
Ratio of the area of the base of a cone and curved surface area of a cone is $3:5$ .If the perpendicular height of a cone is 16 cm.
Find (i) radius of the base (ii) slant height
Answer
610.2k+ views
Hint: By using the definition of cone. Find the volume of the cone. Surface area of the curved surface of a cone. By using both the formulas you can relate them to the given ratio and also use the condition of Pythagora's theorem with radius, height and slant height to get another relation between radius and slant height other than that the first relation. Now, you have 2 relations: first one from the condition of ratio and second one from the condition of Pythagoras theorem. Use the following formula of cone:
1)Area of base $=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
2)Area of curved surface $=\pi rl$
3)Relation of h, r, l $\Rightarrow {{l}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}$
Cone: a cone is a shape formed by using a set of line segments or the lines which connects a common point called apex or vertex to all points of a circle of radius r.
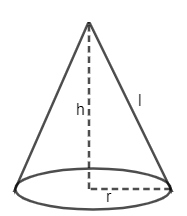
As you can see base of a cone is circle, we get:
Base area $=\pi {{r}^{2}}$ …………………..(1)
As you can see the surface of cone, we can say that:
The curved surface area $=\pi rl$ ……………(2)
As you can see, the right angle triangle formed by h. The Pythagoras:
${{l}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}$ ………………………..(3)
By dividing equation (1) by equation (2) we get ratio as:
$\dfrac{\text{base area}}{\text{curved area}}=\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}}{\pi rl}=\dfrac{3}{5}$
The ratio $3:5$ is given in question. By solving, we get
$l=\dfrac{5}{3}$ …………………..(4)
$h=16cm$ ………………….(5) (given)
By substituting equation (4) and equation (5) in the equation (3), we get
${{\left( \dfrac{5}{3}r \right)}^{2}}=256+{{r}^{2}}$
By simplifying the above equation, we get the equation as:
$25{{r}^{2}}=9\times 256+9{{r}^{2}}$
By simplifying, we can say the values of r to be as:
$r=\sqrt{9\times 16}=3\times 4=12cm$
By substituting r value into equation (4), we get value of l:
$l=\dfrac{5}{3}\times 12=5\times 4=20cm$
By above 2 equations, we say values of r, l be 12, 20 cm respectively.
Hence, we found values of 2 required variables.
Note: Be careful while squaring the r. The negative root is not considered because the radius is always positive. Don’t be confused.
1)Area of base $=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
2)Area of curved surface $=\pi rl$
3)Relation of h, r, l $\Rightarrow {{l}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}$
Cone: a cone is a shape formed by using a set of line segments or the lines which connects a common point called apex or vertex to all points of a circle of radius r.

As you can see base of a cone is circle, we get:
Base area $=\pi {{r}^{2}}$ …………………..(1)
As you can see the surface of cone, we can say that:
The curved surface area $=\pi rl$ ……………(2)
As you can see, the right angle triangle formed by h. The Pythagoras:
${{l}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}$ ………………………..(3)
By dividing equation (1) by equation (2) we get ratio as:
$\dfrac{\text{base area}}{\text{curved area}}=\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}}{\pi rl}=\dfrac{3}{5}$
The ratio $3:5$ is given in question. By solving, we get
$l=\dfrac{5}{3}$ …………………..(4)
$h=16cm$ ………………….(5) (given)
By substituting equation (4) and equation (5) in the equation (3), we get
${{\left( \dfrac{5}{3}r \right)}^{2}}=256+{{r}^{2}}$
By simplifying the above equation, we get the equation as:
$25{{r}^{2}}=9\times 256+9{{r}^{2}}$
By simplifying, we can say the values of r to be as:
$r=\sqrt{9\times 16}=3\times 4=12cm$
By substituting r value into equation (4), we get value of l:
$l=\dfrac{5}{3}\times 12=5\times 4=20cm$
By above 2 equations, we say values of r, l be 12, 20 cm respectively.
Hence, we found values of 2 required variables.
Note: Be careful while squaring the r. The negative root is not considered because the radius is always positive. Don’t be confused.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




