
Rain is falling with the speed of $25\sqrt 3 {\text{ }}m/s$ vertically. The wind blows west to east at a speed of 25 m/s. Find the velocity of rain as experienced by a person standing on ground:
${\text{A}}{\text{. 50 m/s}}$
${\text{B}}{\text{. 100 m/s}}$
${\text{C}}{\text{. 0 m/s}} $
${\text{C}}{\text{. 90 m/s}} $
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: We need to treat the direction of the rain falling down and the direction of the wind as the two vectors. Then drawing the diagram for these vectors, we can get the velocity of rain as experienced by a person standing on ground to be the resultant of two vectors.
Formula used:
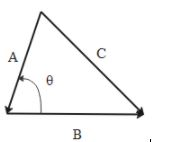
If we have two vectors A and B as shown in the figure then the magnitude of the resultant C is given as
$C = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2} + 2AB\cos \theta } $
Here $\theta $ is the angle between vectors A and B.
Complete step-by-step answer:
If we treat the velocities of the rain and that of the wind to be vectors then we can draw the following diagram where ${V_r}$ is the velocity of the rain falling downwards while ${V_w}$ is the velocity of the wind blowing from west to the east direction.
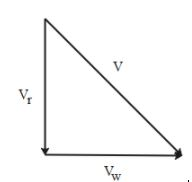
The resultant of these two velocities is equal to V which is the velocity of rain as experienced by a person standing on ground.
We are given the velocities of the rain and of the wind as follows:
$
{V_r} = 25\sqrt 3 m/s \\
{V_w} = 25m/s \\
$
The angle between these vectors is equal to $90^\circ $. Therefore, the resultant of these two vectors is given as
$
V = \sqrt {V_r^2 + V_w^2 + 2{V_r}{V_w}\cos 90^\circ } \\
= \sqrt {V_r^2 + V_w^2 + 0} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( {25\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2} + {{\left( {25} \right)}^2}} \\
= 25\sqrt {3 + 1} = 25\sqrt 4 \\
= 25 \times 2 = 50m/s \\
$
This is the value of the velocity of rain as experienced by a person standing on ground.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The person moving in rain with wind blowing experiences only the resultant of the two vectors. There is an increase in the velocity of the rain drops due to the wind pushing on the raindrops as can be seen from the answer obtained in this question.
Formula used:

If we have two vectors A and B as shown in the figure then the magnitude of the resultant C is given as
$C = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2} + 2AB\cos \theta } $
Here $\theta $ is the angle between vectors A and B.
Complete step-by-step answer:
If we treat the velocities of the rain and that of the wind to be vectors then we can draw the following diagram where ${V_r}$ is the velocity of the rain falling downwards while ${V_w}$ is the velocity of the wind blowing from west to the east direction.

The resultant of these two velocities is equal to V which is the velocity of rain as experienced by a person standing on ground.
We are given the velocities of the rain and of the wind as follows:
$
{V_r} = 25\sqrt 3 m/s \\
{V_w} = 25m/s \\
$
The angle between these vectors is equal to $90^\circ $. Therefore, the resultant of these two vectors is given as
$
V = \sqrt {V_r^2 + V_w^2 + 2{V_r}{V_w}\cos 90^\circ } \\
= \sqrt {V_r^2 + V_w^2 + 0} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( {25\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2} + {{\left( {25} \right)}^2}} \\
= 25\sqrt {3 + 1} = 25\sqrt 4 \\
= 25 \times 2 = 50m/s \\
$
This is the value of the velocity of rain as experienced by a person standing on ground.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The person moving in rain with wind blowing experiences only the resultant of the two vectors. There is an increase in the velocity of the rain drops due to the wind pushing on the raindrops as can be seen from the answer obtained in this question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




