
When rays of light fall on a convex lens, it
A) Converges them
B) Does not bend them
C) Diverges them
D) Enlarges them
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: A lens is a piece of glass or of plastic that has a curved or bent shape. It either focuses or spreads the incident rays. The structure of a convex lens is thicker at the centre and thinner at the edges. While the focal length of a convex lens is positive. It’s structure is curved outwards.
Complete step by step answer:
Step I:
When rays of light fall on a convex lens, then the lens refracts(the incident ray undergoes refraction twice before leaving the convex lens) the incident light rays and merges the light rays at one point. The point where all the light rays meet is called its focus. It is also called a converging lens.
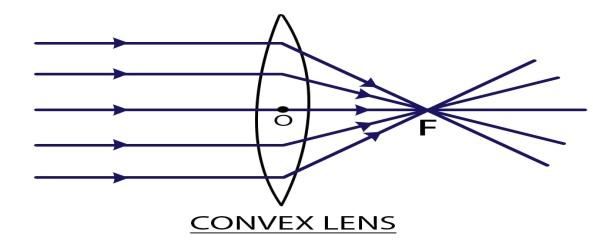
Step II:
Nature of image formed by a Convex Lens:
A convex lens always forms real and inverted images of the object. In some cases, it also forms a virtual image. In that case, the object is placed very near to the lens.
The distance between the centre of the lens and focal point is called focal length of the lens.
Step III:
Since the convex lens always converges the rays.
So option A is the correct answer.
Note: The distance between the focal point and the optical center of the convex lens is known as focal length of the lens. Since the convex lens always forms real images, this means the light rays are converged in a way that the image can be obtained on a screen. The size of the image formed by a convex lens depends on the position of the object. The image obtained can be diminished, of the same size as the object or highly enlarged.
Complete step by step answer:
Step I:
When rays of light fall on a convex lens, then the lens refracts(the incident ray undergoes refraction twice before leaving the convex lens) the incident light rays and merges the light rays at one point. The point where all the light rays meet is called its focus. It is also called a converging lens.

Step II:
Nature of image formed by a Convex Lens:
A convex lens always forms real and inverted images of the object. In some cases, it also forms a virtual image. In that case, the object is placed very near to the lens.
The distance between the centre of the lens and focal point is called focal length of the lens.
Step III:
Since the convex lens always converges the rays.
So option A is the correct answer.
Note: The distance between the focal point and the optical center of the convex lens is known as focal length of the lens. Since the convex lens always forms real images, this means the light rays are converged in a way that the image can be obtained on a screen. The size of the image formed by a convex lens depends on the position of the object. The image obtained can be diminished, of the same size as the object or highly enlarged.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




