage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




