
Reaction of dilute HCl with Maltose gives?
A. D-glucose
B. D-fructose
C. D-glucose and D-fructose
D. D-galactose
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: This molecule can exist in an open-chain and ring form. It is a primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state.
Complete step by step answer:
Maltose is formed from two molecules of glucose. Those two molecules bond together and a water molecule is removed. Maltose is an intermediate product of starch hydrolysis and doesn’t appear to exist freely in nature.
Maltose is a disaccharide with an alpha glycosidic linkage between two D glucose molecules. The carbon atoms undergo mutarotation, which results in an equilibrium mixture of alpha and beta molecules.
Let us see the reaction.
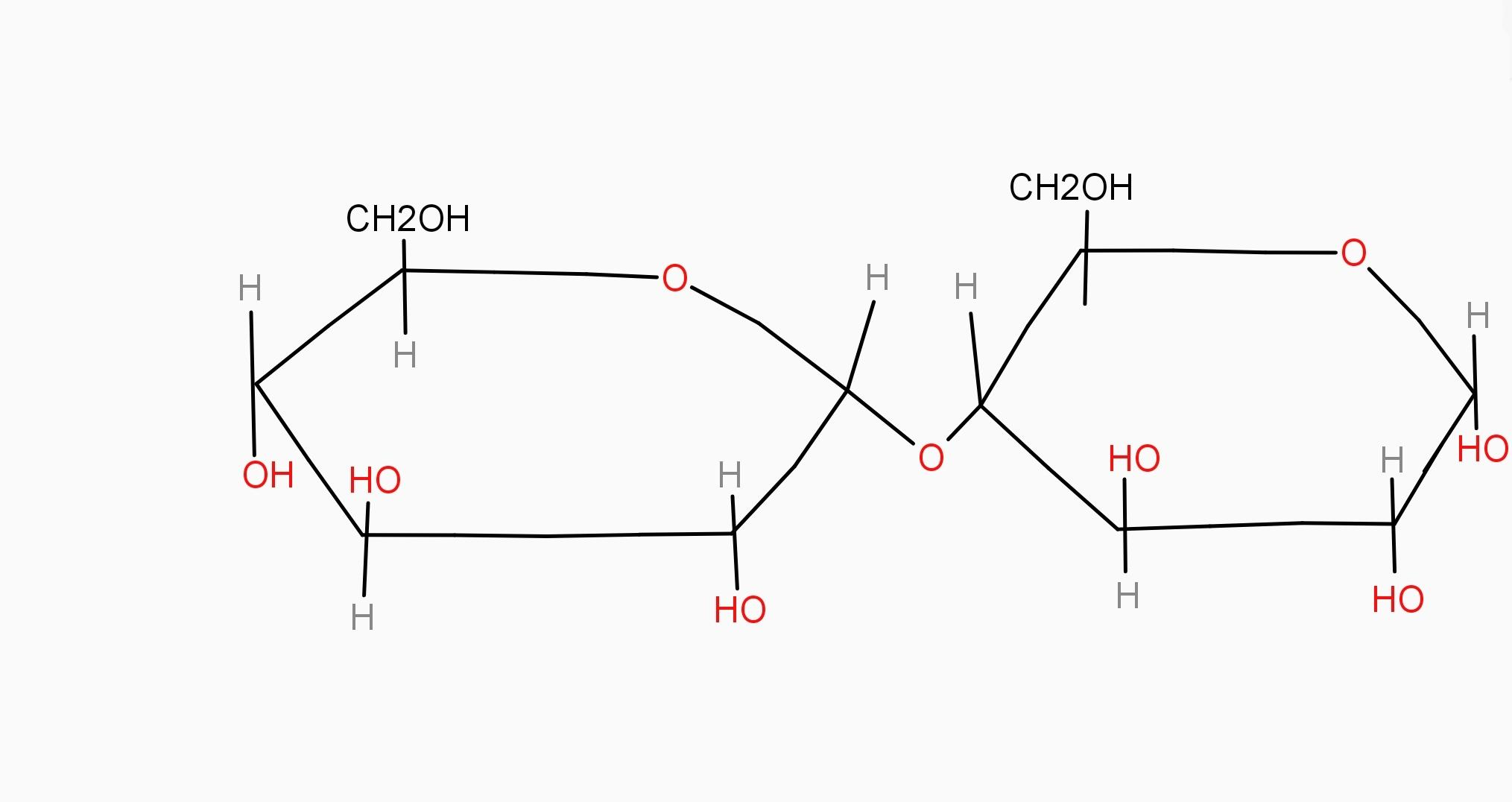
As we know, maltose is a carbohydrate and it is disaccharide and it contains D-glucose which is an example of monosaccharide, due to which when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with maltose, hydrolysis process happens and gives only D-glucose as compound.
D-glucose is a short name given to dextrorotatory glucose. It is one of the stereoisomers of glucose and it occurs in plants as a product of photosynthesis. In humans, it is present in blood with a clinical value of 75-115 mg/dl.
Hence, the reaction of dilute HCl with maltose gives D-glucose. Therefore, option A is the required answer.
Note: Glucose can form formaldehyde under abiotic conditions, so it may well have been available to primitive biochemical conditions. In respiration, through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, glucose is oxidized to eventually form carbon dioxide and water, yielding energy, mostly in the form of ATP.
Complete step by step answer:
Maltose is formed from two molecules of glucose. Those two molecules bond together and a water molecule is removed. Maltose is an intermediate product of starch hydrolysis and doesn’t appear to exist freely in nature.
Maltose is a disaccharide with an alpha glycosidic linkage between two D glucose molecules. The carbon atoms undergo mutarotation, which results in an equilibrium mixture of alpha and beta molecules.
Let us see the reaction.

As we know, maltose is a carbohydrate and it is disaccharide and it contains D-glucose which is an example of monosaccharide, due to which when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with maltose, hydrolysis process happens and gives only D-glucose as compound.
D-glucose is a short name given to dextrorotatory glucose. It is one of the stereoisomers of glucose and it occurs in plants as a product of photosynthesis. In humans, it is present in blood with a clinical value of 75-115 mg/dl.
Hence, the reaction of dilute HCl with maltose gives D-glucose. Therefore, option A is the required answer.
Note: Glucose can form formaldehyde under abiotic conditions, so it may well have been available to primitive biochemical conditions. In respiration, through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, glucose is oxidized to eventually form carbon dioxide and water, yielding energy, mostly in the form of ATP.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




