
What is the ratio of the reading of the ammeter ${{A}_{1}}$ and ${{A}_{2}}$ in the network shown below?
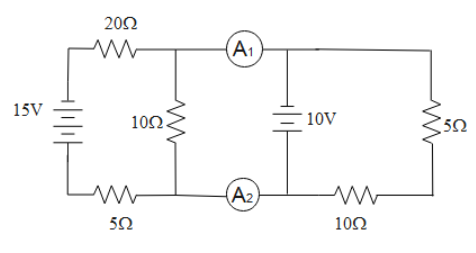
A. $2:1$
B. $4:3$
C.$1:2$
D. $1:1$

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The analysis of the circuit is done with the help of the two fundamental laws popularly known as Kirchhoff’s Laws. There are two postulated laws under Kirchhoff’s laws. These laws are named Kirchhoff’s ${{1}^{st}}$law (current law), and Kirchhoff’s ${{2}^{nd}}$ law (voltage law).
Complete answer:
According to Kirchhoff’s ${{1}^{st}}$ law (current law), it is stated that the net algebraic sum of the current at a node is always zero. In other words, the incoming current will be equal to the outgoing current. It is abbreviated as KVL.
The current always flows from the higher potential to the lower potential to balance the two-terminal. So the $15V$ voltage source will be superior.
The current-flow along the branches can be visualized as in the following diagram,
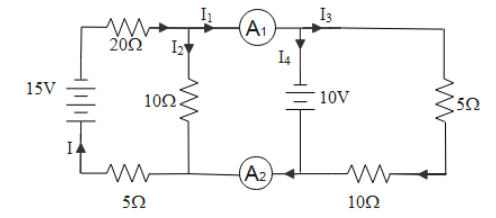
So from the above circuit, the ammeter ${{A}_{1}}$ will show the reading of ${{I}_{1}}$. This current further distributes in branches as ${{I}_{3}}$ and ${{I}_{4}}$. So mathematically we got a relation,
${{I}_{1}}={{I}_{3}}+{{I}_{4}}$
The ammeter ${{A}_{2}}$ will show the reading of current ${{I}_{3}}\And {{I}_{4}}$
${{A}_{{{2}_{reading}}}}={{I}_{3}}+{{I}_{4}}$
From the current distribution in the circuit, it can be said that both the ammeters will show the same reading. So the ratio of this reading will be
${{A}_{1}}:{{A}_{2}}=1:1$
Thus, the correct option to satisfy the question is Option D.
Note:
The sign convention of the current is considered according to the ease of the analyst (the one who is trying to study the nature of the circuit). But the sign configuration should always be in one direction. It's not like that once you consider the current from one side and suddenly you switch the direction of current while applying KCL or KVL.
Complete answer:
According to Kirchhoff’s ${{1}^{st}}$ law (current law), it is stated that the net algebraic sum of the current at a node is always zero. In other words, the incoming current will be equal to the outgoing current. It is abbreviated as KVL.
The current always flows from the higher potential to the lower potential to balance the two-terminal. So the $15V$ voltage source will be superior.
The current-flow along the branches can be visualized as in the following diagram,

So from the above circuit, the ammeter ${{A}_{1}}$ will show the reading of ${{I}_{1}}$. This current further distributes in branches as ${{I}_{3}}$ and ${{I}_{4}}$. So mathematically we got a relation,
${{I}_{1}}={{I}_{3}}+{{I}_{4}}$
The ammeter ${{A}_{2}}$ will show the reading of current ${{I}_{3}}\And {{I}_{4}}$
${{A}_{{{2}_{reading}}}}={{I}_{3}}+{{I}_{4}}$
From the current distribution in the circuit, it can be said that both the ammeters will show the same reading. So the ratio of this reading will be
${{A}_{1}}:{{A}_{2}}=1:1$
Thus, the correct option to satisfy the question is Option D.
Note:
The sign convention of the current is considered according to the ease of the analyst (the one who is trying to study the nature of the circuit). But the sign configuration should always be in one direction. It's not like that once you consider the current from one side and suddenly you switch the direction of current while applying KCL or KVL.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




